select {[distinct | all] columns | *}
[into table_name]
from {tables | views | other select}
[where conditions]
[group by conditions]
[having conditions]
[order by columns];
select 子句:用于选择数据表、视图中的列;
into 子句:用于将原表的结构和数据插入新表中;
from 子句:用于指定数据来源,包括表,视图和其他select语句;
where 子句:用于对检索的数据进行筛选;
group by 子句:用于对检索结果进行分组显示;
having 子句:用于从使用group by子句分组后的查询结果中筛选数据行;
order by 子句:用于对结果集进行排序(包括升序和降序);
简单查询
1.检索所有的列:*
eg:select * from dept;
2.检所指定的列:column_name
eg:select job,ename,empno from emp;
3.带有表达式的select语句:+ - * / ()
eg:select sal*(1+0.1),sal from emp;
4.为列指定别名:as
eg:select empno as "员工编号",ename as "员工名称",job as "职务" from emp;
select empno "员工编号",ename "员工名称",job "职务" from emp;
5.显示不重复记录:distinct
eg:select distinct job from emp;
筛选查询
select columns_list
from table_name
where conditional_expression;
column_list:字段列表;
table_name:表名;
conditional_expression:筛选条件表达式;
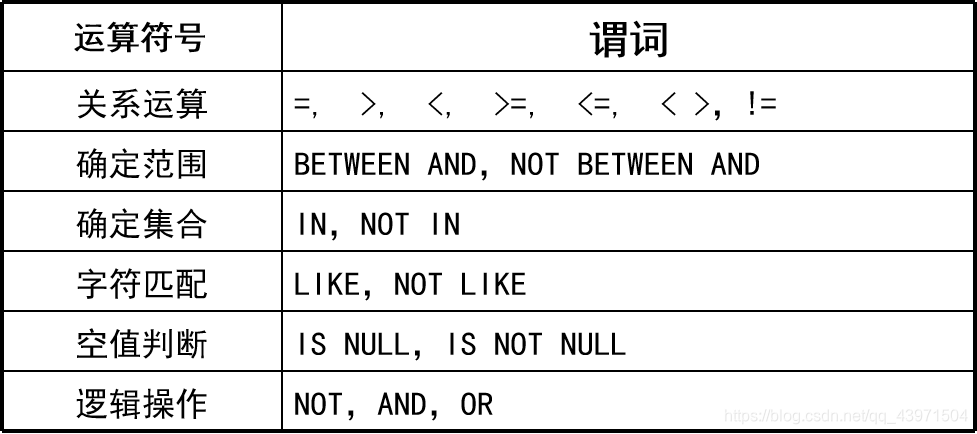
1.比较筛选:=,!=或<>,>,<,>=,<=
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal>1500;
A{operator}any(B):表示A与B中的任何一个元素进行operator运算符的比较,只要有一个比较值为true,就返回数据行;
A{operator}all(B):表示A与B中的所有元素进行operator运算符的比较,只有与所有元素比较值都为true,才返回数据行;
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal<>all(3000,950,800);
2.使用关键字筛选:(not) like,in,between...and,is null
like:需要使用通配符在字符串内查找指定的模式;
%(百分号):代表任意数量的字符;
_(下划线):代表任意一个字符;
eg:select empno,ename,job from emp ename like '%S';
in:用来指定列表搜索条件;
eg:select empno,ename,job from emp where job in('presisent','manager','analyst');
between...and:用来指定范围条件;大于等于第一个值,并且小于等于第二个值;
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal between 2000 and 3000;
is null:用来检测特殊值之间的等价性;空值,未知的、不确定的值,不存在的值;
eg:select empno,ename,comm from scott.emp where comm is null;
3.逻辑筛选:and,or,not
and:逻辑与
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal>=2000 and sal<=3000;
or:逻辑或
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal>=2000 or sal<=3000;
not:逻辑非
eg:select empno,ename,sal from emp where sal>=2000 not sal<=3000;
分组查询
select columns_list
from table_name
[where conditional_expression]
group by columns_list;
columns_list:字段列表;
table_name:表名;
conditional_expression:筛选条件表达式;
按照部门编号和职务列进行分组:
eg:select deptno,job from emp group by deptno,job order by deptno;
通过分组的方式计算每个部门的平均工资:
eg:select deptno as "部门编号",avg(sal) as "平均工资" from emp group by deptno;
首先通过分组的方式计算每个部门的平均工资,然后通过having字句过滤出平均工资大于2000的记录信息:
eg:select deptno as "部门编号",avg(sal) as "平均工资" from emp group by deptno having avg(sal)>2000;
排序查询
select columns_list
from table_name
[where conditional_expression]
[group by columns_list]
order by { order_by_expression [asc |desc]} [ ,.
