SpringBoot工程
通过maven形式创建springboot工程
1. 通过maven形式创建工程
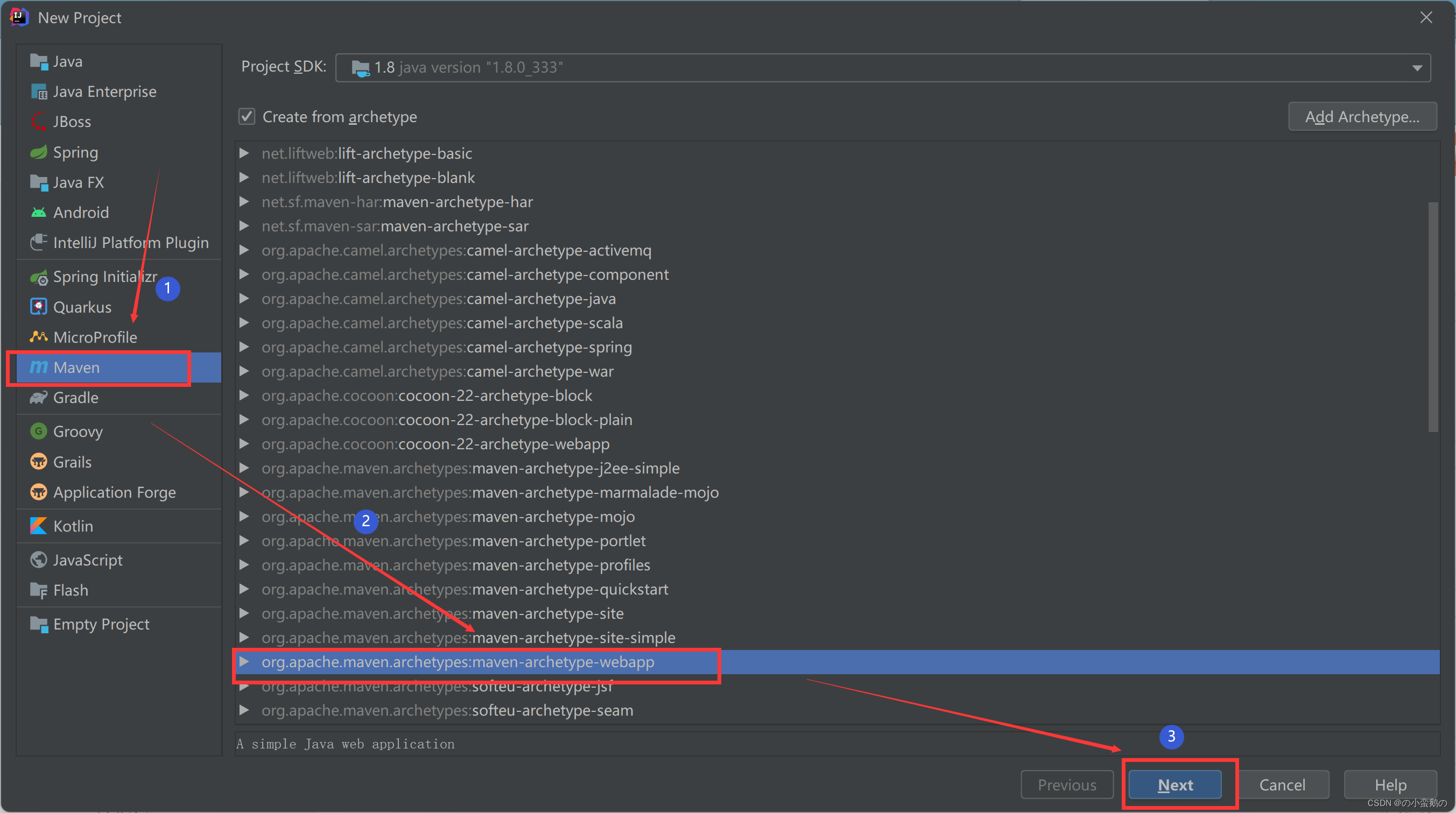
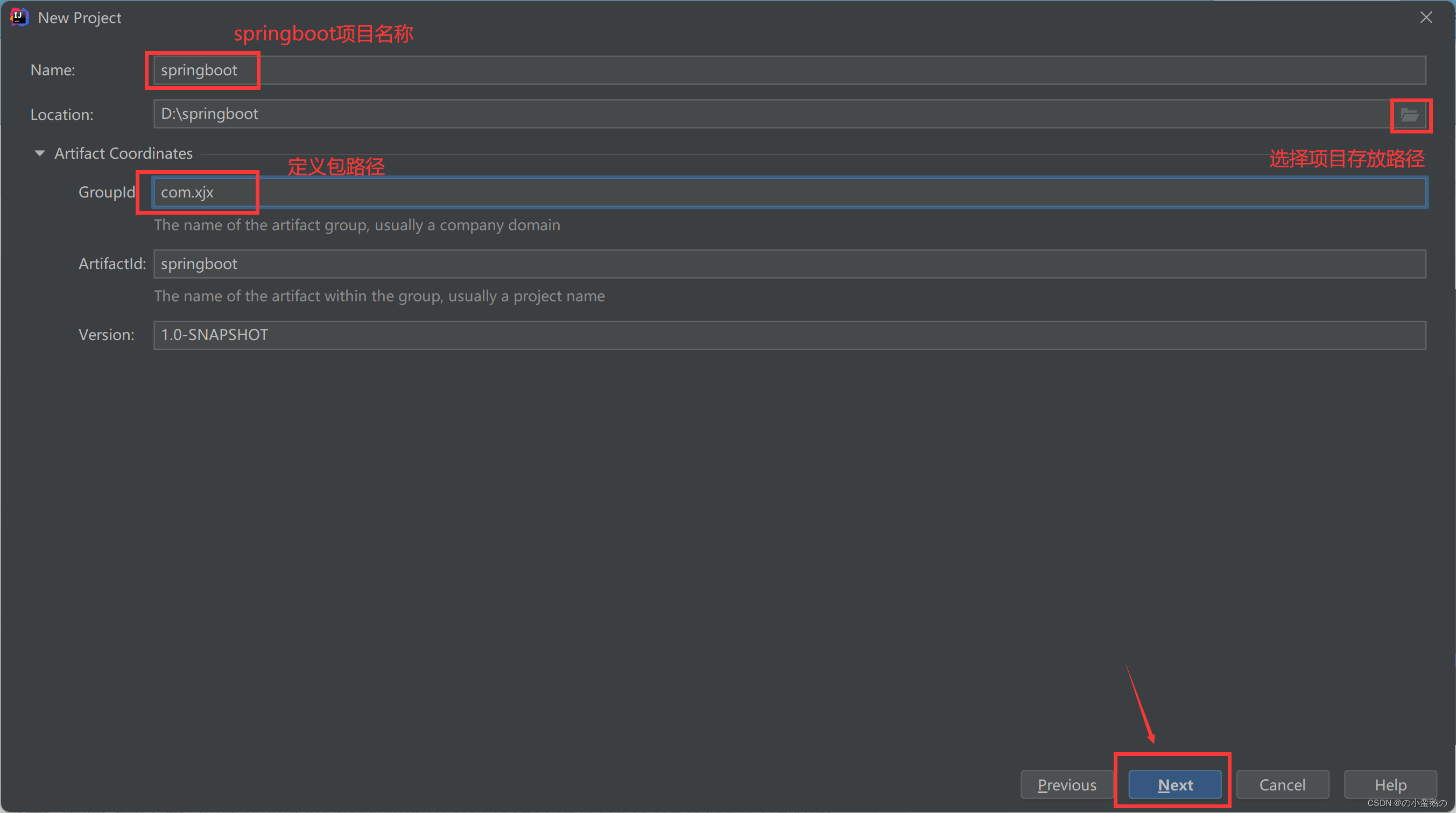
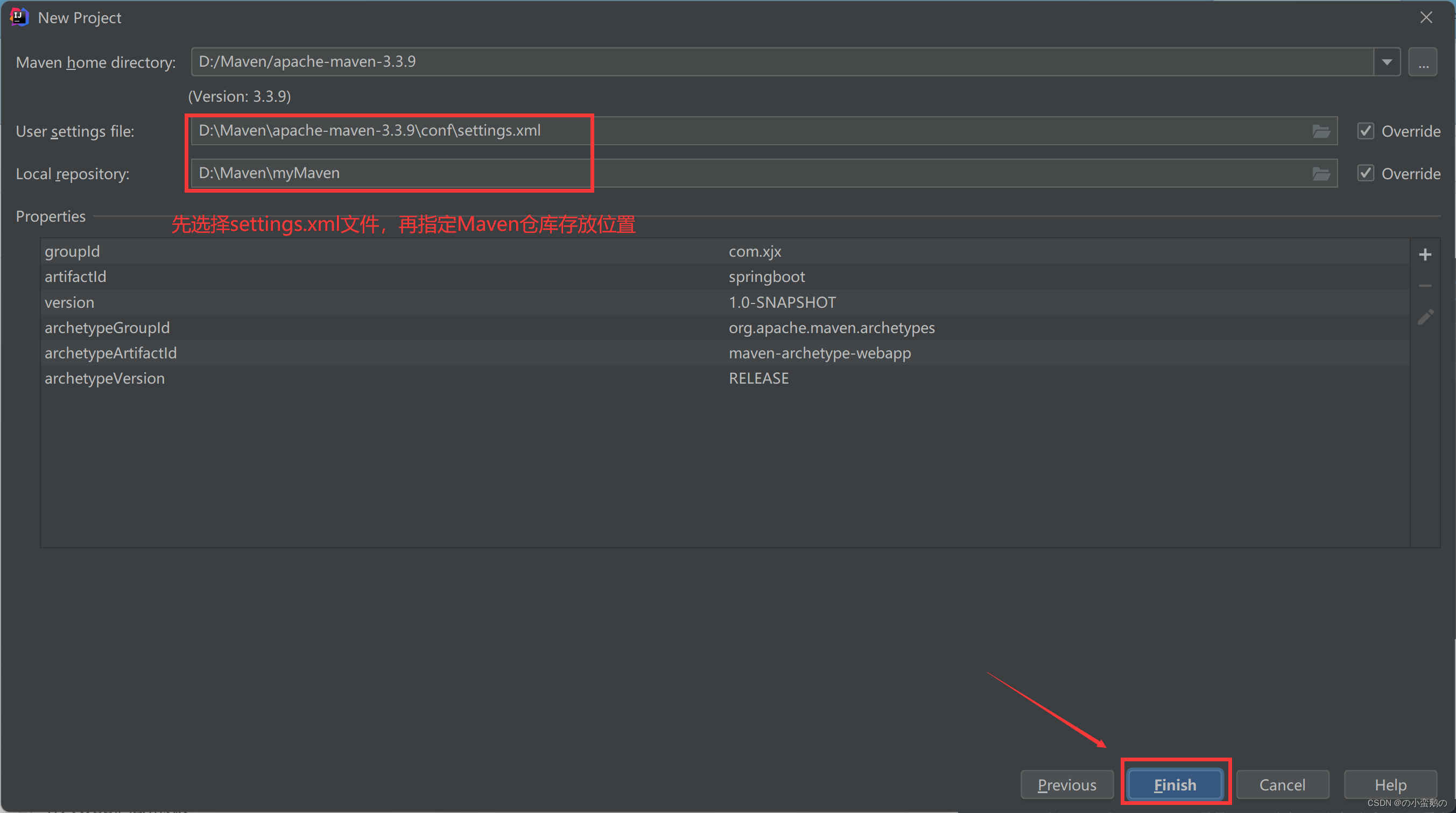
2. 引入web启动依赖
<!-- 1.引入父工程 idea必须是2020以上而且本地仓库必须存在依赖了-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.1</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>maven01</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!--2.引用web启动依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.创建启动类并加入注解
@SpringBootApplication
public class MavenApp1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MavenApp1.class,args);
}
}
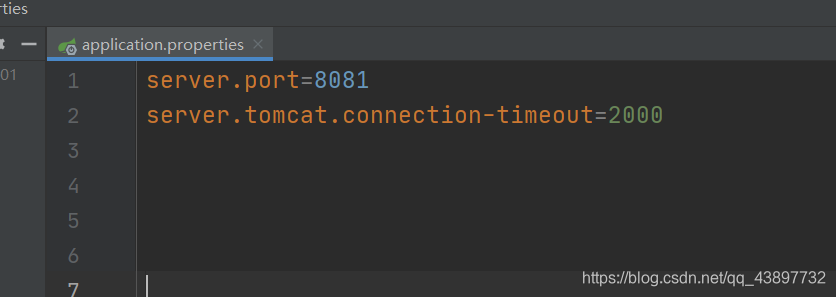
4.springboot工程中常见的配置文件类型
(1) properties属性文件类型
properties格式
(2) yml文件
yml格式
