为什么要使用智能指针
看如下代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int *tmp = new int(20);
if (1)
{
/*
功能代码区
*/
return 0;
}
else
{
/*
功能代码区
*/
}
delete tmp;
}
我们看到当第一个if语句满足条件,程序退出后,并没有正常释放tmp所占有的外部资源造成了资源的浪费,即所谓的内存泄漏。
我们在日常开发的时候可能会经常的碰到这种情况的。所以我们引出了智能指针的概念。
实现一个简单的智能指针
利用对象出自已的作用域自动调用析构函数的特性实现我们自己的智能指针。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class SmartPtr
{
public:
SmartPtr(T *ptr = nullptr)
:_mptr(ptr) {}
~SmartPtr() { delete _mptr; }
T &operator*() { return *_mptr; }
T *operator->() { return _mptr; }
private:
T *_mptr;
};
int main()
{
SmartPtr<int> ptr1(new int);
*ptr1 = 20;
return 0;
}
不带引用计数的智能指针
int main()
{
SmartPtr<int> ptr1(new int);
*ptr1 = 20;
SmartPtr<int> ptr2(ptr1);
return 0;
}
利用上面自己实现的智能指针类,运行上面的代码我们发现程序直接奔溃,因为发生了浅拷贝问题。
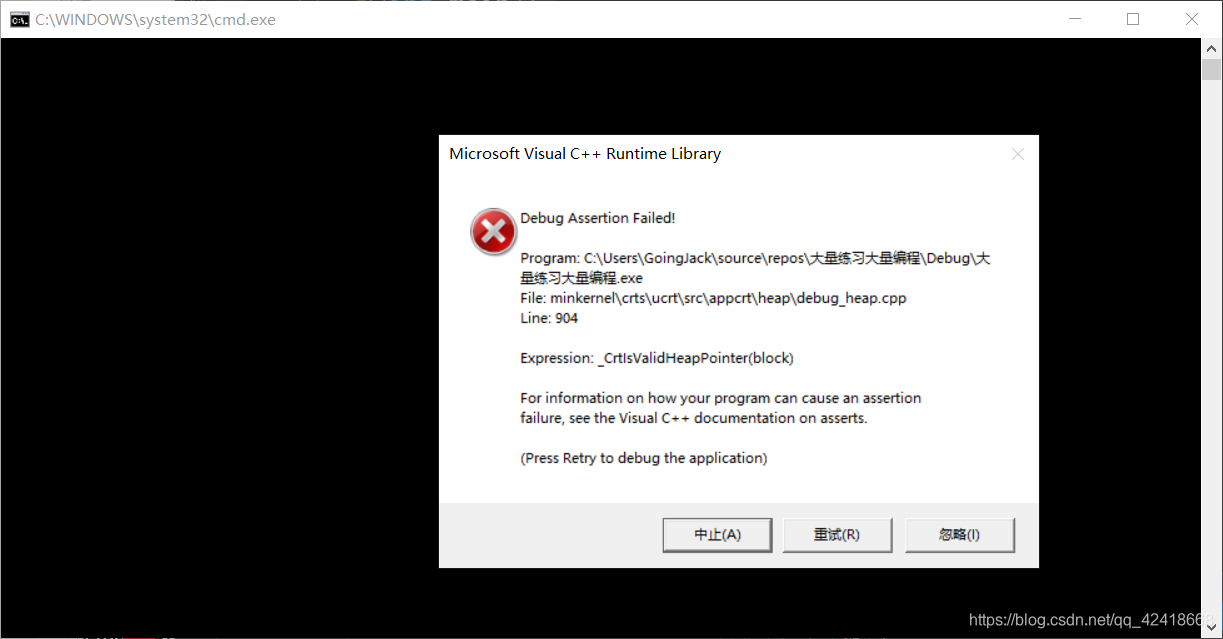
那么怎么解决我们智能指针发生的浅拷贝问题呢????
