双向链表相对于单链表来说,只是多了一个指向前驱节点的指针域,基本实现是差不多的。
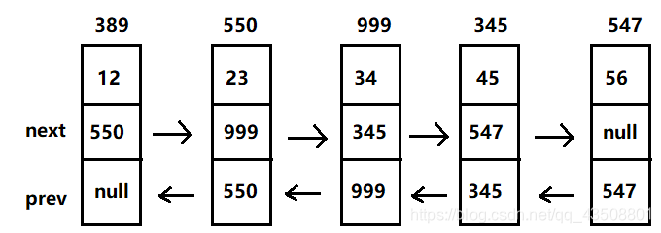
- 以下是关于不带头双向链表的
java语言实现:
package com.DoubleLinked;
public class DoubleLinkedList {
class Node {
private Node prev;
private int data;
private Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
private Node head;
private Node last;//尾节点
public DoubleLinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.last = null;
}
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
//分情况讨论
//第一次插入的节点就是最终的尾节点
if(this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
node.next = this.head;
node.next.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data) {
Node node = new Node(data);
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
this.last = node;
}
}
//寻找inde-1位置的节点
public Node searchIndex(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > getLength()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("index位置不合法");
}
int count = 0;
Node cur = this.head;
while (count != index) {
cur = cur.next;
count++;
}
return cur;
}
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean addIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index == 0) {
addFirst(data);
return true;
}
if (index == getLength()) {
addLast(data);
return true;
}
Node node = new Node(data);
Node cur = searchIndex(index);
node.next = cur;
cur.prev.next = node;
node.prev = cur.prev;
cur.prev = node;
return true;
}
//查看是否包含关键字key
public boolean contains(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == key) {
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
//删除第一次出现key的节点
public int remove(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null){
int oldData = 0;
if (cur.data == key) {
