java学习
java常用类
JDK8之前的API
java.text.SimpleDateFormat类
SimpleDateFormat主要有两个作用 日期转换成字符,字符转换成日期
1、日期转换成字符
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
Date date = new Date();
String format = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
//打印结果 21-3-3 下午10:37 这是一种默认的格式
换一种格式输出
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
Date date = new Date();
String format = sdf.format(date);
System.out.println(format);
//执行结果 2021-03-03 10:52:18
2、字符转换成日期
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat();
Date date = new Date();
try {
Date parse = sdf.parse("21-12-3 下午10:37"); //如果不指定格式而且不使用默认格式会报错
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
换一种格式转换
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
try {
Date parse = sdf.parse("2020-03-03 10:52:18");
System.out.println(parse);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
日期格式参考
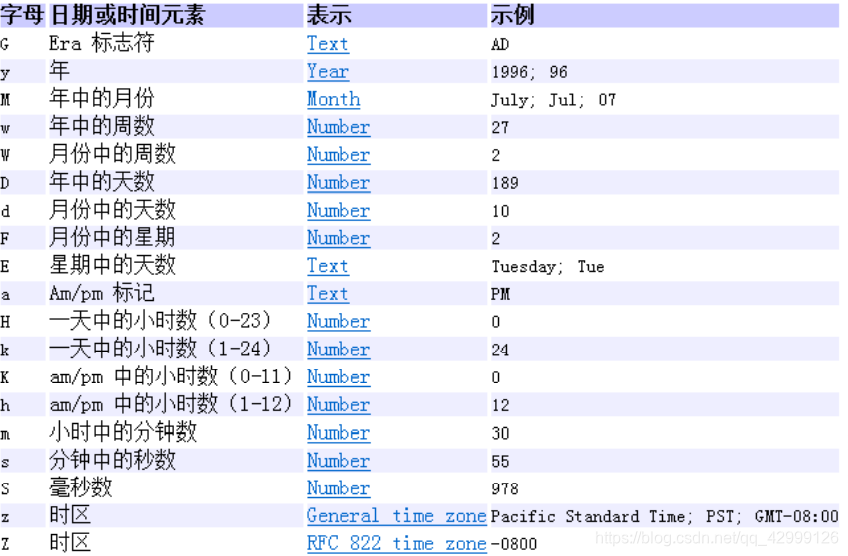
3. java.util.Calendar(日历)类
Calendar是一个抽象基类,主用用于完成日期字段之间相互操作的功能。
获取Calendar实例的方法
方式1:使用Calendar.getInstance()方法
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
方式2:调用它的子类GregorianCalendar的构造器。
GregorianCalendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar();
Calendar常用方法
get()
YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_WEEK、HOUR_OF_DAY 、MINUTE、SECOND
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
int i = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(i);
//执行结果:3
//当前日期是 2021/3/3
set()
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,22);
int i = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(i);
//执行结果 22 某个月份的第22天
add()
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,3);
int i = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
System.out.println(i);
getTime()
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
calendar.add(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,3);
int i = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
Date time = calendar.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
//执行结果 Sat Mar 06 23:44:29 CST 2021
//今天是 2021/3/3 而结果上是多加的三天
JDK8中新日期时间API
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime 类是其中较重要的几个类,它们的实例是不可变的对象,分别表示使用 ISO-8601日历系统的日期、时间、日期和时间。它们提供了简单的本地日期或时间,并不包含当前的时间信息,也不包含与时区相关的信息。
LocalDate代表IOS格式(yyyy-MM-dd)的日期,可以存储 生日、纪念日等日期。
LocalTime表示一个时间,而不是日期。
LocalDateTime是用来表示日期和时间的,这是一个最常用的类之一。
//使用now获取当前日期
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalTime localTime = LocalTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(localDate);
System.out.println(localTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
//使用of()方法,设置指定的年 月 日 时 分 秒
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2021, 10, 5, 18, 56, 59);
System.out.println(localDateTime1);
常用的get操作

//getDayOfMonth() 获取当前月的第几天
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfMonth());
//getDayOfWeek() 获取当前是星期几
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfWeek());
//getDayOfYear() 返回一年中的第几天
System.out.println(localDateTime.getDayOfYear());
//getHour() 获取当前的小时
System.out.println(localDateTime.getHour());
//getMonth() 获取当前的月份
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonth());
//getMonthValue() 获取当前的月份
System.out.println(localDateTime.getMonthValue());
//getSecond() 获取当前的秒数
System.out.println(localDateTime.getSecond());
设置时间的操作这里以设置小时为例
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime.withHour(4);
System.out.println(localDateTime); //2021-03-04T08:22:06.931
System.out.println(localDateTime2); //2021-03-04T04:22:06.931
//在这里可以发现withHour只是重新设置了时间并返回,没有影响到原来的时间
瞬时:Instant
Instant:时间线上的一个瞬时点。 这可能被用来记录应用程序中的事件时间戳。
常用方法

//now()获取本初子午线对应的标准时间
