授权流程
授权的入口有两种,第一种通过拦截器,第二种是注解
首先看下默认的拦截器
public enum DefaultFilter {
anon(AnonymousFilter.class),
authc(FormAuthenticationFilter.class),
authcBasic(BasicHttpAuthenticationFilter.class),
authcBearer(BearerHttpAuthenticationFilter.class),
logout(LogoutFilter.class),
noSessionCreation(NoSessionCreationFilter.class),
perms(PermissionsAuthorizationFilter.class),
port(PortFilter.class),
rest(HttpMethodPermissionFilter.class),
roles(RolesAuthorizationFilter.class),
ssl(SslFilter.class),
user(UserFilter.class),
invalidRequest(InvalidRequestFilter.class);
...
}
查看RolesAuthorizationFilter.class
...
public class RolesAuthorizationFilter extends AuthorizationFilter {
public RolesAuthorizationFilter() {
}
public boolean isAccessAllowed(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, Object mappedValue) throws IOException {
// 获取Subject对象
Subject subject = this.getSubject(request, response);
String[] rolesArray = (String[])mappedValue;
if (rolesArray != null && rolesArray.length != 0) {
Set<String> roles = CollectionUtils.asSet(rolesArray);
// 通过subject.hasAllRoles(roles)来验证角色
return subject.hasAllRoles(roles);
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
再来看下注解的RequiresRoles 、以及对应的AOP处理
package org.apache.shiro.authz.annotation;
...
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RequiresRoles {
String[] value();
Logical logical() default Logical.AND;
}
package org.apache.shiro.authz.aop;
...
public class RoleAnnotationHandler extends AuthorizingAnnotationHandler {
public RoleAnnotationHandler() {
super(RequiresRoles.class);
}
public void assertAuthorized(Annotation a) throws AuthorizationException {
if (a instanceof RequiresRoles) {
RequiresRoles rrAnnotation = (RequiresRoles)a;
String[] roles = rrAnnotation.value();
if (roles.length == 1) {
// getSubject()就是获取Subject对象
this.getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]);
} else if (Logical.AND.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) {
this.getSubject().checkRoles(Arrays.asList(roles));
} else {
if (Logical.OR.equals(rrAnnotation.logical())) {
boolean hasAtLeastOneRole = false;
String[] var5 = roles;
int var6 = roles.length;
for(int var7 = 0; var7 < var6; ++var7) {
String role = var5[var7];
// 等同于 subject.hasRole(role)
if (this.getSubject().hasRole(role)) {
hasAtLeastOneRole = true;
}
}
if (!hasAtLeastOneRole) {
this.getSubject().checkRole(roles[0]);
}
}
}
}
}
}
通过上面两种方式,我们知道正真授权的是Subject对象,而它是一个接口,由子类DelegatingSubject 实现
...
public class DelegatingSubject implements Subject {
public boolean isPermitted(String permission) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.isPermitted(this.getPrincipals(), permission);
}
public boolean isPermitted(Permission permission) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.isPermitted(this.getPrincipals(), permission);
}
public boolean[] isPermitted(String... permissions) {
return this.hasPrincipals() ? this.securityManager.isPermitted(this.getPrincipals(), permissions) : new boolean[permissions.length];
}
public boolean[] isPermitted(List<Permission> permissions) {
return this.hasPrincipals() ? this.securityManager.isPermitted(this.getPrincipals(), permissions) : new boolean[permissions.size()];
}
public boolean isPermittedAll(String... permissions) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.isPermittedAll(this.getPrincipals(), permissions);
}
public boolean isPermittedAll(Collection<Permission> permissions) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.isPermittedAll(this.getPrincipals(), permissions);
}
public void checkPermission(String permission) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkPermission(this.getPrincipals(), permission);
}
public void checkPermission(Permission permission) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkPermission(this.getPrincipals(), permission);
}
public void checkPermissions(String... permissions) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkPermissions(this.getPrincipals(), permissions);
}
public void checkPermissions(Collection<Permission> permissions) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkPermissions(this.getPrincipals(), permissions);
}
public boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.hasRole(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifier);
}
public boolean[] hasRoles(List<String> roleIdentifiers) {
return this.hasPrincipals() ? this.securityManager.hasRoles(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifiers) : new boolean[roleIdentifiers.size()];
}
public boolean hasAllRoles(Collection<String> roleIdentifiers) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.hasAllRoles(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifiers);
}
public void checkRole(String role) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkRole(this.getPrincipals(), role);
}
public void checkRoles(String... roleIdentifiers) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkRoles(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifiers);
}
public void checkRoles(Collection<String> roles) throws AuthorizationException {
this.assertAuthzCheckPossible();
this.securityManager.checkRoles(this.getPrincipals(), roles);
}
public boolean isAuthenticated() {
return this.authenticated;
}
public boolean isRemembered() {
PrincipalCollection principals = this.getPrincipals();
return principals != null && !principals.isEmpty() && !this.isAuthenticated();
}
}
查看hasRole,发现授权委托给了securityManager,而securityManager委托给了Authorizer
public boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier) {
return this.hasPrincipals() && this.securityManager.hasRole(this.getPrincipals(), roleIdentifier);
}
Authorizer 由 子类 ModularRealmAuthorizer 实现
public class ModularRealmAuthorizer implements Authorizer, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
...