oldData = cur.data;
//删除的是头结点
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
//删除的是尾节点
this.last = cur.prev;
}
}
return oldData;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return -1;
}
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key) {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.data == key) {
if (cur == this.head) {
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
this.last.prev = null;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
}
//获取链表的长度
public int getLength() {
int count = 0;
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
}
//打印双向链表
public void display() {
Node cur = this.head;
while (cur != null) {
System.out.println(cur.data + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//清空链表以防内存泄漏
public void clear() {
while (this.head != null) {
Node cur = this.head.next;
this.head.next = null;
this.head.prev = null;
this.head = cur;
}
//释放尾节点的引用
this.last = null;
}
}
package com.DoubleLinked;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleLinkedList list = new DoubleLinkedList();
list.addFirst(10);
list.addLast(20);
list.addFirst(30);
list.addFirst(40);
list.addLast(50);
list.addLast(10);
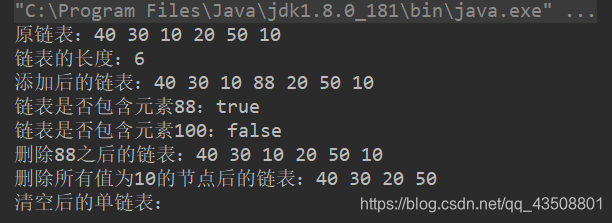
System.out.print("原链表:");
list.display(); //40 30 10 20 50 10
System.out.println("链表的长度:" + list.getLength());
list.addIndex(3, 88);
System.out.print("添加后的链表:");
list.display();//40 30 10 88 20 50 10
System.out.println("链表是否包含元素88:" + list.contains(88));
System.out.println("链表是否包含元素100:" + list.contains(100));
list.remove(88);
System.out.print("删除88之后的链表:");
list.display();
list.removeAllKey(10);
System.out.print("删除所有值为10的节点后的链表:");
list.display();
