双向链表
为什么需要双向链表?
在单链表中,有了next指针,这就使得要查找的下一个结点的时间复杂度为O(1),可是要查找是上一个结点的话,最坏的时间复杂度是O(n)了,所以为了克服这一缺点提出双向链表。
双向链表:双向链表是在单链表的每个结点中,再设置一个指向其前驱结点的指针域。
双向链表中每个结点都有两个指针域:一个指向直接后继,一个指向直接前驱。
双向链表中循环的带头结点的空链表:
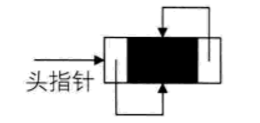
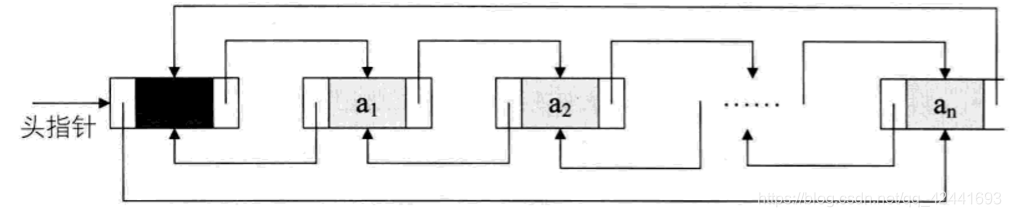
非空的循环的带头结点的双向链表:
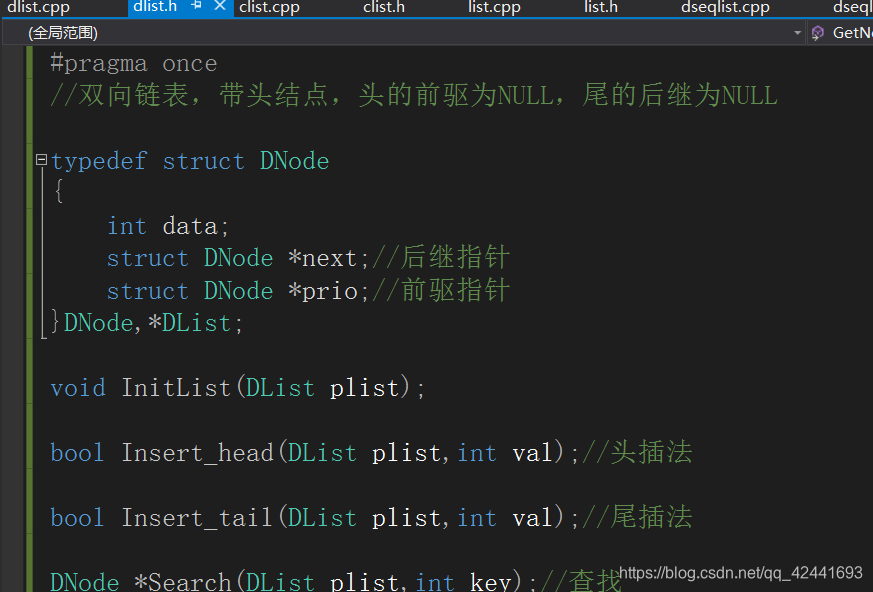
(1)头文件:
实现代码:
#pragma once
//双向链表,带头结点,头的前驱为NULL,尾的后继为NULL
typedef struct DNode
{
int data;
struct DNode *next;//后继指针
struct DNode *prio;//前驱指针
}DNode,*DList;
void InitList(DList plist);
bool Insert_head(DList plist,int val);//头插法
bool Insert_tail(DList plist,int val);//尾插法
DNode *Search(DList plist,int key);//查找
bool Delete(DList plist,int key);//删除
bool IsEmpty(DList plist);//判空
int GetLength(DList plist);//获取长度,数据个数
void Show(DList plist);//打印
DNode *Getprio(DList plist,int key);//获得key的前驱
DNode *GetNext(DList plist,int key);//获得key的后继
void Clear(DList plist);//清空
void Destory(DList plist);//销毁
(2)源文件:
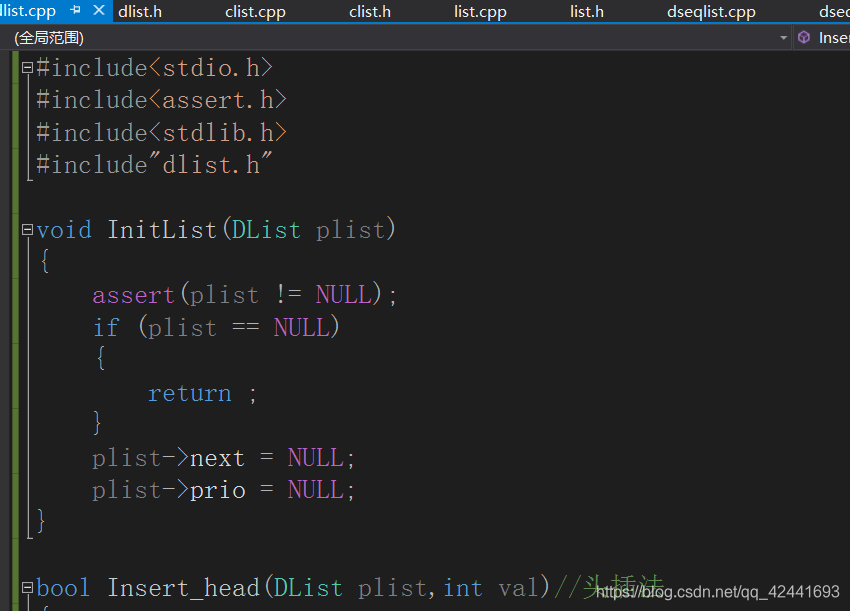
实现代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"dlist.h"
void InitList(DList plist)
{
assert(plist != NULL);
if (plist == NULL)
{
return ;
}
plist->next = NULL;
plist->prio = NULL;
}
bool Insert_head(DList plist,int val)//头插法
{
DNode *p = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
p->data = val;
p->next = plist->next;
plist->next = p;
p->prio = plist;
if (p->next != NULL)
{
p->next->prio = p;
}
return true;
}
bool Insert_tail(DList plist,int val)//尾插法
{
DNode *p = (DNode *)malloc(sizeof(DNode));
p->data = val;
DNode *q;
for (q=plist; q->next != NULL;q=q->next);
p->next = q->next;
p->prio = q;
q->next = p;
return true;
}
DNode *Search(DList plist,int key)//查找
{
for (DNode *p=plist->next; p!=NULL; p=p->next)
{
if (p->data == key)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
bool Delete(DList plist,int key)//删除
{
DNode *p = Search(plist,key);
if (p == NULL)
{
return false;
}
//将p从链表中剔除
p->prio->next = p->next;
if (p->next != NULL)
{
p->next->prio = p->prio;
}
free(p);
return true;
}
bool IsEmpty(DList plist)//判空
{
return plist->next == NULL;
}
int GetLength(DList plist)//获取长度,数据个数
{
int count = 0;
for (DNode *p=plist->next; p!=NULL; p=p->next)
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
void Show(DList plist)//打印
{
for (DNode *p=plist->next; p!=NULL; p=p->next)
{
printf("%d \n",p->data);
}
}
DNode *Getprio(DList plist,int key)//获得key的前驱
{
assert(plist!=NULL);
for (DNode *p=plist; p->next!=NULL; p=p->next)
{
if(p->next->data == key)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
DNode *GetNext(DList plist,int key)//获得key的后继
{
DNode *p = Search(plist,key);
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
return p->next;
}
void Clear(DList plist)//清空
{
Destory(plist);
}
void Destory(DList plist)//销毁
{
DNode *p;
while (plist->next != NULL)
{
p = plist->next;
plist->next = p->next;
free(p);
}
}
测试用例:
1.尾插0-9

