蓝桥杯历年真题及解析.
目录:
A:分数(难度:★)
题目:
1/1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + 1/16 + …
每项是前一项的一半,如果一共有20项,
求这个和是多少,结果用分数表示出来。
类似:
3/2
当然,这只是加了前2项而已。分子分母要求互质。
注意:
需要提交的是已经约分过的分数,中间任何位置不能含有空格。
请不要填写任何多余的文字或符号。
分析:
分析题意可知,分子为2的20次方-1,分母为2的19次方。
pow计算直接输出即可。
答案=1048575/524288
代码:
满分
public class A分数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println((long)(Math.pow(2, 20)-1)+"/"+(long)Math.pow(2, 19));
}
}
B:星期一(难度:★)
题目:
整个20世纪(1901年1月1日至2000年12月31日之间),一共有多少个星期一?
(不要告诉我你不知道今天是星期几)
注意:需要提交的只是一个整数,不要填写任何多余的内容或说明文字。
分析:
计算一下1901.1.1~2000.12.31间有多少天,除以七为整周数,再看一下余数是否凑成1,直接输出即可。
答案=5217
代码:
满分
public class B星期一 {
static int day(int y){
return (y%4==0&&y%100!=0||y%400==0)?366:365;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=0;
for(int i=1901;i<2001;i++){
sum+=day(i);
}
System.out.println(sum/7);
}
}
C:复数幂(难度:★★★)
题目:
设i为虚数单位。对于任意正整数n,(2+3i)^n 的实部和虚部都是整数。
求 (2+3i)^123456 等于多少? 即(2+3i)的123456次幂,这个数字很大,要求精确表示。
答案写成 “实部±虚部i” 的形式,实部和虚部都是整数(不能用科学计数法表示),中间任何地方都不加空格,实部为正时前面不加正号。(2+3i)^2 写成: -5+12i,
(2+3i)^5 的写成: 122-597i
注意:需要提交的是一个很庞大的复数,不要填写任何多余内容。
分析:
JAVA大数运算模拟复数乘法即可
答案太大放不下,建议直接运行代码到txt文件
代码:
满分
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
public class C复数幂 {
public static void main(String[] args){
BigInteger a=new BigInteger("2");
BigInteger b=new BigInteger("3");
BigInteger c=new BigInteger("2");
BigInteger d=new BigInteger("3");
for(int i=2;i<=123456;i++){
BigInteger t=a;
a=a.multiply(c).subtract(b.multiply(d));
b=t.multiply(d).add(b.multiply(c));
}
//控制台太小,打印不了,建议文件输出
// FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("src/Step1/out.txt",true);
// fw.write(a+(b.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)==1?"+":"")+b+"i");
System.out.println(a+(b.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO)==1?"+":"")+b+"i");
// fw.flush();
}
}
D:方格计数(难度:★★)
题目:
如图

所示,在二维平面上有无数个1x1的小方格。
我们以某个小方格的一个顶点为圆心画一个半径为 50000 的圆。
你能计算出这个圆里有多少个完整的小方格吗?
注意:需要提交的是一个整数,不要填写任何多余内容。
分析:
从圆心划分4个象限,只计算第一象限,最终结果*4即可。
累加计算1~50000所对应的值。
答案=7853781044
代码:
满分
public class D方格计数 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long ans=0,i=50000,j=1;
for(;i>0;i--){
for(;j<=50000;j++){
if(i*i+j*j>50000*(long)50000){
ans+=(j-1);
break;
}
}
}
System.out.println(ans*4);
}
}
E:打印图形(难度:★★)
题目:
如下的程序会在控制台绘制分形图(就是整体与局部自相似的图形)。
当n=1,2,3的时候,输出如下:
请仔细分析程序,并填写划线部分缺少的代码。
n=1时:
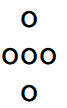
n=2时:

n=3时:

源程序:
public class Main
{
static void show(byte[][] buf){
for(int i=0; i<buf.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<buf[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(buf[i][j]==0? ' ' : 'o');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void draw(byte[][] buf, int x, int y, int size){
if(size==1){
buf[y][x] = 1;
return;
}
int n = ________________________ ; // 填空
draw(buf, x, y, n);
draw(buf, x-n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x+n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x, y-n ,n);
draw(buf, x, y+n ,n);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
final int N = 3;
int t = 1;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) t *= 3;
byte[][] buf = new byte[t][t];
draw(buf, t/2, t/2, t);
show(buf);
}
}
分析:
观察发现,主函数内有 t * 3 多次,所以推测 size / 3;
验证后正确。
答案=size/3
代码:
满分
public class E打印图形
{
static void show(byte[][] buf){
for(int i=0; i<buf.length; i++){
for(int j=0; j<buf[i].length; j++){
System.out.print(buf[i][j]==0? ' ' : 'o');
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void draw(byte[][] buf, int x, int y, int size){
if(size==1){
buf[y][x] = 1;
return;
}
int n = size/3;//________________________ ; // 填空
draw(buf, x, y, n);
draw(buf, x-n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x+n, y ,n);
draw(buf, x, y-n ,n);
draw(buf, x, y+n ,n);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
final int N = 3;
int t = 1;
for(int i=0; i<N; i++) t *= 3;
byte[][] buf = new byte[t][t];
draw(buf, t/2, t/2, t);
show(buf);
}
}
F:航班时间(难度:★★★)
题目:
【问题背景】
小h前往美国参加了蓝桥杯国际赛。小h的女朋友发现小h上午十点出发,上午十二点到达美国,于是感叹到“现在飞机飞得真快,两小时就能到美国了”。
小h对超音速飞行感到十分恐惧。仔细观察后发现飞机的起降时间都是当地时间。由于北京和美国东部有12小时时差,故飞机总共需要14小时的飞行时间。
不久后小h的女朋友去中东交换。小h并不知道中东与北京的时差。但是小h得到了女朋友来回航班的起降时间。小h想知道女朋友的航班飞行时间是多少。
【问题描述】
对于一个可能跨时区的航班,给定来回程的起降时间。假设飞机来回飞行时间相同,求飞机的飞行时间。
【输入格式】
从标准输入读入数据。
一个输入包含多组数据。
输入第一行为一个正整数T,表示输入数据组数。
每组数据包含两行,第一行为去程的 起降 时间,第二行为回程的 起降 时间。
起降时间的格式如下
h1:m1:s1 h2:m2:s2
或
h1:m1:s1 h3:m3:s3 (+1)
或
h1:m1:s1 h4:m4:s4 (+2)
表示该航班在当地时间h1时m1分s1秒起飞,
第一种格式表示在当地时间 当日 h2时m2分s2秒降落
第二种格式表示在当地时间 次日 h3时m3分s3秒降落。
第三种格式表示在当地时间 第三天 h4时m4分s4秒降落。
对于此题目中的所有以 h: m:s 形式给出的时间, 保证 ( 0<=h<=23, 0<=m,s<=59 ).
【输出格式】
输出到标准输出。
对于每一组数据输出一行一个时间hh:mm:ss,表示飞行时间为hh小时mm分ss秒。
注意,当时间为一位数时,要补齐前导零。如三小时四分五秒应写为03:04:05。
【样例输入】
3
17:48:19 21:57:24
11:05:18 15:14:23
17:21:07 00:31:46 (+1)
23:02:41 16:13:20 (+1)
10:19:19 20:41:24
22:19:04 16:41:09 (+1)
【样例输出】
04:09:05
12:10:39
14:22:05
【限制与约定】
保证输入时间合法,飞行时间不超过24小时。
分析:
字符串处理问题,处理过程比较复杂,但不是很难,
细心搞一搞没问题。
后期再考虑优化一下代码。
代码:

