直接内存
- 常见于NIO操作,一般用于数据缓存
- 分配回收成本较高,但读写性能高
- 不受JVM内存回收管理
普通java缓存区的操作,因为java无法直接读取系统缓存区,系统缓存区的数据还得复制一份
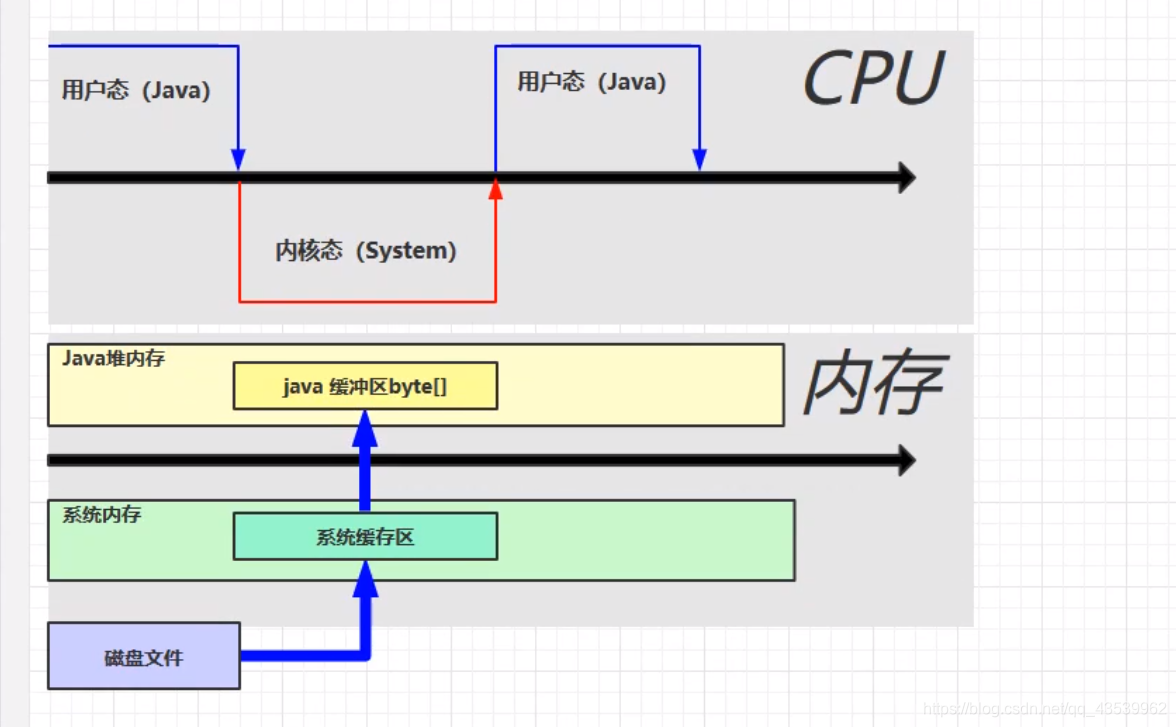
直接内存的缓存读写操作,就相当于单独出一个内存java能读取,系统也能读取那么就减少了一次复制

allocateDirect源码
内存分配

DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private
super(-1, 0, cap, cap);
boolean pa = VM.isDirectMemoryPageAligned();
int ps = Bits.pageSize();
long size = Math.max(1L, (long)cap + (pa ? ps : 0));
Bits.reserveMemory(size, cap);
long base = 0;
try {
// 分配一个内存
base = unsafe.allocateMemory(size);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
Bits.unreserveMemory(size, cap);
throw x;
}
// 通过unsafe对象设置为直接内存
unsafe.setMemory(base, size, (byte) 0);
if (pa && (base % ps != 0)) {
// Round up to page boundary
address = base + ps - (base & (ps - 1));
} else {
address = base;
}
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
att = null;
}
内存释放
cleaner = Cleaner.create(this, new Deallocator(base, size, cap));
该方法表示GC该对象的时候触发的clean方法,因为直接内存不受JVM管理,必须得调用unsafe.freeMemory手动释放
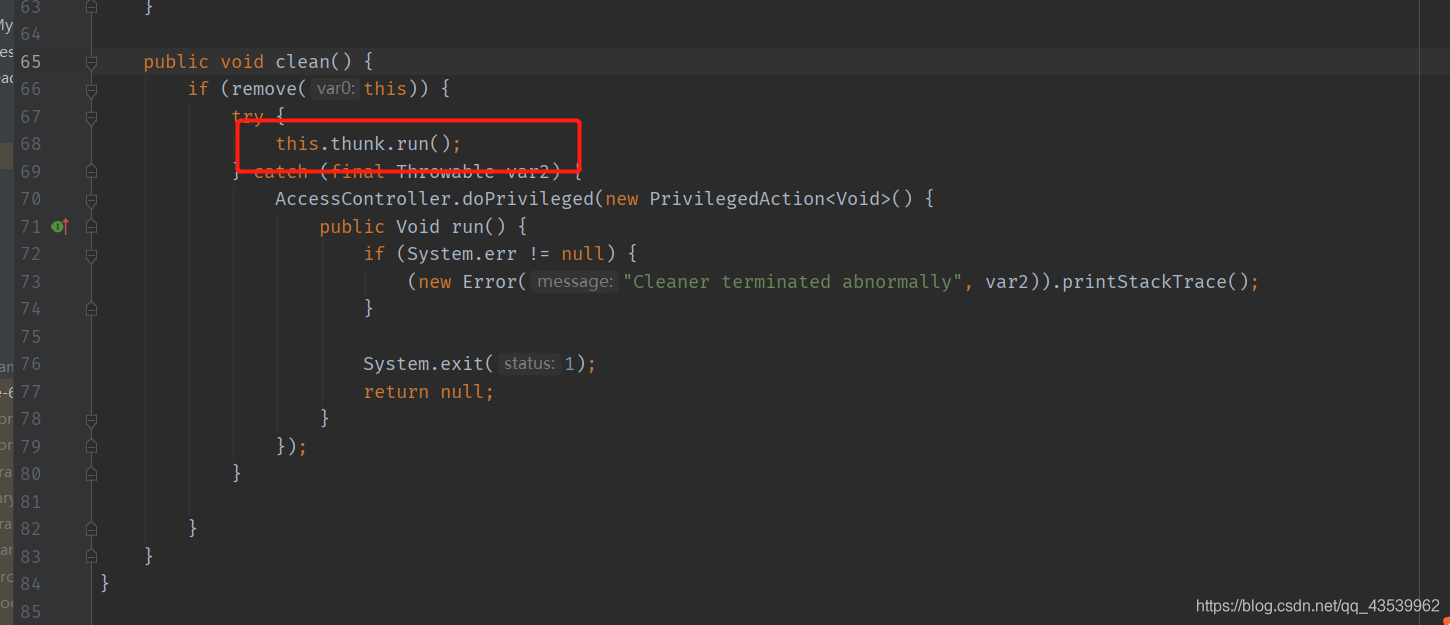
发现调用了一个任务对象

发现调用的正是传入的new Deallocator(base, size, cap)


发现传入的是一个Runnable的实现类,里面的run方法调用了unsafe.freeMemory()方法,也就是说内存释放并不是用完就会释放,而是在对象被垃圾回收掉后才会被释放,如果想自行释放只需要自行调用unsafe.freeMemory()

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








