SpringBoot整合视图层:Thymeleaf语法
SpringBoot学习目录
创建项目
修改pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.hzk</groupId>
<artifactId>1springboot</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<!-- 修改jdk版本 -->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<springboot-thymeleaf.version>3.0.2.RELEASE</springboot-thymeleaf.version>
<thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.0.4</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- springBoot 的启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springBoot 的启动器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
变量输出与字符串操作
Thymeleaf 内置对象
注意语法:调用内置对象一定要用#;大部分的内置对象都以 s 结尾,如:strings、numbers、dates
| 表达式 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| th:text | 在页面输出值 |
| th:value | 可以将一个值放入到input标签的value中 |
| ${#strings.isEmpty(key)} | 判断字符串是否为空,如果为空返回 true,否则返回 false |
| ${#strings.contains(msg,‘T’)} | 判断字符串是否包含指定的子串,如果包含返回 true,否则返回 false |
| ${#strings.startsWith(msg,‘a’)} | 判断当前字符串是否以子串开头,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false |
| ${#strings.endsWith(msg,‘a’)} | 判断当前字符串是否以子串结尾,如果是返回 true,否则返回 false |
| ${#strings.length(msg)} | 返回字符串的长度 |
| ${#strings.indexOf(msg,‘h’)} | 查找子串的位置,并返回该子串的下标,如果没找到则返回-1 |
| ${#strings.substring(msg,13)} | 截取子串,用户与 jdk String 类下 SubString 方法相同 |
| ${#strings.substring(msg,13,15)} | 截取子串,用户与 jdk String 类下 SubString 方法相同 |
| ${#strings.toUpperCase(msg)} | 字符串转大写 |
| ${#strings.toLowerCase(msg)} | 字符串转小写 |
日期格式处理
| 表达式 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ${#dates.format(key)} | 格式化日期,默认的以浏览器默认语言为格式化标准 |
| ${#dates.format(key,‘yyy/MM/dd’)} | 按照自定义的格式做日期转换 |
| ${#dates.year(key)} | 获取日期的年 |
| ${#dates.month(key)} | 获取日期的月 |
| ${#dates.day(key)} | 获取日期的日 |
条件判断
1.th:if
@RequestMapping("/test1")
public String test1(Model model){
model.addAttribute("sex", "男");
return "thy";
}
<span th:if="${sex} == ' 男 '">性别:男</span>
<span th:if="${sex} == ' 女 '">性别:女</span>
2.th:switch
@RequestMapping("/test2")
public String test2(Model model){
model.addAttribute("id", "2");
return "thy";
}
<div th:switch="${id}">
<span th:case="1">ID 为 1</span>
<span th:case="2">ID 为 2</span>
<span th:case="3">ID 为 3</span>
</div>
迭代遍历
1.th:each
@RequestMapping("/test3")
public String test3(Model model){
List<Users> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Users(1,"小王",18));
list.add(new Users(2,"小明",19));
list.add(new Users(3,"小红",17));
model.addAttribute("list", list);
return "thy";
}
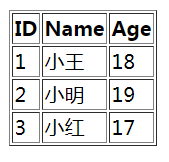
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="u : ${list}">
<td th:text="${u.userid}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.userage}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
2.th:each状态变量
@RequestMapping("/test4")
public String test4(Model model){
List<Users> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new Users(1,"小王",18));
list.add(new Users(2,"小明",19));
list.add(new Users(3,"小红",17));
model.addAttribute("list", list);
return "thy";
}
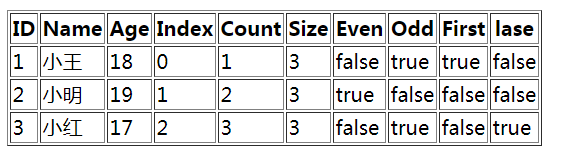
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
<th>Index</th>
<th>Count</th>
<th>Size</th>
<th>Even</th>
<th>Odd</th>
<th>First</th>