import java.util.*;
public class F航班时间 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int t=sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
int val[]={60*60,60,1};
while(t-->0){
String to=sc.nextLine();
String qd_to[]=to.split(" ");
String to_qf[]=qd_to[0].split(":");
String to_dd[]=qd_to[1].split(":");
int t1_qf=Integer.valueOf(to_qf[0])*val[0]+Integer.valueOf(to_qf[1])*val[1]+Integer.valueOf(to_qf[2])*val[2];
int t1_dd=Integer.valueOf(to_dd[0])*val[0]+Integer.valueOf(to_dd[1])*val[1]+Integer.valueOf(to_dd[2])*val[2];
int t1=t1_dd-t1_qf;
if(qd_to.length==3){
t1+=Integer.valueOf(qd_to[2].substring(2, 3))*24*60*60;
}
String come=sc.nextLine();
String qd_come[]=come.split(" ");
String come_qf[]=qd_come[0].split(":");
String come_dd[]=qd_come[1].split(":");
int t2_qf=Integer.valueOf(come_qf[0])*val[0]+Integer.valueOf(come_qf[1])*val[1]+Integer.valueOf(come_qf[2])*val[2];
int t2_dd=Integer.valueOf(come_dd[0])*val[0]+Integer.valueOf(come_dd[1])*val[1]+Integer.valueOf(come_dd[2])*val[2];
int t2=t2_dd-t2_qf;
if(qd_come.length==3){
t2+=Integer.valueOf(qd_come[2].substring(2, 3))*24*60*60;
}
int time=(t1+t2)/2;
int dd=time/(24*60*60),hh=(time%(24*60*60))/(60*60),mm=(time%(60*60))/60,ss=time%60;
System.out.println((hh<10?"0"+hh:hh)+":"+(mm<10?"0"+mm:mm)+":"+(ss<10?"0"+ss:ss)+(dd!=0?" (+"+dd+")":""));
}
}
}
G:三体攻击(难度:★★★★)
题目:



分析:
//稍等
代码:
//稍等
H:全球变暖(难度:★★★★)
题目:
你有一张某海域NxN像素的照片,".“表示海洋、”#"表示陆地,如下所示:
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
其中"上下左右"四个方向上连在一起的一片陆地组成一座岛屿。例如上图就有2座岛屿。
由于全球变暖导致了海面上升,科学家预测未来几十年,岛屿边缘一个像素的范围会被海水淹没。具体来说如果一块陆地像素与海洋相邻(上下左右四个相邻像素中有海洋),它就会被淹没。
例如上图中的海域未来会变成如下样子:
.......
.......
.......
.......
....#..
.......
.......
请你计算:依照科学家的预测,照片中有多少岛屿会被完全淹没。
【输入格式】
第一行包含一个整数N。 (1 <= N <= 1000)
以下N行N列代表一张海域照片。
照片保证第1行、第1列、第N行、第N列的像素都是海洋。
【输出格式】
一个整数表示答案。
【输入样例】
7
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
..####.
...###.
.......
【输出样例】
1
资源约定:
峰值内存消耗(含虚拟机) < 256M
CPU消耗 < 1000ms
分析:
这是一个DFS题目,我们录入数据后首先搜索查一下陆地的岛屿数目。
与此同时我们给每一个岛屿进行编号,当我们发现有某个岛屿无法被淹没时加入HashSet。
最终岛屿数减去hashset内的岛屿数量即被淹没的所有岛屿的数量。
代码:

import java.util.*;
public class H全球变暖 {
// public static String[] strArray = new String[1010];
public static char[][] ca = new char[1010][1010];
public static int n;
public static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
public static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static int[][] overWhelm = new int[1010][1010];// 判断该陆地是否会被淹没,1表示会被淹没,大于1的数表示剩下的小岛
public static int[][] v = new int[1010][1010];// 判断该陆地是否已经搜索过
public static long num = 0;// 所有小岛数
public static Queue<Node> que = new LinkedList<>();
public static void BFS() {
// for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// ca[i] = strArray[i].toCharArray();
// }
int d_num = 2;// 用来表示不同的小岛
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (ca[i][j] == '#' && v[i][j] == 0) {
Node node = new Node(i, j);
que.add(node);
v[i][j] = 1;
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
Node tempNode = que.remove();
check(tempNode.coordX, tempNode.coordY, d_num);
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tempx = tempNode.coordX + dx[k];
int tempy = tempNode.coordY + dy[k];
if (tempx >= 0 && tempy >= 0 && tempx < n && tempy < n) {
if (ca[tempx][tempy] == '.') {// 上下左右存在海洋,会被淹没
continue;
}
if (ca[tempx][tempy] == '#' && v[tempx][tempy] == 0) {
que.add(new Node(tempx, tempy));
v[tempx][tempy] = 1;
}
}
}
}
num++;
d_num++;
}
}
}
}
// 判断上下左右是否有海洋
public static void check(int tempx, int tempy, int d_num) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int tax = tempx + dx[k];
int tay = tempy + dy[k];
// 边界之外全是海洋
if (tax < 0 || tay < 0 || tax >= n || tay >= n) {
overWhelm[tempx][tempy] = 1;
break;
}
if (ca[tax][tay] == '.') {
overWhelm[tempx][tempy] = 1;
break;
}
overWhelm[tempx][tempy] = d_num;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
n = in.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
// strArray[i] = in.next();
ca[i]=in.next().toCharArray();
BFS();// 广搜
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();// 存放的是未被淹没的小岛
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (overWhelm[i][j] > 1)
set.add(overWhelm[i][j]);
System.out.println(num - (long) set.size());
}
static class Node {
int coordX;
int coordY;
Node(int x, int y) {
coordX = x;
coordY = y;
}
}
}
I:倍数问题(难度:★★★★★)
题目:
【题目描述】
众所周知,小葱同学擅长计算,尤其擅长计算一个数是否是另外一个数的倍数。但小葱只擅长两个数的情况,当有很多个数之后就会比较苦恼。现在小葱给了你 n 个数,希望你从这 n 个数中找到三个数,使得这三个数的和是 K 的倍数,且这个和最大。数据保证一定有解。
【输入格式】
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包括 2 个正整数 n, K。
第二行 n 个正整数,代表给定的 n 个数。
【输出格式】
输出到标准输出。
输出一行一个整数代表所求的和。
【样例输入】
4 3
1 2 3 4
【样例输出】
9
【样例解释】
选择2、3、4。

分析:
//稍等
代码:
//稍等
J:付账问题(难度:★★★★★)
题目:
【题目描述】
几个人一起出去吃饭是常有的事。但在结帐的时候,常常会出现一些争执。
现在有 n 个人出去吃饭,他们总共消费了 S 元。其中第 i 个人带了 ai 元。幸运的是,所有人带的钱的总数是足够付账的,但现在问题来了:每个人分别要出多少钱呢?
为了公平起见,我们希望在总付钱量恰好为 S 的前提下,最后每个人付的钱的标准差最小。这里我们约定,每个人支付的钱数可以是任意非负实数,即可以不是1分钱的整数倍。你需要输出最小的标准差是多少。
标准差的介绍:标准差是多个数与它们平均数差值的平方平均数,一般用于刻画这些数之间的“偏差有多大”。形式化地说,设第 i 个人付的钱为 bi 元,那么标准差为 :
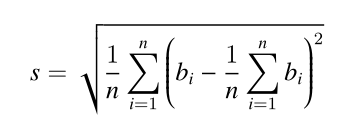
【输入格式】
从标准输入读入数据。
第一行包含两个整数 n、S;
第二行包含 n 个非负整数 a1, …, an。
【输出格式】
输出到标准输出。
输出最小的标准差,四舍五入保留 4 位小数。
保证正确答案在加上或减去 10^−9 后不会导致四舍五入的结果发生变化。
【样例输入】
5 2333
666 666 666 666 666
【样例输出】
0.0000
【样例解释】
每个人都出 2333/5 元,标准差为 0。
再比如:
【样例输入】
10 30
2 1 4 7 4 8 3 6 4 7
【样例输出】
0.7928
【数据约定】
对于 10% 的数据,所有 ai 相等;
对于 30% 的数据,所有非 0 的 ai 相等;
对于 60% 的数据,n ≤ 1000;
对于 80% 的数据,n ≤ 10^5;
对于所有数据,n ≤ 5 × 10^5, 0 ≤ ai ≤ 10^9。
分析:
//稍等
代码:
//稍等
算法交流群:


























 4378
4378

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










