一、查询
1.1基础查询语句
和其他的数据库一样,select * from 表名。
select * from hr.employees
1.2算术表达式
简单的加减乘除。
select salary *12 from hr.employees //计算年薪
1.3别名
在查询结果中,给一个查询结果列另取一个名字
select salary*12 as "年薪" from hr.employees

1.4字符串连接
select last_name,first_name from hr.employees
分别查询,不进行字符串连接
select last_name || first_name 姓名 from hr.employees
把姓和名连接在一起,并且显示在同一个字段中
select last_name || ' ' || first_name 姓名 from hr.employees
在上面的基础上,在两个字段中间加上空格
1.5重复行(去重)
select department_id from hr.employees
这是不进行去重查询部门id,有的员工在一个部门,可能会看到重复的部门id
select distinct department_id from hr.employees
这是进行去重,消除重复的部门id号
select department_id from hr.employees group by department_id having count(department_id ) > 1
也可以这样。
1.6条件限定
只查询工资高于5000的员工
select * from hr.employees where salary > 5000
常用的条件限定表达式:
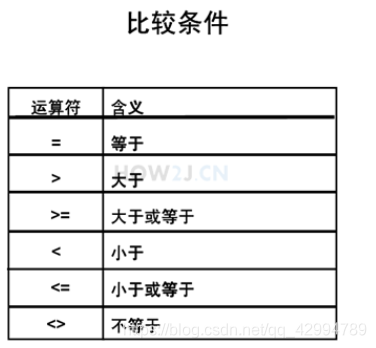
闭区间between and
select * from hr.employees where salary between 3000 and 5000
查询工资在3000到5000之间的员工,闭区间,也就是大于等于3000,小于等于5000.
或者in
select * from hr.employees where salary in(3000,6000)
薪水要么等于3000,要么等于6000。
模糊查询like
select * from hr.employees where first_name like '%a_'
名字里倒数第二个字母是a的员工,%表示任意匹配,有或者没有都可以。
是否为空is null
select * from hr.employees where department_id is null
查询部门id为空的员工
1.7逻辑条件
常用的逻辑条件:

与and
select * from hr.employees where salary between 3000 and 5000
select * from hr.employees where salary>=3000 and salary<=5000
and和between效果是一样的,不过and灵活一些。
或or
select * from hr.employees where first_name like '%a_' or first_name like '_a%'
要么名字倒数第二个是a,要么名字正数第二个字母是a。
非not
select * from hr.employees where first_name not like '%a_'
排除名字倒数第二个字母是a的员工。
1.8排序查询
select * from hr.employees order by salary desc/asc
根据工资倒排序。
1.9关联查询(多表查询)
select e.first_name,e.department_id from hr.employees e
查询员工名称和部门id,还需要部门名称,该怎么做?
select d.department_id,d.department_name from hr.departments d
直接查询部门表?可这样无法对应员工名称的关系啊。
所以,我们需要将两张表进行关联
select e.first_name,d.partment_name from hr.employees e left join hr.departments d on e.department_id = d.department_id
这样就能关联查询了,值得一提的是,left join是进行表关联,on是指定关联字段。
查询有员工的部门的平均工资,要求显示部门编号,部门名,部门所在地(需要多表关联查询: employees, department, location)
select avg(e.salary), e.department_id,d.department_name,l.street_address from hr.employees e
left join hr.departments d
on e.department_id = d.department_id
left join hr.locations l
on d.location_id = l.location_id
上面是三个表的多表查询

1.10统计函数
count:统计月薪高于5000的有多少人
select count(*) from hr.employees e where e.salary > 5000
max,min:统计id为100的部门最高薪水和最低薪水是多少
select max(salary),min(salary) from hr.employees e where e.department_id = 100
avg:统计平均工资
select avg(salary) from hr.employees e
1.11分组查询
分组查询常常和统计函数结合起来使用。
按照部门进行分组,查看每个部门的平均薪资是多少,如果没有分组查询,就需要进行多次查询,再手动汇总。
select avgf(salary) from hr.employees e where e.department_id = 90
select avgf(salary) from hr.employees e where e.department_id = 100
select avgf(salary) from hr.employees e where e.department_id = 110
……
如果使用分组查询:
select avg(salary),e.department_id from hr.employees e group by e.department_id

