@线程池
线程池
消费者线程
1 消费者线程统一到ThreadFunc函数中执行,初始时消费者线程判断任务队列为空,会挂起在条件变量上。
2 消费者线程被唤醒后,首先检查退出码,判断是否需要退出,如果需要退出的就主动解锁并退出
之所以消费者线程自动退出的目的是,不让管理者线程承担过多的工作,管理者线程应该只是负责统一的管理,
即管理者线程设置线程退出码,之后的退出工作完全由消费者线程自己完成。
3 消费者线程只是取任务,执行任务,无任务挂起
管理者线程
1 管理者线程需要做两件事:
1.1 当任务数比较多时,能够合理的增加线程数
1.2 当任务数比较少时,能够合理的减少线程数
2 增加线程数
2.1 管理者增加消费者的线程通过忙碌线程数和当前创建的线程数的占比来确定,并且线程数的总数不能超过最大线程数
2.2 此设计的线程池的占比设计为70%,即当忙碌线程数大于等于创建线程数的70%时,就会一次增加10个线程(占比需要合理设计,这里的70只是粗略的设计)
3 减少线程数
3.1 管理者减少消费者的线程数同样通过忙碌线程数和当前创建的线程数来确定,并且线程数最小不能小于最小线程数
3.2 此设计的线程池较少条件为空闲线程数大于等于忙碌线程数的两倍,
则每次退出10个(管理者线程只是设置线程退出码,唤醒消费者线程,实际上是消费者线程自己结束)
(同样,线程数的退出条件也应该合理设计,这里只是粗略设计)
代码
threadPool.h
#ifndef __MYTHREADPOOL__
#define __MYTHREADPOOL__
#include <pthread.h>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <queue>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
class ThreadPool{
public:
typedef std::shared_ptr<ThreadPool> ptr;
typedef std::function<void(void*)> task;
//线程池构造函数
ThreadPool() = default;
ThreadPool(int min, int max);
~ThreadPool();
bool init();
bool addTask(task t, void*);
static void* ThreadFunc(void *);
static void* ThreadManager(void *);
private:
bool m_bQuit = false;
int m_minThreadNum = 8;//如何设计
int m_maxThreadNum = 100;//如何设计
int m_curThreadNum = 8;
int m_busyTHreadNum = 0;
int m_threadExitCode = 0;
pthread_t m_ManagerId;
std::list<pthread_t> m_lThreadId;
std::queue<pair<task, void*> > m_qTask;
//线程安全
pthread_mutex_t m_mutex;
pthread_cond_t m_cond;
};
#endif
threadPool.cc
include "../include/threadPool.h"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#define THREADINCREMENT 10
#define THREADDECREMENT 10
ThreadPool::ThreadPool(int min, int max){
m_minThreadNum = min;
m_maxThreadNum = max;
m_curThreadNum = min;
m_busyTHreadNum = 0;
int res = pthread_mutex_init(&m_mutex, NULL);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool pthread_mutex init failed");
exit(1);
}
res = pthread_cond_init(&m_cond, NULL);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool pthread_cond init failed");
exit(1);
}
}
ThreadPool::~ThreadPool(){
m_bQuit = true;
pthread_mutex_destroy(&m_mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&m_cond);
}
bool ThreadPool::init(){
//创建管理者线程
int res = pthread_create(&m_ManagerId, NULL, ThreadManager, this);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool::init pthread_create manager failed");
return false;
}
pthread_t tid;
//创建消费者线程
for(int i = 0; i < m_minThreadNum; ++i){
res = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, ThreadFunc, this);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool::init pthread_create consumer failed");
return false;
}
m_lThreadId.push_back(tid);
}
return true;
}
bool ThreadPool::addTask(task t, void *arg){
auto ta = std::make_pair(t, arg);
//加锁
pthread_mutex_lock(&m_mutex);
m_qTask.push(ta);
pthread_cond_signal(&m_cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&m_mutex);