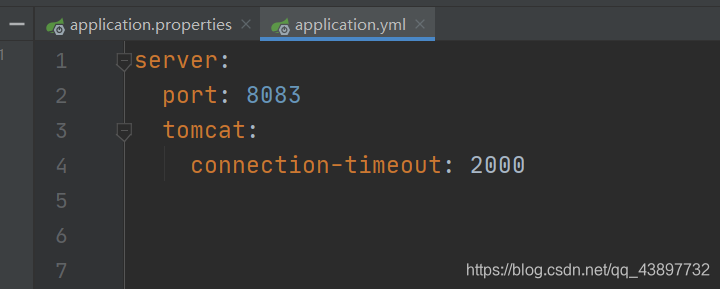
5.Java如何读取spring boot配置文件中的内容
(1) 通过@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “student”)读取配置文件中前缀为student的配置内容
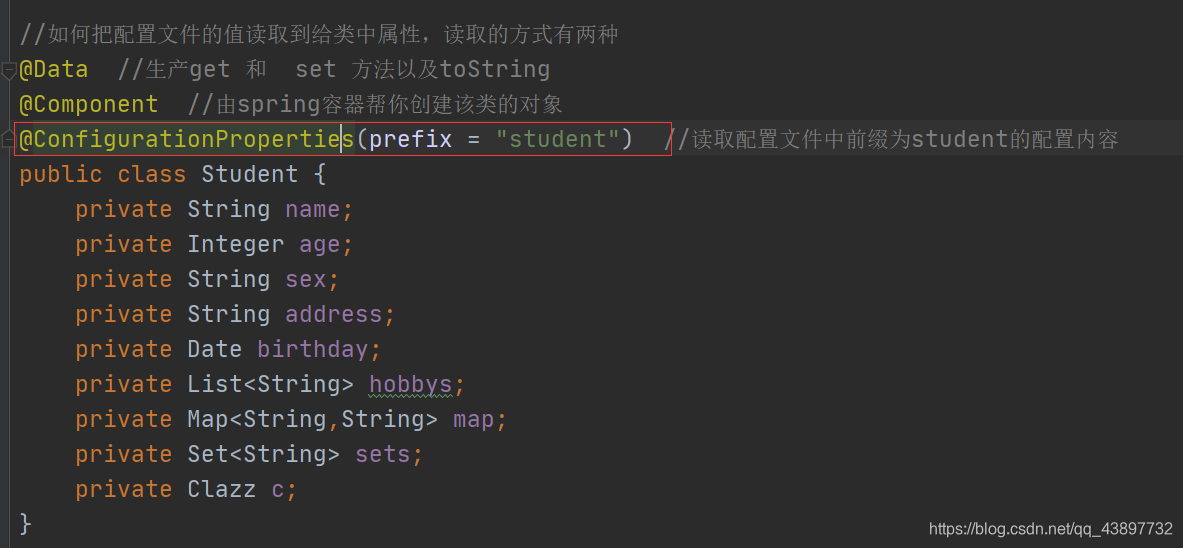
(2) properties配置文件的内容
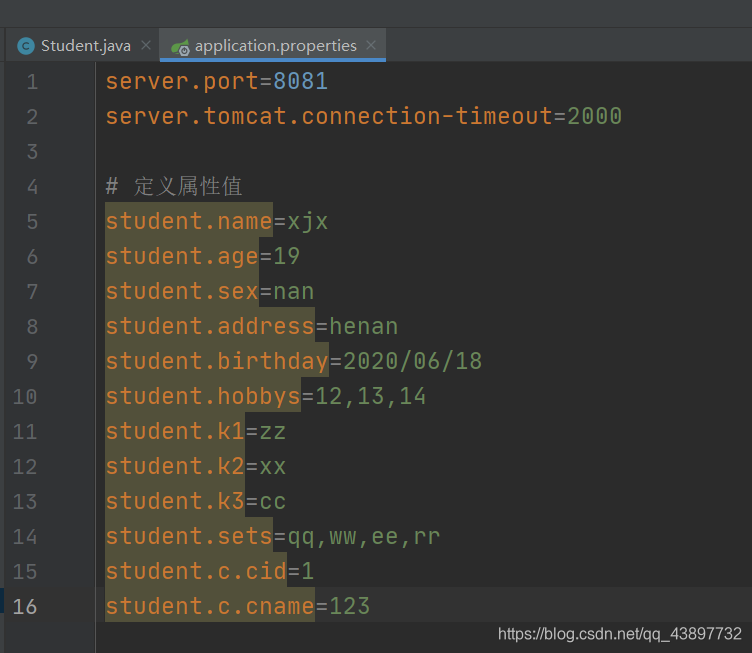
(3) yml文件的配置内容
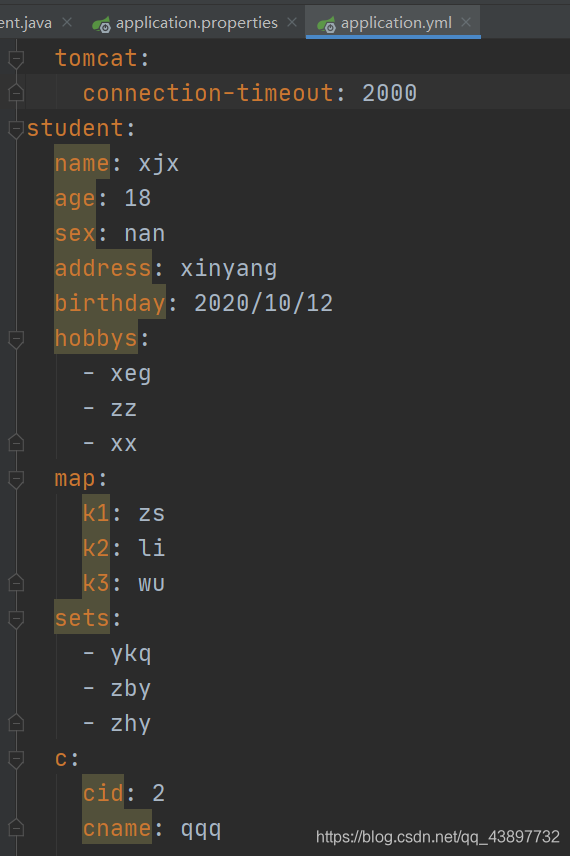
(4) 通过@Value注解来读取
//如何把配置文件的值读取到给类中属性,读取的方式有两种
@Data //生产get 和 set 方法以及toString
@Component //由spring容器帮你创建该类的对象
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") //读取配置文件中前缀为student的配置内容
public class Student {
@Value("${student.name}")
private String name;
@Value("${student.age}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${student.sex}")
private String sex;
@Value("${student.address}")
private String address;
