基本概念
首先我们要知道,一个程序在运行过程中可能会遇到程序终止的情况,一般这种情况可以分成两大类
一类是可以处理,非致命性的,正确处理之后程序可以进行,就是我们说的 异常
另一类是不能进行简单的恢复执行,程序遇到了严重的不正常情况,是致命性的,称之为 错误 , 包括 虚拟机错误,动态连接失败等
异常 按照性质,又分为 编译时异常 跟 运行时异常
编译时异常,程序正确,外部条件不满足引发的异常,源代码(.java文件)编译成字节码(.class文件)编译不通过
运行时异常,程序错误,程序存在bug, 比如我们常见的
数组角标越界异常 java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(就是定义了一个只能存5个元素的数组,结果存了6个)
还有就是空指针异常 java.lang.NullPointerException 等等

异常处理
在java 中 ,处理异常主要有两种方式
-
一种是交由java 预设处理机制,(简单来说就是往上抛 ) 用关键字throws
这种方法有点贱了,就是我发现这边有异常,我不去处理,我标记一下,往上抛,等你调用我的时候,你再去处理这个异常
public static int throwMyException() throws ArithmeticException {
return 0;
}
- 另一种方法就是 将异常进行捕获,自己拉的屎自己处理干净 ,别人调用你时就不用再处理异常
捕获异常使用 try和catch 关键字 ,try/catch 代码块放在异常可能出现的地方
try{
int[] array = new int[2];
System.out.println("获取角标为的元素 :" + array[3]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
System.out.println("数组角标越界了!!!");
}
}
打印结果:
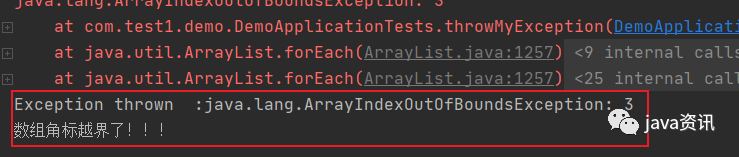
可以看出,当try 里面程序出现异常时,执行catch里面的代码,将异常进行捕获
捕获异常时,还有一个关键字finally ,指的是,不论程序是否发生异常,都会执行finally里面的代码块,例如:
try{
int[] array = new int[2];
System.out.println("获取角标的元素 :" + array[3]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
System.out.println("数组角标越界了!!!");
} finally {
System.out.println("程序发生异常,我是一定会执行的方法");
}

再看未发生异常的情况
try{
int[] array = new int[2];
System.out.println("获取角标的元素 :" + array[1]);
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exception thrown :" + e);
System.out.println("数组角标越界了!!!");
} finally {
System.out.println("程序没有发生异常,我是一定会执行的方法");
}
打印结果:

因为数组里面没有数据,整形默认值为 0
自定义异常 (扩展)
先说说为什么要自定义异常 ?
自定义异常 能更加直观地返回错误数据给前端,便于统一进行处理,话不多说,直接来看实现过程,记得收藏,后续业务需求 ,工作中 100% 可以用到
首先编写一个 封装API的错误码
/**
* 封装API的错误码
* @author: xrp
*/
public interface IErrorCode {
/** getCode
* @return long
*/
long getCode();
/** getMessage
* @return String
*/
String getMessage();
}
接着写一个自定义异常类 ,ApiException 并且 继承 运行时异常
**
* @author xrp
* @date: 2022/03/23/13:37
*/
public class ApiException extends RuntimeException {
private IErrorCode errorCode;
public ApiException(IErrorCode errorCode) {
super(errorCode.getMessage());
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
public ApiException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public ApiException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
public ApiException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public IErrorCode getErrorCode() {
return errorCode;
}
public void setErrorCode(IErrorCode errorCode) {
this.errorCode = errorCode;
}
}
最后写一个全局异常处理器 GlobalExceptionHandler
/**
* @author xrp
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(value = ApiException.class)
public ResponseMessage<Object> handle(ApiException e) {
if (e.getErrorCode() != null) {
return ResultUtils.failed(e.getErrorCode());
}
return ResultUtils.failed(e.getMessage());
}
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(value = MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
public ResponseMessage<Object> handleValidException(MethodArgumentNotValidException e) {
BindingResult bindingResult = e.getBindingResult();
String message = null;
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldError();
if (fieldError != null) {
message = fieldError.getField()+fieldError.getDefaultMessage();
}
}
return ResultUtils.validateFailed(message);
}
@ResponseBody
@ExceptionHandler(value = BindException.class)
public ResponseMessage<Object> handleValidException(BindException e) {
BindingResult bindingResult = e.getBindingResult();
String message = null;
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldError();
if (fieldError != null) {
message = fieldError.getField()+fieldError.getDefaultMessage();
}
}
return ResultUtils.validateFailed(message);
}
}
ResultUtils 为返回前端构造工具 ,一般公司会同一封装
使用断言
package com.safedog.doffice.common.utils.securityutils;
/**
*
* @author xrp
*/
public class Asserts {
public static void fail(String message) {
throw new ApiException(message);
}
public static void fail(IErrorCode errorCode) {
throw new ApiException(errorCode);
}
}
接下来我们就可以使用了,例如
if(!xxxxx) {
Asserts.fail("CRON表达式不正确")
}
以上便是本期 java异常全部内容了,打开微信扫一扫,获取程序员必备书籍,面试宝典


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