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now);
//设置偏移时间
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = now.atOffset(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8));
System.out.println(offsetDateTime);
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter 类
这个类类似于SimpleDateFormat,这个类提供了3种格式化的方法
预定义的标准格式。如:
ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;ISO_LOCAL_DATE;ISO_LOCAL_TIME
//格式化方式1
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter format = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;
//日期 ---》 字符串
String str1 = format.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str1);
//字符串 --》日期
TemporalAccessor parse = format.parse("2021-03-04T08:44:47.794");
System.out.println(parse);
本地化相关的格式。FormatStyle.LONG 、 FormatStyle.MEDIUM、FormatStyle.SHORT
如:ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG)
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
//日期 ---》 字符串
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.LONG);
String str = formatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str);
//字符串 --》日期
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse("2021年3月4日 上午08时52分56秒");
System.out.println(parse);
自定义的格式。如:ofPattern(“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”)
//自定义日期的格式
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
//日期 ---》 字符串
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String str = formatter.format(localDateTime);
System.out.println(localDateTime);
System.out.println(str);
//字符串 --》日期
TemporalAccessor parse = formatter.parse("2021-03-04 09:00:11");
System.out.println(parse);
Java比较器
Java实现对象排序的方式有两种:
1、自然排序:java.lang.Comparable
2、定制排序:java.util.Comparator
方式一:自然排序:java.lang.Comparable
实现 Comparable 的类必须实现 compareTo(Object obj) 方法,两个对象即
通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小。
如果当前对象this大于形参对象obj,则返回正整数,
如果当前对象this小于形参对象obj,则返回负整数,
如果当前对象this等于形参对象obj,则返回零。
Comparable 的典型实现:(默认都是从小到大排列的)
String:按照字符串中字符的Unicode值进行比较
Character:按照字符的Unicode值来进行比较
数值类型对应的包装类以及BigInteger、BigDecimal:按照它们对应的数值大小进行比较
Boolean:true 对应的包装类实例大于 false 对应的包装类实例
Date、Time等:后面的日期时间比前面的日期时间大
package com.niu.base.bean;
//商品类
public class Goods implements Comparable{
private String name;
private double price;
public Goods() {
}
public Goods(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Goods{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Goods){
Goods goods = (Goods)obj;
if (this.price>goods.price){
return 1;
}else if (this.price<goods.price){
return -1;
}else{
return this.name.compareTo(goods.name);
}
}
throw new RuntimeException("传入的数据类型不符合要求");
}
}
/**
* 实现 Comparable 的类必须实现 compareTo(Object obj) 方法,两个对象即
* 通过 compareTo(Object obj) 方法的返回值来比较大小。
* 如果当前对象this大于形参对象obj,则返回正整数,
* 如果当前对象this小于形参对象obj,则返回负整数,
* 如果当前对象this等于形参对象obj,则返回零。
*
* 自定义的类如果需要排序,必须让自定义的类实现comparable接口重写compareTo(Object obj)方法
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Goods[] arr = new Goods[5];
arr[0] = new Goods("xiaomi",50);
arr[1] = new Goods("huawei",65);
arr[2] = new Goods("haier",20);
arr[3] = new Goods("shenzhou",30);
arr[4] = new Goods("dell",20);
Arrays.sort(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
方式二:定制排序:java.util.Comparator
/**
* 重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法,
* 比较o1和o2的大小:如果方法返回正整数,则表示o1大于o2;
* 如果返回0,表示相等;
* 返回负整数,表示o1小于o2。
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
//自己指定排序的规则
String[] arr = new String[]{"AA","CC","KK","MM","GG"};
Arrays.sort(arr, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
return -o1.compareTo(o2);
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
集合
集合框架的概述
一、为什么要使用集合,数组有哪些弊端?
