一:
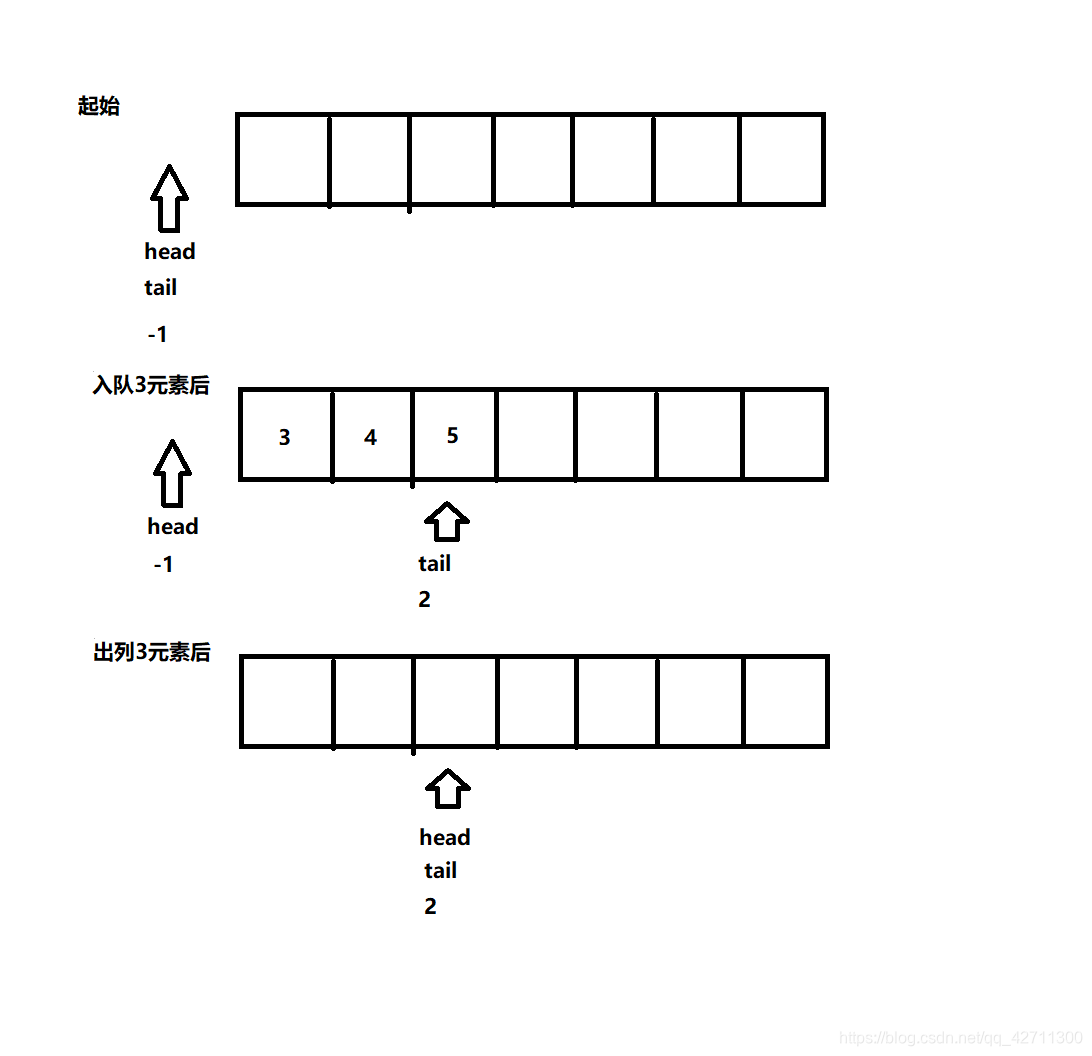
顺序表写法的循环队列
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ref1(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<e;i=i+c)
#define ref2(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<=e;i=i+c)
#define ref3(i,e,s,c) for(int i=e;i>=s;i=i-c)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXSIZE=1000010;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct {
ElemType elem[MAXSIZE];
int head,tail;
}Queue;
void initQueue(Queue *q){
q->head=-1;
q->tail=-1;
}
int empty(Queue q){
if(q.tail==q.head) return 1;
return 0;
}
void push(Queue *q,ElemType x){
if((q->tail+1)%MAXSIZE==q->head) cout<<"Queue is Full!\n";
else{
q->tail=(q->tail+1)%MAXSIZE;
q->elem[q->tail]=x;
}
}
ElemType pop(Queue *q){
if(q->head==q->tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
return -1;
}
else{
q->head=(q->head+1)%MAXSIZE;
return q->elem[q->head];
}
}
ElemType front(Queue *q){
if(q->head==q->tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
return -1;
}
else{
return q->elem[(q->head+1)%MAXSIZE];
}
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
二:链表存储队列
head和tail指针变化情况与上面相同,只是存储结构不同
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ref1(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<e;i=i+c)
#define ref2(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<=e;i=i+c)
#define ref3(i,e,s,c) for(int i=e;i>=s;i=i-c)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXSIZE=1000010;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Node{ //数据元素结点的结构
ElemType elem;
Node *next;
}node;
typedef struct { //队列头尾指针结构体
Node *head,*tail;
}LinkQueue;
void initQueue(LinkQueue *q){
Node *p;
p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->next=NULL;
q->head=p;
q->tail=p;
}
int empty(LinkQueue Q){
if(Q.tail==Q.head) return 1;
return 0;
}
void push(LinkQueue *Q,ElemType x){
Node *p;
p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->elem=x;
p->next=NULL;
Q->tail->next=p;
Q->tail=p;
}
ElemType pop(LinkQueue *Q){
Node *p; ElemType x;
if(Q->head==Q->tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