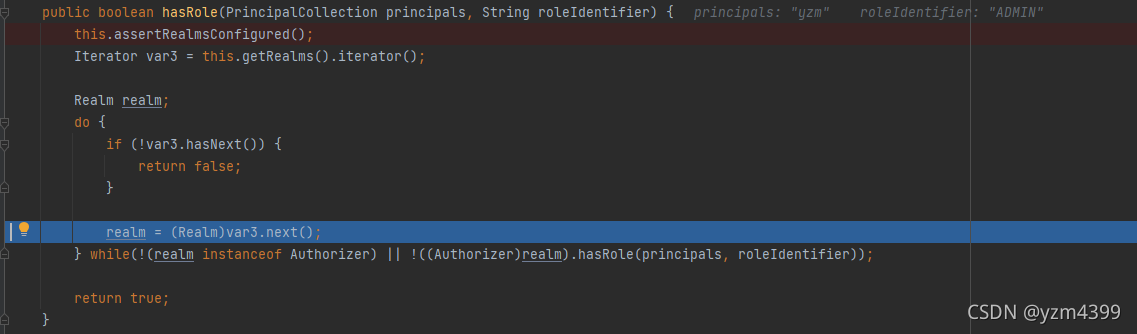
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principals, String roleIdentifier) {
this.assertRealmsConfigured();
Iterator var3 = this.getRealms().iterator();
Realm realm;
// 遍历所有的Realm
do {
if (!var3.hasNext()) {
return false;
}
realm = (Realm)var3.next();
// 再次调用hasRole,这次是由 Authorizer的另一个子类AuthorizingRealm实现的
} while(!(realm instanceof Authorizer) || !((Authorizer)realm).hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier));
return true;
}
...
}
Authorizer的另一个子类AuthorizingRealm
public abstract class AuthorizingRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm implements Authorizer, Initializable, PermissionResolverAware, RolePermissionResolverAware {
...
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String roleIdentifier) {
// 获取AuthorizationInfo授权对象
AuthorizationInfo info = this.getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return this.hasRole(roleIdentifier, info);
}
protected AuthorizationInfo getAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
if (principals == null) {
return null;
} else {
AuthorizationInfo info = null;
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("Retrieving AuthorizationInfo for principals [" + principals + "]");
}
// 先从缓存获取授权对象
Cache<Object, AuthorizationInfo> cache = this.getAvailableAuthorizationCache();
Object key;
if (cache != null) {
...
}
if (info == null) {
// 缓存没有,调用自身doGetAuthorizationInfo抽象方法
info = this.doGetAuthorizationInfo(principals);
...
}
return info;
}
}
// 该方法是由我们自定义的Realm实现的
protected abstract AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection var1);
...
}
doGetAuthorizationInfo()抽象方法就是我们自定义Realm里面实现的授权方法,返回具体角色信息和权限信息的 AuthorizationInfo 授权对象
...
public class MyShiroRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
...
@Override
public boolean supports(AuthenticationToken token) {
return token instanceof UsernamePasswordToken;
}
/**
* 授权方法
*/
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
String username = (String) principalCollection.getPrimaryPrincipal();
// 查询用户,获取角色ids
User user = userService.lambdaQuery().eq(User::getUsername, username).one();
List<Integer> roleIds = Arrays.stream(user.getRIds().split(","))
.map(Integer::parseInt)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
// 查询角色,获取角色名、权限ids
List<Role> roles = roleService.listByIds(roleIds);
Set<String> roleNames = new HashSet<>(roles.size());
Set<Integer> permIds = new HashSet<>();
roles.forEach(role -> {
roleNames.add(role.getRName());
Set<Integer> collect = Arrays.stream(
role.getPIds().split(",")).map(Integer::parseInt).collect(Collectors.toSet());
permIds.addAll(collect);
});
// 获取权限名称
List<Permissions> permissions = permissionsService.listByIds(permIds);
List<String> permNames = permissions.stream().map(Permissions::getPName).collect(Collectors.toList());
SimpleAuthorizationInfo authorizationInfo = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
authorizationInfo.addRoles(roleNames);
authorizationInfo.addStringPermissions(permNames);
return authorizationInfo;
}
/**
* 认证方法
*/
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
...
}
}
AuthorizingRealm#hasRole 获取到授权对象之后,调用自身的hasRole()方法
public boolean hasRole(PrincipalCollection principal, String roleIdentifier) {
// 获取AuthorizationInfo授权对象
AuthorizationInfo info = this.getAuthorizationInfo(principal);
return this.hasRole(roleIdentifier, info);
}
// 返回true,则允许访问
protected boolean hasRole(String roleIdentifier, AuthorizationInfo info) {
return info != null && info.getRoles() != null && info.getRoles().contains(roleIdentifier);
}
测试
definitionMap.put("/admin/**", "roles[ADMIN]");
1.登录yzm,访问/admin
2.来到roles过滤器,subject.hasAllRoles(roles)
3.DelegatingSubject#hasAllRoles
4 ModularRealmAuthorizer#hasAllRoles 调用自身this.hasRole(principals, roleIdentifier)
5 AuthorizingRealm#hasRole、getAuthorizationInfo
6 自定义的MyShiroRealm
7 组装好角色权限信息返回AuthorizationInfo对象给AuthorizingRealm

































 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