@Value("${student.birthday}")
private Date birthday;
@Value("${student.hobbys}")
private List<String> hobbys;
// @Value("${student.map}")
private Map<String,String> map;
@Value("${student.sets}")
private Set<String> sets;
//自定义的一个类
//@Value("${student.c.id}")
private Clazz c;
}
如果通过@value读取的为properties 不能读取map以及自定义的类型。 如果读取的yml那么只能读取基本数据类型以及String和date类型
6.springboot如何注册web三大组件
- Servlet
- Filter:过滤器
- Listener:监听器
(1) 创建一个spring类
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("经过了doGet方法");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("经过了doPost方法");
}
}
(2)创建一个配置类
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean servletBean(){
ServletRegistrationBean servletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean();
servletRegistrationBean.setServlet(new MyServlet());
servletRegistrationBean.setName("myServlet");
servletRegistrationBean.addUrlMappings("/my");
return servletRegistrationBean;
}
}
(3)注册Filter,创建一个过滤器类
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~经过了过滤器~~~~~~~~~~");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);//放行
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
(4)注册该过滤器到Springboot容器中
//注册Filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean filterBean(){
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
filterRegistrationBean.setName("myFilter");
filterRegistrationBean.setFilter(new MyFilter());
filterRegistrationBean.addUrlPatterns("/*");
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
(5)注册该监听器到Springboot容器中
//注册Listener
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
ServletListenerRegistrationBean servletListenerRegistrationBean = new ServletListenerRegistrationBean();
servletListenerRegistrationBean.setListener(new ListeberConfig());
return servletListenerRegistrationBean;
}








 这篇博客详细介绍了如何创建SpringBoot工程,包括通过maven构建,引入web依赖,创建启动类。接着,讨论了SpringBoot中properties和yml配置文件的使用,并展示了Java如何读取配置内容。最后,文章阐述了SpringBoot注册web三大组件——Servlet、Filter和Listener的步骤。
这篇博客详细介绍了如何创建SpringBoot工程,包括通过maven构建,引入web依赖,创建启动类。接着,讨论了SpringBoot中properties和yml配置文件的使用,并展示了Java如何读取配置内容。最后,文章阐述了SpringBoot注册web三大组件——Servlet、Filter和Listener的步骤。
















 655
655

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