<th>lase</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="u,var : ${list}">
<td th:text="${u.userid}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.username}"></td>
<td th:text="${u.userage}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.index}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.count}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.size}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.even}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.odd}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.first}"></td>
<td th:text="${var.last}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
状态变量属性
1,index:当前迭代器的索引 从 0 开始
2,count:当前迭代对象的计数 从 1 开始
3,size:被迭代对象的长度
4,even/odd:布尔值,当前循环是否是偶数/奇数 从 0 开始
5,first:布尔值,当前循环的是否是第一条,如果是返回 true 否则返回 false
6,last:布尔值,当前循环的是否是最后一条,如果是则返回 true 否则返回 false
3.th:each迭代Map
@RequestMapping("/test5")
public String test5(Model model){
Map<String, Users> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("u1", new Users(1,"小王",18));
map.put("u2", new Users(2,"小明",19));
map.put("u3", new Users(3,"小红",17));
model.addAttribute("map", map);
return "thy";
}
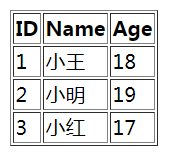
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="maps : ${map}">
<td th:each="entry:${maps}"
th:text="${entry.value.userid}" ></td>
<td th:each="entry:${maps}"
th:text="${entry.value.username}"></td>
<td th:each="entry:${maps}"
th:text="${entry.value.userage}"></td>
</tr>
</table>
域对象操作
HttpServletRequest、HttpSession、ServletContext
@RequestMapping("show")
public String show(HttpServletRequest request,Model model){
request.setAttribute("req", "HttpServletRequest");
request.getSession().setAttribute("sess", "HttpSession");
request.getSession().getServletContext().setAttribute("app", "Application");
return "thy";
}
<div>
Request:<span th:text="${#httpServletRequest.getAttribute('req')}"></span><br/>
Session:<span th:text="${session.sess}"></span><br/>
Application:<span th:text="${application.app}"></span>
</div>
URL表达式
th:href="@{}"
//可通过html名字进行访问跳转,如http://localhost:8080/thy,跳转到thy.html
@RequestMapping("/{page}")
public String pageInfo(@PathVariable String page,Integer id){
return page;
}
1.绝对路径
<a th:href="@{http://www.baidu.com}">绝对路径</a>
<!-- 等同于 -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com">绝对路径</a>
2.相对路径
<!-- 相对于当前项目的根,相对于项目的上下文的相对路径 -->
<a th:href="@{/show}">相对路径</a>
<!-- 相对于服务器路径的根 -->
<a th:href="@{~/project2/resourcename}">相对于服务器的根</a>
3.实现参数传递
<!-- 在url中实现参数传递 -->
<a th:href="@{/show(id=1,name=zhagnsan)}">相对路径-传参</a>
<!-- 在url中通过restful风格进行参数传递 -->
<a th:href="@{/path/{id}/show(id=1,name=zhangsan)}"> 相对路径-传参-restful</a>





 本文是关于SpringBoot中Thymeleaf的使用教程,涵盖内容包括:创建项目、配置pom.xml、变量与字符串操作、日期格式处理、条件判断(th:if, th:switch)、迭代遍历(th:each及状态变量)、域对象操作(如HttpServletRequest等)以及URL表达式的使用。"
53113548,5714274,利用二叉树解析代数表达式,"['数据结构', '算法', '二叉树', '编程实践']
本文是关于SpringBoot中Thymeleaf的使用教程,涵盖内容包括:创建项目、配置pom.xml、变量与字符串操作、日期格式处理、条件判断(th:if, th:switch)、迭代遍历(th:each及状态变量)、域对象操作(如HttpServletRequest等)以及URL表达式的使用。"
53113548,5714274,利用二叉树解析代数表达式,"['数据结构', '算法', '二叉树', '编程实践']
















 1400
1400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