columns_list:字段列表;
table_name:表名;
conditional_expression:筛选条件表达式;
order_by_expression:表示要排序的列名或表达式;
asc:表示按升序排序,默认的排序方式;
desc:表示按降序排序;
多表关联查询
1.内连接:
是根据指定的连接条件进行连接查询,只有满足连接条件的数据才会出现在结果集中;
标准SQL语句的连接方式:
select table1.column,talbe2.column[,…]
from table1 [inner] join table2 [join …]
ON condition;
Oracle扩展的连接方式:
select table1.column,talbe2.column[,…]
from table1,table2[,…]
where condition;
等值内连接:使用等号(=)指定连接条件的连接查询;
非等值内连接:连接条件中的运算符不是等号而是其他关系运算符;
自身内连接:在同一个表或视图中进行连接,相当于同一个表作为两个或多个表使用;
eg: 查询10号部门员工的员工号、员工名、工资、部门号和部门名称;
select empno,ename,sal,emp.deptno,dname
from emp join dept
on emp.deptno=10 and emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
select empno,ename,sal,emp.deptno,dname
from emp,dept
where emp.deptno=10 and emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
eg: 查询10号部门员工的工资等级;
select empno,ename,sal,grade
from emp join salgrade
on sal>losal and sal<hisal
where deptno=10;
select empno,ename,sal,grade
from emp,salgrade
where sal>losal and sal<hisal and deptno=10;
eg: 查询所有员工的员工号、员工名和该员工领导的员工名、员工号;
select worker.empno,worker.ename, manager.empno,manager.ename
from emp worker join emp manager
on worker.mgr=manager.empno;
select worker.empno,worker.ename,manager.empno,manager.ename
from emp worker,emp manager
where worker.mgr=manager.empno;
2.外连接:
是在内连接的基础上,将某个连接表中不符合连接条件的记录加入结果集中;
左外连接:指在内连接的基础上,将连接操作符左侧表中不符合连接条件的记录加入结果集中,
与之对应的连接操作符右侧表列用NULL填充;
标准SQL语句的连接方式:
select table1.column,table2.column[,…]
from table1 left [outer] join table2[,]
on table1.column <operator> table2.column[,…];
Oracle扩展的连接方式:
select table1.column,table2.column[,…]
from table1, table2[,…]
where table1.column <operator> table2.column(+)[…];
右外连接:指在内连接的基础上,将连接操作符右侧表中不符合连接条件的记录加入结果集中,
与之对应的连接操作符左侧表列用NULL填充;
标准SQL语句的连接方式:
select table1.column,table2.column[,…]
from table1 right [outer] join table2[,]
on table1.column <operator> table2.column[,…];
Oracle扩展的连接方式:
select table1.column,table2.column[,…]
from table1, table2[,…]
where table1.column(+) <operator> table2.column[…];
全外连接:指在内连接的基础上,将连接操作符两侧表中不符合连接条件的记录加入结果集中;
在Oracle数据库中,外连接的表示方式:
select table1.column, table2.column[,…]
from table1 full [outer] join table2[,…]
on table1.column1 = table2.column2[…];
eg: 查询10号部门的部门名、员工号、员工名和所有其他部门的名称;
select dname,empno,ename
from dept left join emp
on dept.deptno=emp.deptno and dept.deptno=10;
select dname,empno,ename
from dept,emp
where dept.deptno=emp.deptno(+) and emp.deptno(+)=10;
eg: 查询20号部门的员工号、员工名及其部门名称,和所有其他部门的员工号、员工名;
select empno,ename,dname
from dept right join emp
on dept.deptno=emp.deptno and dept.deptno=20;
select empno,ename,dname
from dept,emp
where dept.deptno(+)=emp.deptno and dept.deptno(+)=20;
eg: 查询所有的部门名和员工名;
select dname,ename
from emp full join dept
on emp.deptno=dept.deptno;
3.自然连接:
是指在检索多个表时,Oracle会将第一个表中的列与第二个表中具有相同名称的列进行自动连接;
用户不需要明确指定进行连接的列,由Oracle系统自动完成;
自然连接中不能为列指定限定词(即表名或表的别名);
自然连接使用natural join关键字来实现;
eg: 检索工资大于2000的记录;
select empno,ename,job,dname
from emp natural join dept
where sal>2000;
4.自连接:
“自引用式”外键是指表中的一个列可以是该表的一个外键;
eg: 查询所有管理者所管理的下属员工信息;
select em2.ename as "上层管理者",em1.ename as "下属员工"
from emp em1 left join emp em2
on em1.mgr=em2.empno
order by em1.mgr;
5.交叉连接:
又称为“笛卡儿积连接”,是两个或多个表之间的无条件连接;
一个表中所有记录分别与其他表中所有记录进行连接,交叉连接的执行结果是一个笛卡尔积;
如果进行连接的表中分别有n1,n2,n3…条记录,那么交叉连接的结果集中将有n1×n2×n3×…条记录;
交叉连接使用cross join关键字来实现;
以下情况可以出现交叉连接:
连接条件省略;连接条件非法;一个表的所有行被连接到另一个表的所有行;
eg: 通过交叉连接dept表和emp表,计算出查询结果的行数;
select count(*)
from dept cross join emp;








 这篇博客详细介绍了各种数据库查询技术,包括简单查询、筛选、分组、排序和多表关联查询。重点讲解了内连接、外连接、自然连接、自连接以及交叉连接的应用场景和示例,帮助读者深入理解数据检索的方法。
这篇博客详细介绍了各种数据库查询技术,包括简单查询、筛选、分组、排序和多表关联查询。重点讲解了内连接、外连接、自然连接、自连接以及交叉连接的应用场景和示例,帮助读者深入理解数据检索的方法。
















 1186
1186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