值得一提的是,分组的时候,查询字段只能是统计函数或者被分组的字段,例如department_id,因此id是所有部门都共有的,如果用department_name来进行分组,那就每个组就只有一个部门,没有意义。
1.12having
以部门进行分组,找出部门平均薪资高于5000的数据。
select avg(salary),e.department_id from hr.employees e group by e.department_id having avg(salary) > 5000
1.13子查询
子查询也就是可以简单地理解成同时执行多条sql语句,将一条sql语句的结果作为条件来执行另一条sql语句。
select e.salary from hr.employees e where e.first_name = 'Bruce'
查询出Bruce的月薪,得到数据是6000。
select count(*) from hr.employees e where e.salary > 6000
统计月薪高于6000的人数
这需要两条sql语句、两次操作,通过子查询的话一条sql就足够了:
select count(*) from hr.employees e where e.salary >
(
select e.salary from hr.employees e where e.first_name = 'Bruce'
)
小括号后面的即为子查询
1.14分页查询
只查出5条数据
select * from hr.employees e where rownum <= 5
查出薪水最高的5-10条数据
select * from
(select rownum r,e1.* from
(
select e.* from hr.employees e order by e.salary desc
)e1
)e2 where e2.r >=5 and e2.r <= 10
二、增删改
创建表:
create table hero(
id number,
name varchar2(30),
hp number
)
插入数据:
insert into hero (id,name,hp) values(1,'炸弹人',450);
commit;
创建序列:
--序列从1开始,每次增加1,最大9999999
create sequence hero_seq
increment by 1
start with 1
maxvalue 9999999
使用序列:
--获取下一个值
select hero_seq.nextval from dual
--获取当前值
select hero_seq.currval from dual
作为id插入到表中(oracle没有id自增长,只能通过序列实现了):
insert into hero (id,name,hp,mp,damage,armor,speed) values(hero_seq.nextval,'炸弹人',450,);
修改字段:
--修改一个字段
update hero set damage = 46 where id = 22;
--修改多个字段
update hero set damage = 46,hp = 33 where id = 22;
删除数据:
--删除某条数据
delete from hero where id = 21
--删除一个表里所有的数据
delete from hero
--舍去一个表里数据的数据(无事务,作用于全表),不能恢复,不能回滚!
truncate table hero
--删除表,不能回滚
drop table hero
修改表结构:
--增加一列
alter table hero add (kills number)
--修改某列
alter table hero modify(name varchar2(300))
--删除某列
alter table hero drop column kills
三、索引
创建索引:
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段名);
一次创建多个索引:
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段名1,字段名2);
也可以基于函数创建索引:
create index 索引名 on 表名(字段-100)
查看当前用户下的索引:
select index_name,index_type,table_name,uniqueness from user_indexes;
查看当前用户下的索引(具体到列):
select index_name,table_name,column_name,column_position from user_ind_columns;
删除索引:
drop index 索引名;
四、实用语句
分页查询
select * from (select rownum r,e. * from 要分页的表 e where rownum<=m*n) t where r>m*n-m;--每页显示m条数据,查询第n页数据
全局查询库中某用户下是否有某个值:
declare
v_Sql varchar2(2000);
v_count number;
begin
for xx in (select t.OWNER, t.TABLE_NAME, t.COLUMN_NAME from dba_tab_columns t where t.OWNER = 'EAM200723(用户名)') loop
begin
v_Sql := 'select count(1) from ' || xx.owner || '.' || xx.table_name ||' where ' || xx.column_name || ' like ''%DELL3.jpg(值名称)%'' ';
execute immediate v_Sql
into v_count;
if (v_count >= 1) then
dbms_output.put_line(xx.table_name || ':' || xx.column_name);
end if;
exception
when others then
null;
end;
end loop;
end;
查看表空间名称、路径、大小
select file_name,tablespace_name,bytes from dba_data_files
拓展表空间文件
ALTER TABLESPACE NNC_DATA01 ADD DATAFILE
'D:\APP\YANGC\ORADATA\ORCL\NNC_DATA01_7.DBF'