x=-1;
}
else{
p=Q->head->next;
Q->head->next=p->next;
//若删除的队首元素刚好也是队尾,需要给tail重新设地址,否则下面的free会导致地址悬空,出错
if(p->next==NULL) Q->tail=Q->head;
x=p->elem;
free(p);
}
return x;
}
ElemType front(LinkQueue Q){
Node *p;
if(Q.head==Q.tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
return -1;
}
else{
p=Q.head->next;
return p->elem;
}
}
int main()
{
LinkQueue Q;
initQueue(&Q);
return 0;
}
三:应用
(1)
报数问题:设有n个人站成一排,从左到右的编号分别为1~n,从左到右报数“1,2,3,1,2,3”数到“1,2”的人立即站到队伍的最右端,数到“3”的人出列。报数过程反复进行,直到n个人都出列为止。要求给出他们的出列顺序。
例如,当n=10时,初始序列为
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
则出列顺序为
3 6 9 2 7 1 8 5 10 4
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ref1(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<e;i=i+c)
#define ref2(i,s,e,c) for(int i=s;i<=e;i=i+c)
#define ref3(i,e,s,c) for(int i=e;i>=s;i=i-c)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAXSIZE=1000010;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct Node{ //数据元素结点的结构
ElemType elem;
Node *next;
}node;
typedef struct { //队列头尾指针结构体
Node *head,*tail;
}LinkQueue;
void initQueue(LinkQueue *q){
Node *p;
p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->next=NULL;
q->head=p;
q->tail=p;
}
int empty(LinkQueue Q){
if(Q.tail==Q.head) return 1;
return 0;
}
void push(LinkQueue *Q,ElemType x){
Node *p;
p=(Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->elem=x;
p->next=NULL;
Q->tail->next=p;
Q->tail=p;
}
ElemType pop(LinkQueue *Q){
Node *p; ElemType x;
if(Q->head==Q->tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
x=-1;
}
else{
p=Q->head->next;
Q->head->next=p->next;
if(p->next==NULL) Q->tail=Q->head;
x=p->elem;
free(p);
}
return x;
}
ElemType front(LinkQueue Q){
Node *p;
if(Q.head==Q.tail){
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
return -1;
}
else{
p=Q.head->next;
return p->elem;
}
}
int main()
{
LinkQueue Q;
initQueue(&Q);
int n;
cin>>n;
ref2(i,1,n,1){
push(&Q,i);
}
int k=0;
while(!empty(Q)){
int x=pop(&Q);
if(k<2){
push(&Q,x);
}
else cout<<x<<" ";
k=(k+1)%3;
}
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