这里有俩种,
首先,不带引用计数的智能指针,系统中有三个
(库里面有的)
auto_ptr
(C++新标准)
scoped_ptr
unique_ptr
auto_ptr 不推荐使用这个;
auto_ptr(auto_ptr& _Right) noexcept
: _Myptr(_Right.release())
{ // construct by assuming pointer from _Right auto_ptr
}
_Ty * release() noexcept
{ // return wrapped pointer and give up ownership
_Ty * _Tmp = _Myptr;
_Myptr = nullptr;
return (_Tmp);
}
我们根据auto_ptr的拷贝构造函数可以看出来:
每次给另外一个对象拷贝构造的时候,就把被拷贝构造的底层指针置为空,无法再次访问了。所以我们并不推荐使用这个智能指针,除非你的应用场景特别简单的情况下可以使用。
scoped_ptr
scoped_ptr(const scoped_ptr<T>&) = delete;
scoped_ptr operator=(const scoped_ptr<T>&)=delete;
推荐使用
unique_ptr(它本身相当于提供了带右值引用的拷贝构造函数和赋值函数,带左值得拷贝构造和赋值函数和scoped_ptr一样被删除(delete)掉了。)
unique_ptr<int> p1(new int);
unique_ptr<int> p2(std::move(p1));
这里相当于调用了move语义转化将p1持有得资源移动到p2上。移动完成后,p1不再持有任何资源,也无法访问了。
自己简单实现带引用计数的智能指针
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
class RefCnt
{
public:
RefCnt(T *ptr = nullptr) :mptr(ptr)
{
if (mptr != nullptr)
mcount = 1;
}
void addRef() { mcount++; }//添加引用计数
int delRef() { return --mcount; }
private:
T *mptr;
int mcount;
};
template<typename T>
class SmartPtr
{
public:
SmartPtr(T *ptr = nullptr)
:_mptr(ptr)
{
mpRefCnt = new RefCnt<T>(_mptr);
}
~SmartPtr()
{
if (0 == mpRefCnt->delRef())
{
delete _mptr;
_mptr = nullptr;
}
}
T &operator*() { return *_mptr; }
T *operator->() { return _mptr; }
SmartPtr(const SmartPtr<T> &src)
:_mptr(src._mptr)
, mpRefCnt(src.mpRefCnt)
{
if (_mptr != nullptr)
mpRefCnt->addRef();
}
SmartPtr<T>& operator=(const SmartPtr<T> &src)
{
if (this == &src)
return *this;
if (mpRefCnt->delRef() == 0)
{
delete _mptr;
}
_mptr = src._mptr;
mpRefCnt = src.mpRefCnt;
mpRefCnt->addRef();
return *this;
}
private:
T *_mptr;
RefCnt<T> *mpRefCnt;
};
int main()
{
/*
带引用计数得智能指针shared_ptr和weak_ptr
带引用计数:多个智能指针可以管理同一个资源。
给每一个资源,匹配一个引用计数
智能指针 ->申请资源 -> 引用计数+1
智能指针 -> 释放资源 ->引用计数-1
*/
SmartPtr<int> ptr1(new int);
SmartPtr<int> ptr2(ptr1);
SmartPtr<int> ptr3;
ptr3 = ptr2;
*ptr1 = 10;
cout << *ptr3 << " " << *ptr2 << endl;
}
结果:
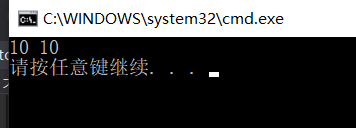
可见带引用计数的ptr可以使得多个智能指针引用同一块内存。
shared_ptr强智能指针 可以改变资源的引用的计数
weak_ptr弱智能指针 不会改变资源的引用的计数
弱智能指针观察强智能指针,强智能指针观察资源。
强智能指针循环引用是什么问题?什么结果?如何解决。
shared_ptr交叉问题??
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()" << endl; }
shared_ptr<B> _ptrb;
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()" << endl; }
shared_ptr<A> _ptra;
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A> pa(new A());
shared_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->_ptrb = pb;
pb->_ptra = pa;
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;
}
结果: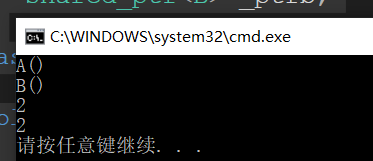
无法达到析构的条件,造成了严重的资源泄漏问题。
解决办法:定义地方使用强智能指针,引用的地方使用弱智能指针。
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()" << endl; }
weak_ptr<B> _ptrb;
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()" << endl; }
weak_ptr<A> _ptra;
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A> pa(new A());
shared_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->_ptrb = pb;
pb->_ptra = pa;
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;
}
结果:
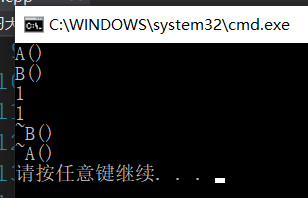
没有任何问题。成功调用析构函数。
又一个问题。。
我们无法使用弱智能指针来访问或者修改资源,,,即没有给weak_ptr提供*和->的运算符重载函数。。。。
但是我们可以通过weak_ptr::lock()提升为强智能指针来调用资源。
举例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
class B;
class A
{
public:
A() { cout << "A()" << endl; }
~A() { cout << "~A()" << endl; }
weak_ptr<B> _ptrb;
void funA()
{
cout << "A的一个非常好用的一个方法" << endl;
}
};
class B
{
public:
B() { cout << "B()" << endl; }
~B() { cout << "~B()" << endl; }
void funB()
{
shared_ptr<A> ptmp = _ptra.lock();
ptmp->funA();
}
weak_ptr<A> _ptra;
};
int main()
{
shared_ptr<A> pa(new A());
shared_ptr<B> pb(new B());
pa->_ptrb = pb;
pb->_ptra = pa;
cout << pa.use_count() << endl;
cout << pb.use_count() << endl;
pb->funB();
}








 本文深入探讨了智能指针的概念及其实现方式,包括不带引用计数和带引用计数的智能指针,并讨论了其在C++中的应用,如auto_ptr、scoped_ptr、unique_ptr等,以及解决循环引用问题的方法。
本文深入探讨了智能指针的概念及其实现方式,包括不带引用计数和带引用计数的智能指针,并讨论了其在C++中的应用,如auto_ptr、scoped_ptr、unique_ptr等,以及解决循环引用问题的方法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








