7-1 AnalyzeNumbers.java from page 219 (示例学习)
用户输入个数,找到大于平均值的项的数目
class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//0 create a Scanner
java.util.Scanner input = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
//1 decide the number of items
System.out.print("enter the number of items:");
int n = input.nextInt();
double[] numbers = new double[n];
//2 initialize sum
double sum = 0;
//3 deciede the numbers in the array
System.out.print("enter the numbers:");
for (int i = 0; i < n ; i++) {
numbers[i] = input.nextDouble();
//4 sum
sum += numbers[i];
}
//5 count the average
double average = sum / n;
//6 decide whether the number is larger than average
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++) {
if (numbers[i] > average) {
count++;
}
}
//7 display
System.out.println("average is " + average);
System.out.println("number of elements above the average is " + count);
}
}
7-2 DeckOfCards.java from page 221(示例学习)
打乱一副牌的顺序,随机选择4张
class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//0 initialize the array
int[] deck = new int[52];
String[] suits = {"Spades", "Hearts" ,"Diamonds" , "Clubs"};
String[] ranks = {"Ace", "2" , "3","5","6","7","8","9","10","Jack","Queen","King"};
//1 initialize the cards
for (int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++) {
deck[i] = i;
}
//2 shuffle the cards
for (int i = 0; i < deck.length; i++) {
//generate an index randomly
int index = (int)(Math.random() * deck.length);
int temp = deck[i];
deck[i] = deck[index];
deck[index] = temp;
}
//3 display the 1st 4 cards
for (int i = 0; i < 4 ;i++) {
String suit = suits[deck[i] / 13];
String rank = ranks[deck[i] % 13];
System.out.println("card number " + deck[i] + ":"
+rank+" of " + suit);
}
}
}
7-3 TestPassArray.java from page 225
比较传递基本数据类型值与传递数组引用变量给方法的不同
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {1, 2};
// swap elements using the swap method
System.out.println("before invoking swap");
System.out.println("array is {" + a[0] + " , " + a[1] + "}");
swap(a[0], a[1]);
System.out.println("after invoking swap");
System.out.println("array is {" + a[0] + " , " + a[1] + "}");
//swap elements using the swapFirstTwoInArray method
System.out.println("before invoking swapFirstTwoInArray method");
System.out.println("array is {" + a[0] + " , " + a[1] + "}");
swapFirstTwoInArray(a);
System.out.println("after invoking swap");
System.out.println("array is {" + a[0] + " , " + a[1] + "}");
}
/** swap 2 variables */
public static void swap(int n1,int n2) {
int temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;
}
/** swap the 1st 2 elements in the array*/
public static void swapFirstTwoInArray(int[] array) {
int temp = array[0];
array[0] = array[1];
array[1] = temp;
}
}
7-4 CountLetterArray.java from page 227(示例学习)
随机生成100个小写字母,并将其放入一个字符数组中,对数组中每个字母出现的次数进行计数
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//0 declare and create an array
char[] chars = createArray();
//1 display the array
System.out.println("the lowercase letters are:");
displayArray(chars);
//2 count the occurrences of each letter
int[] counts = countLetters(chars);
//3 display counts
System.out.println();
System.out.println("the occurrences of each letter are:");
displayCounts(counts);
}
//** create an array of characters */
public static char[] createArray() {
//declare an array of characters and create it
char[] chars = new char[100];
//create lowercase letters randomly and assign
//them to the array
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
chars[i] = getRandomLetter('a','z');
}
//return the array
return chars;
}
//** display the array of characters */
public static void displayArray(char[] chars) {
//display the characters in the array 20 on each line
for (int i = 0;i < chars.length; i++) {
if((i+1) % 20 == 0)
System.out.println(chars[i]);
else
System.out.print(chars[i] + " ");
}
}
//** count the occurrences of each letter */
public static int[] countLetters(char[] chars) {
//declare and create an array of 26 int
int[] counts = new int[26];
//for eac lowercase letter in the array ,count it
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++)
counts[chars[i] -'a']++;
return counts;
}
//** create an array of characters */
public static void displayCounts(int[] counts) {
for (int i = 0; i < counts.length; i++)
if ( ( i + 1) % 10 == 0)
System.out.println(counts[i]+" "+(char)(i+'a'));
else