list.clear();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.print("清空后的单链表:");
list.display();
}
}
java中如何查看内存是否泄漏?以上述代码为例:
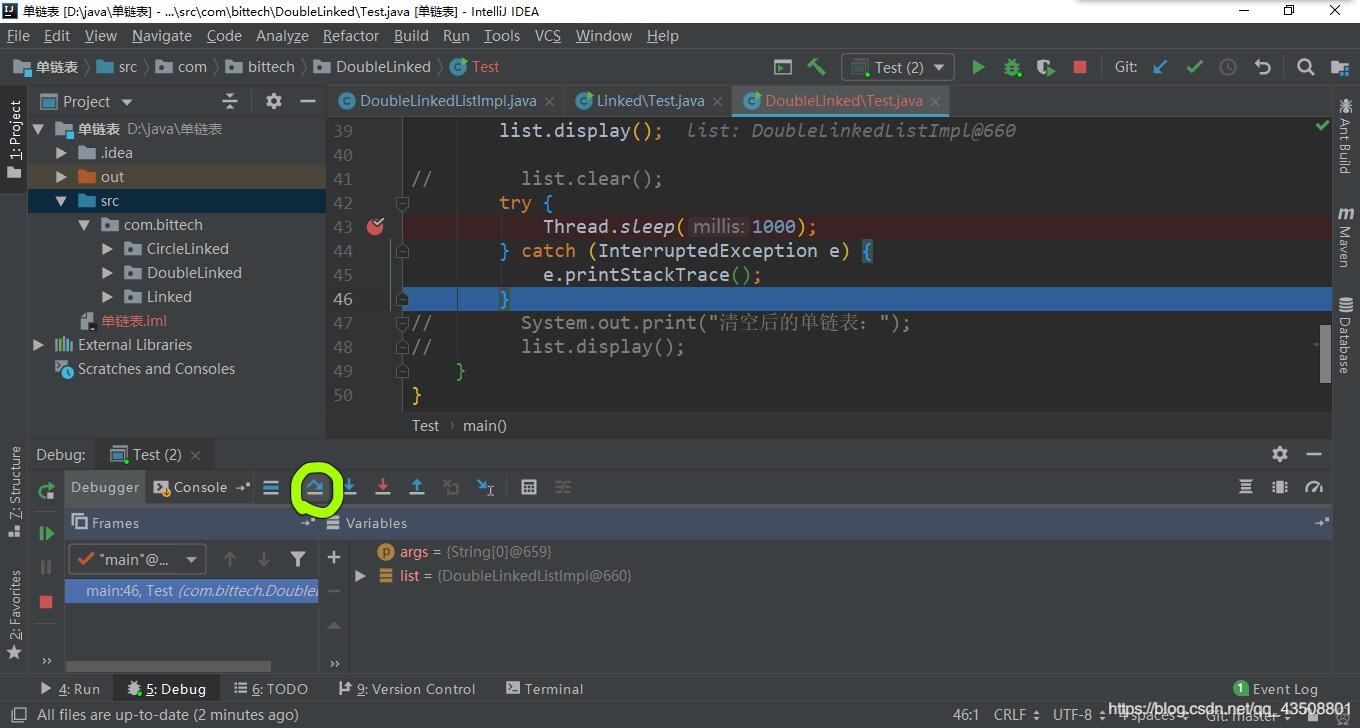
① 假设先不调用调用clear()方法,在Thread.sleep()处打断点。
② 点击右上角的甲壳虫图标。
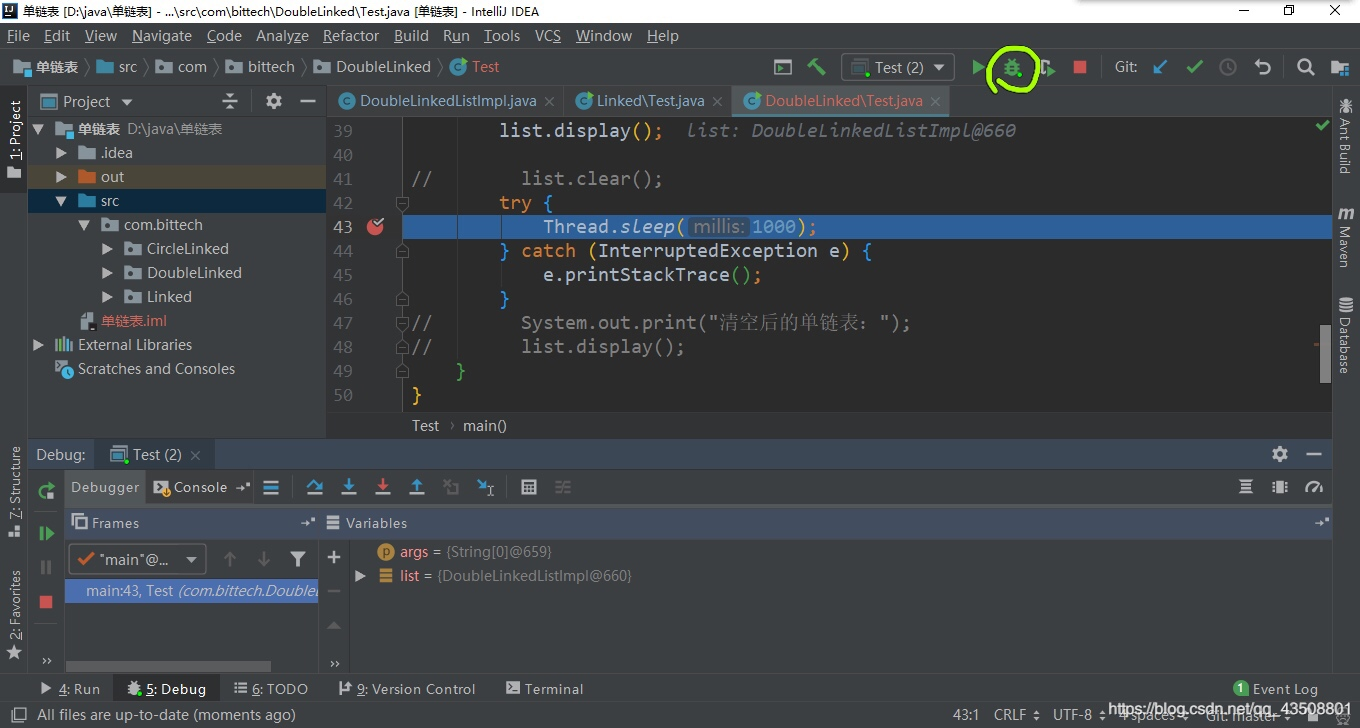
③ 启动cmd命令行,输入如下命令:
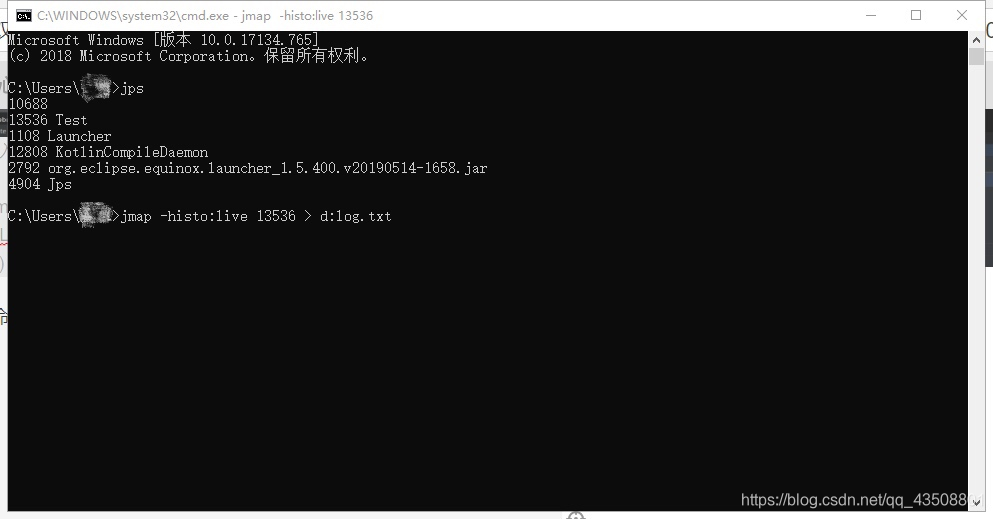
④ 将代码运行至下一行。
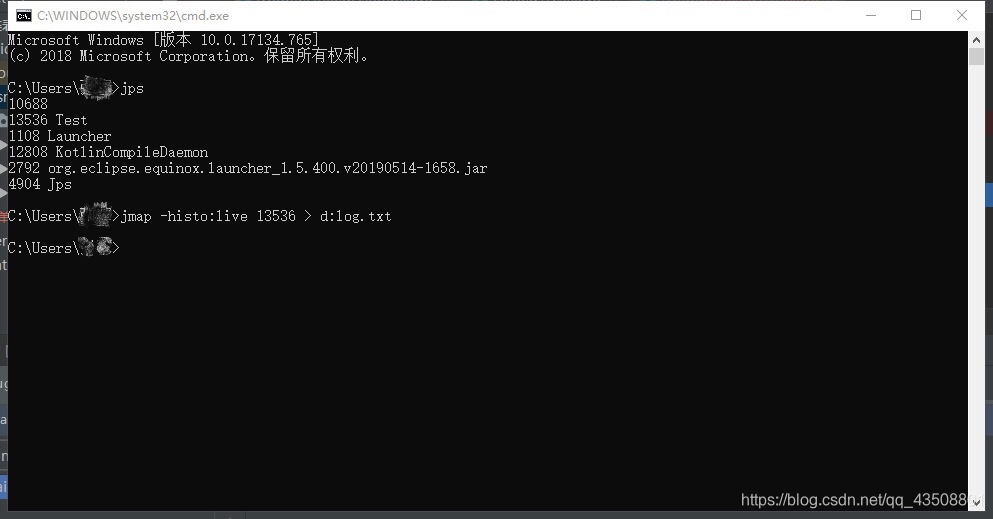
⑤ 再次回到命令行,发现已经运行完成。
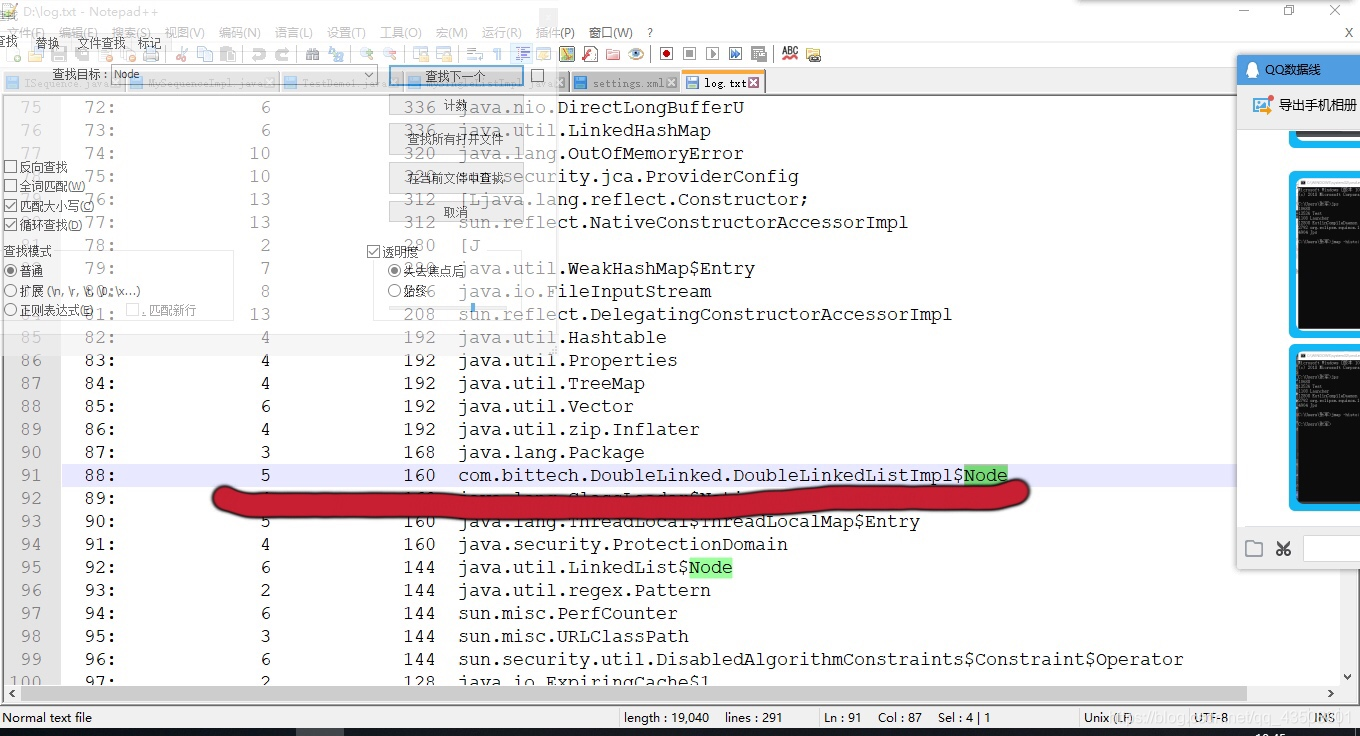
⑥ 打开D:log.txt文件,输入Ctrl+F查找有无Node节点的内存泄漏。发现有5个节点还没有被回收。
⑦ 调用clear()方法之后再重复上述步骤。这次就不会再有内存泄漏了。
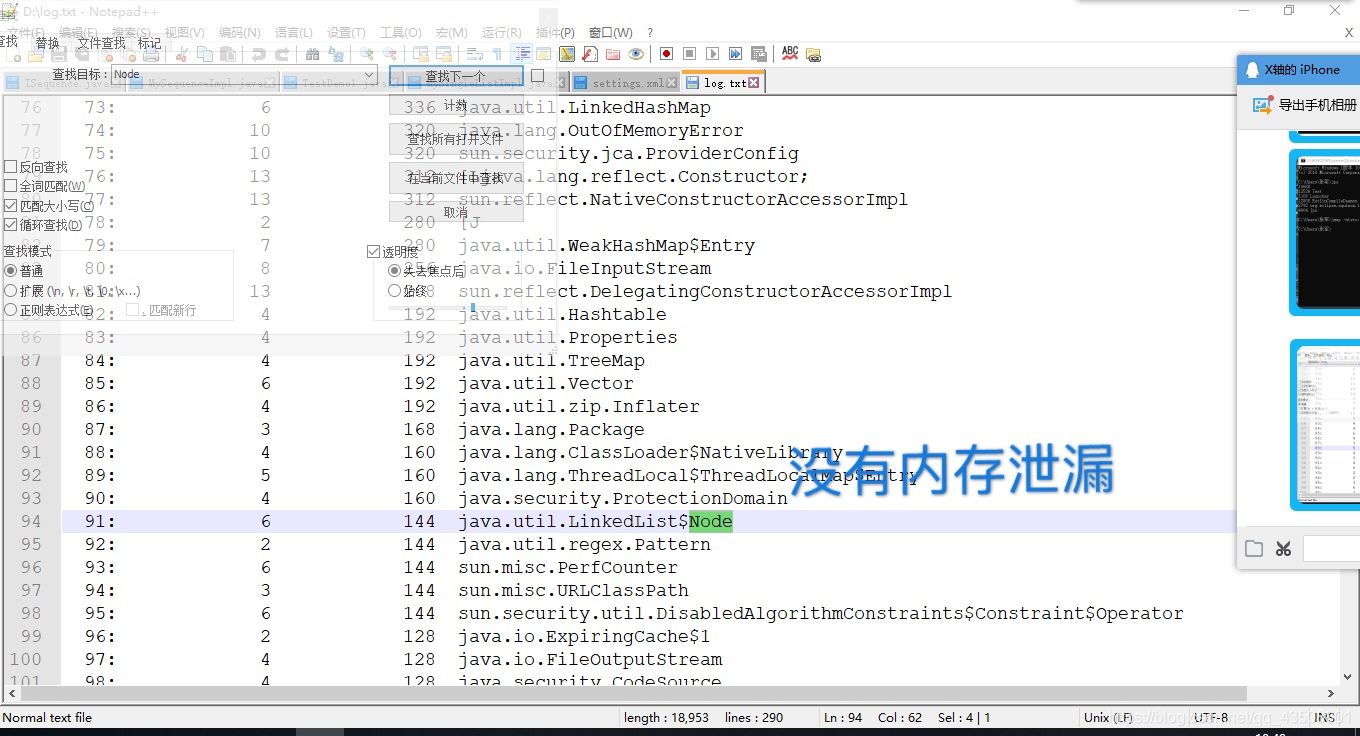








 博客介绍了双向链表与单链表的差异,着重讲述不带头双向链表的语言实现。还给出在Java中查看内存是否泄漏的方法,通过设置断点、使用命令行等步骤,检测到未调用方法时有5个节点内存未回收,调用方法后无内存泄漏。
博客介绍了双向链表与单链表的差异,着重讲述不带头双向链表的语言实现。还给出在Java中查看内存是否泄漏的方法,通过设置断点、使用命令行等步骤,检测到未调用方法时有5个节点内存未回收,调用方法后无内存泄漏。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