size 7167M autoextend on ;
查看用户占用空间大小
select *
from (select owner || '.' || tablespace_name name, sum(b) g
from (select owner,
t.segment_name,
t.partition_name,
round(bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024, 2) b,
tablespace_name
from dba_segments t)
where owner not in
('SYS', 'OUTLN', 'SYSTEM', 'TSMSYS', 'DBSNMP', 'WMSYS')
group by owner || '.' || tablespace_name)
order by name
查看表空间使用情况
select total.tablespace_name,
round(total.MB, 2) as Total_MB,
round(total.MB - free.MB, 2) as Used_MB,
round((1 - free.MB / total.MB) * 100, 2) as Used_Pct
from (select tablespace_name, sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024 as MB
from dba_free_space
group by tablespace_name) free,
(select tablespace_name, sum(bytes) / 1024 / 1024 as MB
from dba_data_files
group by tablespace_name) total
where free.tablespace_name = total.tablespace_name;
impdp命令导入dmp文件
-- 创建用户并授权
create user nc200717 identified by nc200717 default tablespace nnc_data01 temporary tablespace temp;
grant connect,dba to nc200717 ;
create or replace directory DB020710 as 'D:\DB020710\';
grant read,write on directory DB020710 to nc200717 ;
--执行导入语句
impdp 用户名/密码 dumpfile=DMP文件名,多个使用空格隔开 directory=目录名 remap_schema=源用户:目标用户 logfile=日志文件名;
imp命令导入dmp文件
imp 用户名/密码@数据库实例名 -- 创建实例
file=C:\data\filename.dmp -- 配置待导入的dmp文件
log=C:\data\logname.log -- 配置要导入时生成的日志文件地址(可不配置)
[fromuser=source用户名 -- 配置dmp导出的数据库的用户名(仅在根据用户名导入数据时配置)
touser=target用户名 -- 配置dmp要导入的数据库的用户名(仅在根据用户名导入数据时配置)
|full=y] -- 配置导入文件中的全部内容,有可能有多个用户的内容
ignore=y; -- 配置导入的时候,如果没有表,创建表并导入数据,如果已经存在的表,忽略创建表,但不忽略导入。
(注意:full=y 和 fromuser、touser 只能二选一)
创建表空间:
CREATE TABLESPACE TRAFFIC
LOGGING
DATAFILE '/home/oracle/tablespace/TRAFFIC.DBF'
SIZE 32M
AUTOEXTEND ON
NEXT 32M MAXSIZE UNLIMITED
EXTENT MANAGEMENT LOCAL;
删除表空间数据文件
ALTER TABLESPACE TEST DROP DATAFILE 3;
五、触发器
触发器语法:
create [or replace] trigger triggername
after|before of --触发动作:之前/之后
[insert][[or] update [of 列列表]][[or] delete]
on table/view --表/视图
[referencing{:old [as] old/:new [as] new}] --引用新表老表
[for each row] --行级模式
[when(condition)] --条件
pl/sql_block; --pl/sql语句(begin...end)
例子:
1.delete
create or replace trigger test_delete
after delete --执行删除后触发
on pam_turnaround --触发器所在的表
for each row --行级
begin
--可执行部分
if(:old.def6='Y') then
raise_application_error(-20001,'导入单据不允许删除');--自定义异常编码:-20000 到-20999
end if;
end;
2.insert
create or replace trigger test_insert
after insert
on pam_turnaround
for each row
begin
if(:new.creator='dwl') then
raise_application_error(-20002,'制单人为dwl的单据不允许新增');
end if;
end;
3.update
create or replace trigger test_update
after update
of dr--只有修改具体的这个字段才会触发
on pam_turnaround
for each row --行级
begin
--可执行部分
if(:old.def6='Y') then
raise_application_error(-20001,'导入单据不能删除');
end if;
end;
启用或禁用触发器
ALTER TRIGGER trigger_name DISABLE
ALTER TRIGGER trigger_name ENABLE
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