System.out.print(counts[i]+" "+(char)(i +'a')+" ");
}
//**get the random chars*/
public static char getRandomLetter(char ch1,char ch2) {
return (char)(ch1 + Math.random()* (ch2 - ch1 + 1));
}
}
7-5 VarArgsDemo.java from page 230
打印出个数不定的列表中最大值的方法
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
printMax(34,3,3,2,56.5);
printMax(new double[]{1,2,3});
}
//
public static void printMax(double...numbers) {
if (numbers.length == 0) {
System.out.println("no argument passed"); //no array passed in
return;
}
double result = numbers[0];
for ( int i = 0 ; i < numbers.length ; i++)
if (numbers[i] > result)
result = numbers[i];
System.out.println("the max value is " + result);
}
}
7-6 LinearSearch.java from page 231
线性查找法查找关键字,与数组中的元素逐个比较
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] list = {1,4,4,2,5,-3,6,2};
int i = linearSearch(list,4); //1
int j = linearSearch(list,-4);//-1
int k = linearSearch(list,-3);//5
System.out.println("i = " + i+ ", j = "+ j +", k = "+ k);
}
//**the method for finding a key in the list*/
public static int linearSearch(int[] list, int key) {
for ( int i = 0 ; i < list.length;i++) {
if ( key == list[i])
return i;
}
return -1;
}
}
7-7 BinarySearch.java from page 233
二分查找法,并返回插入位置
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] list = {2,4,7,10,11,45,50,59,60,66,69,70,79};
int i = BinarySearch(list,2); //0
int j = BinarySearch(list,11);//4
int k = BinarySearch(list,12);//-6 -k-1
int l = BinarySearch(list,1);//-1
int m = BinarySearch(list,3);//-2
System.out.println("i = " + i);
System.out.println("j = " + j);
System.out.println("k = " + k);
System.out.println("l = " + l);
System.out.println("m = " + m);
}
//**use binary search to find the key in the list*/
public static int BinarySearch(int[] list, int key) {
int low = 0;
int high = list.length - 1;
while (high >= low) {
int mid = (high + low) / 2;
if (key < list[mid])
high = mid - 1;
else if (key==list[mid])
return mid;
else
low = mid + 1;
}
return -low-1; //now high < low,key not found
}
}
7-8 SelectionSort.java from page 235
数字排序(没有解释输出)
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] list = {1,9,4.5,6.6,5.7,-4.5};
selectionSort(list);
System.out.println(list);
}
/** the method for sorting the numbers*/
public static double[] selectionSort(double[] list) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
//find the minimum in the list[i..list.length-1]
double currentMin = list[i];
int currentMinIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.length; j++) {
if (currentMin > list[i]) {
currentMin = list[i];
currentMinIndex = i;
}
}
//swap list[i] with list[currentMinIndex] if necessary
if (currentMinIndex != i)
list[currentMinIndex] = list[i];
list[i] = currentMin;
}
return list;
}
}
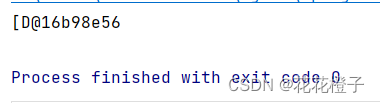
返回地址↑
无返回↓
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double[] list = {1,9,4.5,6.6,5.7,-4.5};
selectionSort(list);
}
/** the method for sorting the numbers*/
public static void selectionSort(double[] list) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.length; i++) {
//find the minimum in the list[i..list.length-1]
double currentMin = list[i];
int currentMinIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < list.length; j++) {
if (currentMin > list[i]) {
currentMin = list[i];
currentMinIndex = i;
}
}
//swap list[i] with list[currentMinIndex] if necessary
if (currentMinIndex != i)
list[currentMinIndex] = list[i];
list[i] = currentMin;
}
}
}
7-9 Calculator.java from page 238(示例学习)
开发程序完成完成两个整数的算术运算
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//0 check number of strings passed
if (args.length != 3) {
System.out.println("usage: java Calculator operand1 operator operand2");
System.exit(1);
}
//1 initialize the result of the operation
int result = 0;
//2 determine the operator
switch (args[1].charAt(0)) {
case '+':result = Integer.parseInt(args[0])+ Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
break;
case '-':result = Integer.parseInt(args[0])+Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
break;
case '.':result = Integer.parseInt(args[0])+Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
break;
case '/':result = Integer.parseInt(args[0])+Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
break;
}
//3 display result
System.out.println(args[0]+' '+args[1]+' '+args[2]+"="+result );
}
}


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










