默认的拷贝构造函数
如果一个类中没有定义拷贝构造函数,则系统会自动提供一个默认拷贝构造函数,用来根据已有对象创建新对象;我们要知道这个默认的拷贝构造函数采用的是"浅拷贝“,并非"深拷贝“。
深拷贝与浅拷贝的区别
浅拷贝只是对指针的拷贝,拷贝后两个指针指向同一个内存空间;深拷贝不仅对指针拷贝,对指针指向的内容也进行拷贝,深拷贝后的两个指针分别指向不同的内存空间
浅拷贝带来的问题
1. 浅拷贝后的两个指针指向同一内存空间,在对象块结束,调用析构函数时,会造成同一块资源析构两次,即delete同一块内存两次,造成程序崩溃
2. 浅拷贝的两个指针,任何一方的改变都会影响到另一方
编码看一下两者的区别
浅拷贝:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student();
~Student();
private:
int num;
char *name;
};
Student::Student()
{
name = new char('a');
cout << "name=" << *name << endl;
cout << "Constructor called" << endl;
}
Student::~Student()
{
delete name;
cout << "Destructor called" << endl;
}
int main()
{
//花括号让s1、s2变为局部变量,方便测试
{
Student s1;
Student s2(s1);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}


由以上的调试结果可知,程序运行出错,下面我们自定义个深拷贝构造函数
深拷贝
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
Student();
~Student();
Student(const Student &s);
private:
int num;
char *name;
};
Student::Student()
{
name = new char('a');
cout << "name=" << *name << endl;
cout << "Constructor called" << endl;
}
Student::~Student()
{
delete name;
cout << "Destructor called" << endl;
}
Student::Student(const Student &s) //自定义拷贝构造函数
{
name = new char('a');
memcpy(name, s.name, sizeof(s.name));
cout << "Copy constructor called" << endl;
}
int main()
{
//花括号让s1、s2变为局部变量,方便测试
{
Student s1;
Student s2(s1);
}
system("pause"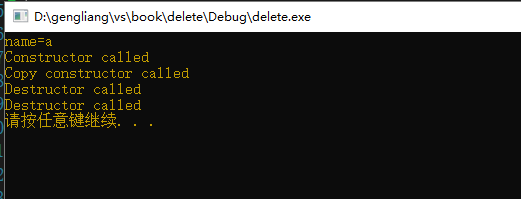);
return 0;
}
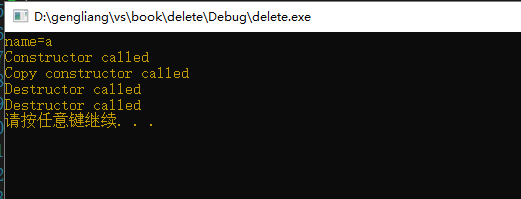
一切正常
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