return true;
}
void* ThreadPool::ThreadFunc(void *arg){
//将线程设置成分离态
int res = pthread_detach(pthread_self());
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool::ThreadFunc pthread detach failed");
exit(1);
}
ThreadPool* This = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(!This->m_bQuit){
//有任务从任务队列取任务,无任务挂起
pthread_mutex_lock(&This->m_mutex);
while(This->m_qTask.empty()){
//上锁
int res = pthread_cond_wait(&This->m_cond, &This->m_mutex);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool::ThreadFunc pthread cond wait fail");
}
//检查退出码
if(This->m_threadExitCode > 0){
cout << "thread[" << pthread_self() << "]exit\n";
--This->m_curThreadNum;
for(auto it = This->m_lThreadId.begin(); it != This->m_lThreadId.end(); ++it){
if(*it == pthread_self()){
This->m_lThreadId.erase(it);
break;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&This->m_mutex);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
auto t = This->m_qTask.front();
This->m_qTask.pop();
++This->m_busyTHreadNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&This->m_mutex);
//执行任务
t.first(t.second);
pthread_mutex_lock(&This->m_mutex);
--This->m_busyTHreadNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&This->m_mutex);
}
return NULL;
}
void* ThreadPool::ThreadManager(void *arg){
ThreadPool *This = (ThreadPool*)arg;
while(!This->m_bQuit){
pthread_mutex_lock(&This->m_mutex);
int busy = This->m_busyTHreadNum;
int cur = This->m_curThreadNum;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&This->m_mutex);
//空闲线程
int free = This->m_maxThreadNum - busy;
//如果忙碌线程大于等于当前拥有线程的70%:一次增加十个
int percent = (float)busy / cur * 100;
if(percent >= 70 && This->m_curThreadNum < This->m_maxThreadNum){
pthread_t tid;
int tmp = min(THREADINCREMENT, This->m_maxThreadNum - cur);
This->m_curThreadNum += tmp;
for(int i = 0; i < tmp; ++i){
int res = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, ThreadFunc, This);
if(res){
perror("ThreadPool::Manager pthread_create consumer failed");
return NULL;
}
This->m_lThreadId.push_back(tid);
}
cout << "ThreadPool::ThreadManager increment " << tmp << "thread\n";
}
//如果空闲线程是忙碌线程的两倍:空闲线程缩减十个
if(free >= busy*2 && This->m_curThreadNum >= This->m_minThreadNum){
This->m_threadExitCode = min(THREADDECREMENT, This->m_curThreadNum - This->m_minThreadNum);
//唤醒退出线程
for(int i = 0; i < This->m_threadExitCode; ++i){
pthread_cond_signal(&This->m_cond);
}
}
pthread_mutex_lock(&This->m_mutex);
cout << "total:" << This->m_maxThreadNum << " busy: " << This->m_busyTHreadNum << " cur: " << This->m_curThreadNum << endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&This->m_mutex);
sleep(1);
}
return NULL;
}
改进
本线程池只是简单的实现,还有很多需要改进的地方。
- 锁的设计:细粒度锁代替粗粒度锁,提高并发性(此线程池的任务添加,消费者取任务,管理者管理任务都是用的一把锁)
- 增加线程数的条件
- 退出线程数的条件
线程池结果图

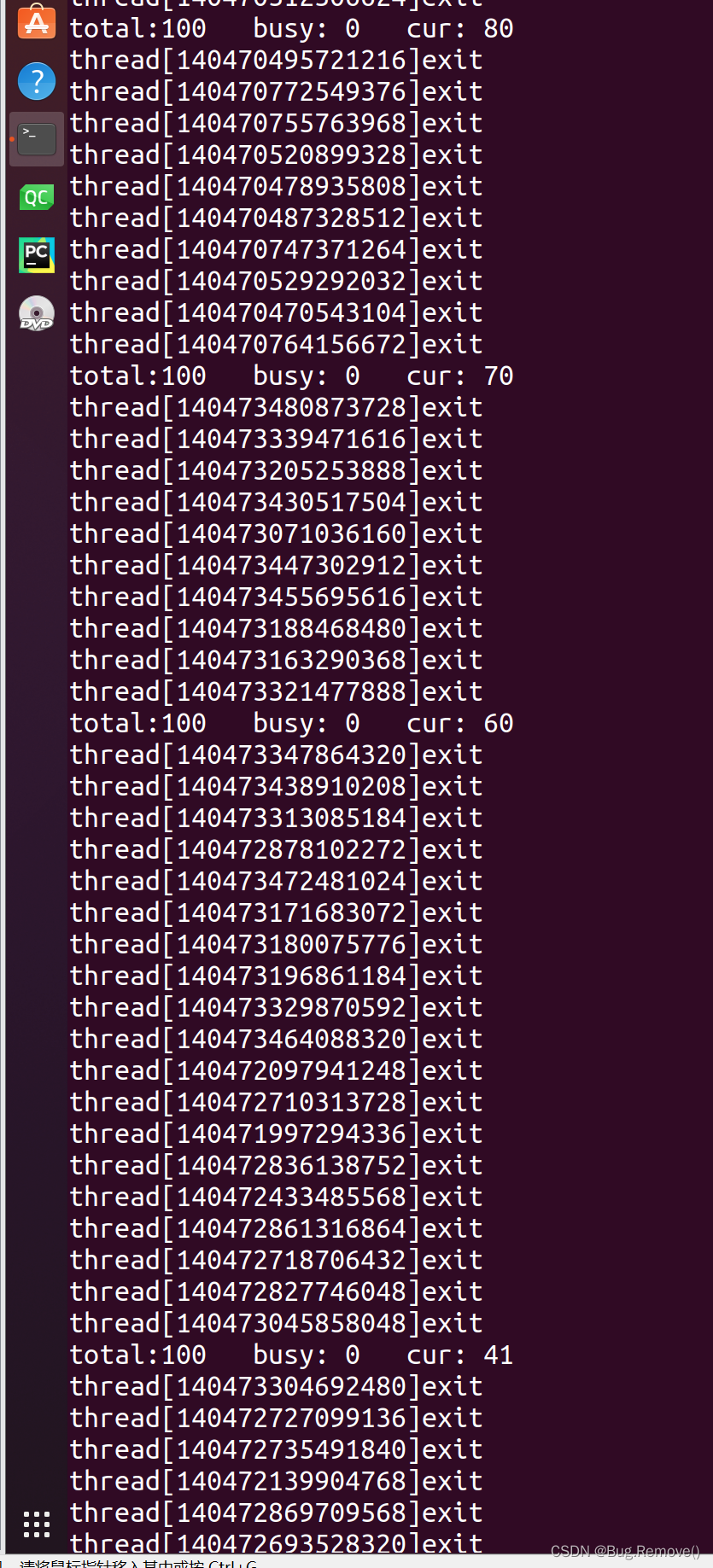



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