集合(collection)针对多个数据进行存储的结构,简称java容器
使用数组存储有什么不方便的地方?
1.使用数组长度一旦确定下来就不能改变了
2.数组针对添加,删除操作不方便,效率也不高
3.数组存储数据的特点要求是有序并且是连续的,如果针对无序,不可重复的场景的需求不能满足
二、集合中的分类
ava集合框架分类
java集合框架可以分为Collection和Map两种体系
Collection接口:存放的是单列的数据,用来存储一个一个的对象
List:元素是有序的,可重复的集合
主要的实现类: ArrayList、 LinkedList、Vector
Set: 元素是无序的,不可重复的集合
主要的实现类: HashSet、LinkedHashSet、 TreeSet
Map接口:双列数据,保存k-v的映射关系,一对一对的数据
主要的实现类: HashMap、 Hashtable、 LinkedHashMap、Properties 、 TreeMap
集合的继承关系
Collection的继承关系

Map集合的继承关系

Collection集合中常用方法
1.添加
add(Object obj)
addAll(Collection coll)
//add
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add("LL");
collection.add("YY");
collection.add(new Date());
collection.add(456);
//addAll
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection.add("LL");
collection.add("YY");
collection.add(new Date());
collection.add(456);
collection1.add("NN");
collection1.add("YY");
collection.addAll(collection1);
System.out.println(collection.size());
2.获取有效元素的个数
int size()
collection.size()
3.清空集合
void clear()
collection.clear();
4.判断集合中的元素是否为空
boolean isEmpty()
boolean empty = collection.isEmpty();
5.是否包含某个元素
boolean contains(Object obj):是通过元素的equals方法来判断是否是同一个对象
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
//contains()
boolean isContains = collection.contains(new Person("jack", 22));
System.out.println(isContains);
boolean containsAll(Collection c):也是调用元素的equals方法来比较的。拿两个集合的元素挨个比较。
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection1.add(123);
collection1.add(456);
System.out.println(collection.containsAll(collection1));
6.删除操作
boolean remove(Object obj) :通过元素的equals方法判断是否是要删除的那个元素。只会删除找到的第一个元素
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
collection.remove(123);
System.out.println(collection.size());
boolean removeAll(Collection coll):取当前集合的差集
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection1.add(123);
collection1.add(456);
System.out.println(collection1.size());
7.取两个集合的交集,并返回到当前的集合
boolean retainAll(Collection c):把交集的结果存在当前集合中,不影响c
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection1.add(123);
collection1.add(456);
collection.retainAll(collection1);
System.out.println(collection);
8.集合是否相等,需要当前集合和形参集合的元素都相同
boolean equals(Object obj)
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection1.add(123);
collection1.add(456);
boolean equals = collection.equals(collection1);
System.out.println(equals);
9.转成对象数组
Object[] toArray()
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Object[] objects = collection.toArray();
for (Object obj:objects) {
System.out.println(obj);
}
10.获取集合对象的哈希值
hashCode()
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
collection. hashCode()
11.遍历
iterator():返回迭代器对象,用于集合遍历
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("jack",22));
collection.add(false);
Iterator iterator = collection.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
List接口
List接口的特点
1、集合中的元素是有序的,可重复的
2、List集合常用的实现类ArrayList,LinkedList、Vector
这三个类有哪些异同?