2.头插数字25
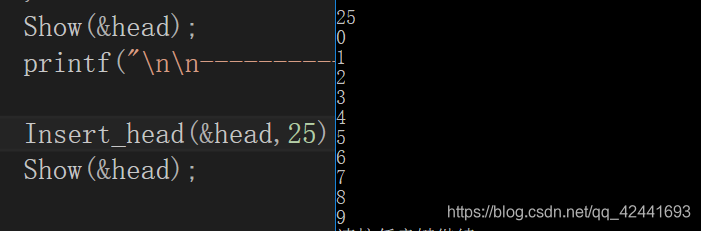
3.获取长度(把头插25去掉了)

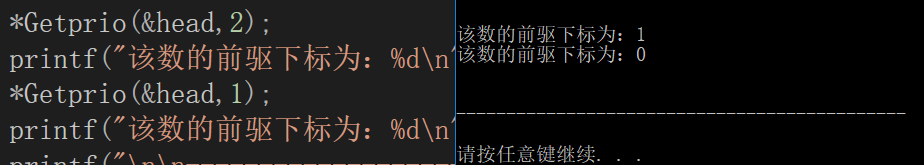
4.查找8

5.查找前驱下标
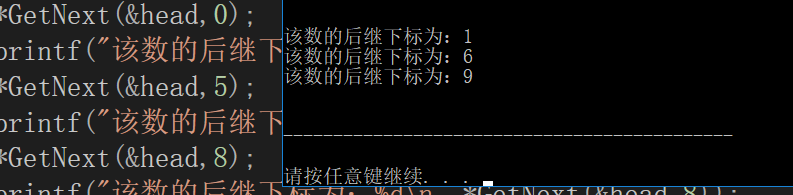
6.查找后继下标
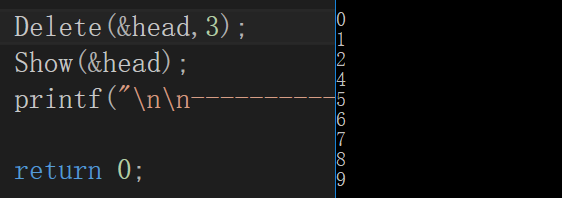
7.删除3
8.清空

9.销毁
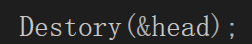
























 693
693

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