相同点:这三个类都实现了List接口,存储数据的特点相同,有序的,可重复的数据
不同点:
ArrayList:List接口的主要实现类,线程不安全的,执行的效率高,底层使用Object[]存储
LinkedList:底层使用双向链表实现,对于频繁的插入,删除的操作使用LinkedList操作比ArrayList效率要高
Vectory:老的实现类,线程安全的效率低下,底层也是使用Object[]数组
ArrayList 在jdk7的情况下
ArrayList list = new ArrayList() //地层帮助我们创建了一个长度为10的Object[]数组elementData,类似于单例模式的饿汉式
ArrayList 在jdk8的情况下
ArrayList list = new ArrayList() //底层帮我们创建了一个空的Object数组,类似于单例模式的懒汉式
在第一次调用add方法的时候,底层才会创建长度为10的数组
List集合中的常用方法
void add(int index, Object ele):在index位置后面插入ele元素
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
list.add(1,"newele");
boolean addAll(int index, Collection eles):从index位置开始将eles中的所有元素添加进来
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list1.add("hello1");
list1.add("hello2");
list1.add("hello3");
list.addAll(1,list1);
Object get(int index):获取指定index位置的元素
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
Object o = list.get(0);
int indexOf(Object obj):返回obj在集合中首次出现的位置
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
int i = list.indexOf(456);
System.out.println(i);
int lastIndexOf(Object obj):返回obj在当前集合中末次出现的位置
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
list.add(456);
int i = list.lastIndexOf(456);
System.out.println(i);
Object remove(int index):移除指定index位置的元素,并返回此元素
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
list.add(456);
Object remove = list.remove(3);
System.out.println(remove);
Object set(int index, Object ele):设置指定index位置的元素为element
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(123);
list.add(456);
list.add("nyc");
list.add(456);
list.set(1,"haha");
System.out.println(list);
Set接口
set接口存储数据的特点:无序的、不可重复的
set接口的框架
Collection接口:单列集合,用来存储一个一个的对象
set接口作为Collection接口的实现类:存储无序的、不可重复的数据。
HashSet作为set接口的主要实现类:线程不安全,可以存储null值
LinkedHashSet:是HashSet的子类,遍历内部的数据可以按添加的顺序去遍历
TreeSet:可以按照添加对象的指定属性,进行排序
无序性:在这无序性不等于随机性,存储的数据在底层中并非按照数组索引的顺序添加,而是根据数据的哈希值进行添加
不可重复性:保证添加的元素按照 equals()判断时候,不能返回true
向Set集合中添加数据,一定要重写hashCode()和equals()这两个方法
反射机制
反射的概述
Reflection(反射)是被视为动态语言的关键,反射机制允许程序在执行期
借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息,并能直接操作任意对象的内
部属性及方法。
加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个
类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。我们可
以通过这个对象看到类的结构。这个对象就像一面镜子,透过这个镜子看
到类的结构,所以,我们形象的称之为:反射。

反射能干什么
java反射机制提供的功能
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
在运行时获取泛型信息
在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
在运行时处理注解
生成动态代理
反射相关的主要的API
java.lang.Class:代表一个类
java.lang.reflect.Method:代表类的方法
java.lang.reflect.Field:代表类的成员变量
java.lang.reflect.Constructor:代表类的构造器
在没有使用反射之前,我们通常这样使用
javaBean
package com.niu.java;
public class Person {
private String name;
public int age;
public Person() {
}
private Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("你好,我是一个人");
}
private String showNation(String nation){
System.out.println("我的国籍是:"+nation);
return nation;
}
}
Person p1 = new Person("Tom", 12);
p1.age=10;
System.out.println(p1.toString());
p1.show();
//在person类的外部,不能通过Person类的对象调用其内部私有的结构,比如 私有的属性、方法、构造器
学习反射之后的第一个例子
Class clazz = Person.class;
Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Object obj = cons.newInstance("Tom", 12);
Person p = (Person) obj;
System.out.println(p.toString());
反射的简单使用
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
Class clazz = Person.class;
//1、通过反射,创建Person对象
Constructor cons = clazz.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
Object obj = cons.newInstance("Tom", 12);
Person p = (Person) obj;
System.out.println(p.toString());
//通过反射,调用对象指定的属性、方法
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
age.set(p,10);
System.out.println(p.toString());
//调用方法
Method show = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("show");
show.invoke(p);
//通过反射,可以调用Person类的私有结构
Constructor cons1 = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
cons1.setAccessible(true);
Person p1 = (Person) cons1.newInstance("Jerry");
System.out.println(p1);
//通过反射,访问私有的属性
Field name = clazz.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(p1,"HanMeiMei");
System.out.println(p1);
//通过反射,调用私有的方法
Method showNation = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("showNation", String.class);
showNation.setAccessible(true);
String nation = (String) showNation.invoke(p1, "中国");
System.out.println(nation);
}
待更新…

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








