STL和泛型编程
本学习笔记是基于侯捷老师的STl和泛型编程课程
1. STL六大部件基础介绍 (Components)
容器(Containers)
分配器(Allocator)
算法(Algorithms)
迭代器(Iterators)
适配器(Adapters)
仿函数(Functors)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int ia[6]={27,210,12,47,109,83};
vector<int,allocator<int>> vi(ia,ia+6);
cout<<count_if(vi.begin(), vi.end(),
not1(bind2nd(less<int>(),40))); //计算>=40的个数
return 0;
}
2. 时间复杂度
目前常見的 Big-oh 有下列幾種情形:
1.O(1)或O©:稱為常數時間(constant time)
2.O(n):稱為線性時間(dinear time)
3.O(log2n):稱為次線性時間(sub-lincar time)
4.O(n2):稱為平方時間(quadratic time)
5.O(n):稱為立方時間(cubic time)
6.O(2n):稱為指數時間(exponential time)
7.O(nlog2n):介於線性及二次方成長的中間之行為模式。
3. "前闭后开"区间

c.end( )不是容器的部分,所以要遍历容器的话,需要用如下代码
Container<T> c;
...
Container<T>::iterator ite =c.begin();
for ( ; ite != c.end;++ite)
...
4. Range-besed for statement (since cpp11)
for( dec1 : coll){
statement
}
for(int i : {2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}){
std::cout << i << std::endl;
}
std::vector<double> vec;
...
for ( auto elem : vec){
std::cout << elem << std:endl;
}
for( auto& elem : vec){
elem *= 3; //将vec容器中的元素✖️3
}
auto适度使用可以简化代码量
list<string> c;
...
list<string>::iterator ite;
ite = :find(c.begin(), c.end() ,target);
// 🔽
// 🔽 可以写成下面类型
// 🔽
list<string> c;
...
auto ite = :find(c.begin(), c.end() ,target);
5. 容器-结构与分类
容器分为:
序列式容器 (sequence containers)
关联式容器 (associative containers)
不定序容器 (Unordered Containers)
红色部分是cpp11 增加的东西
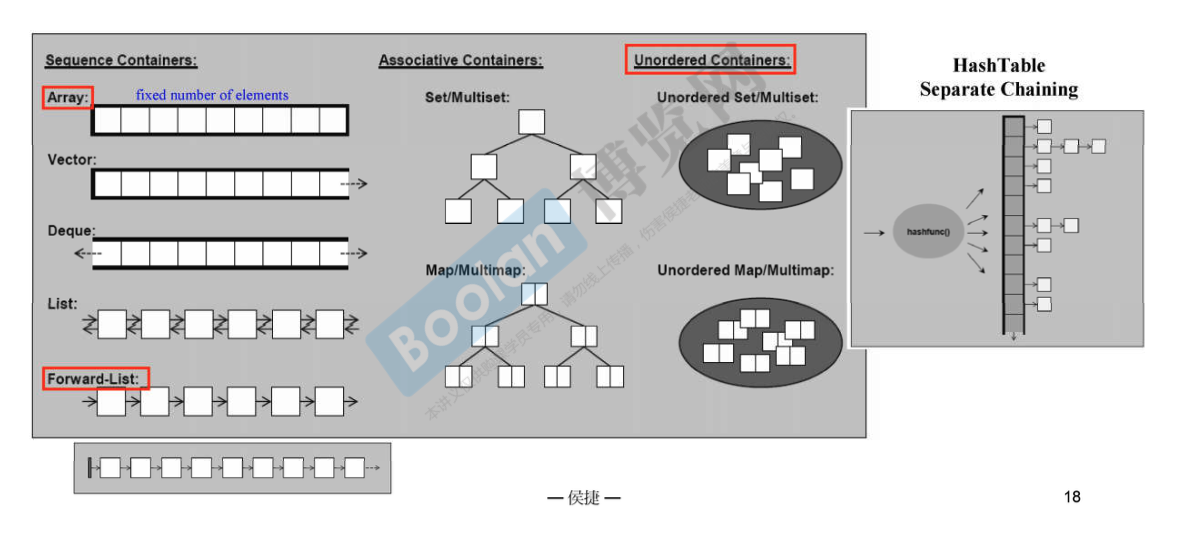
Arrays:连续空间,在一开始就分配好,不可修改.
Vector:空间不够时会自动增长,分配器会给自动扩充.
Deque:队列,前后可以扩充.
List:链表,双向环状链表,
Forward-List:单向链表,使用内存比List小.
Set/Multiset:内部由红黑树构建. Multi意味容器内可以有重复元素
Map/Multimap:同上👆🏻. key-value.
5.1 Array
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target=0;
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): ";
cin >> target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target=0;
char buf[10];
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): ";
cin >> target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b){
return ( *(long*)a - *(long*)b );
}
int compareStrings(const void* a, const void* b)
{
if ( *(string*)a > *(string*)b )
return 1;
else if ( *(string*)a < *(string*)b )
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> //qsort, bsearch, NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_array()
{
cout << "\ntest_array().......... \n";
array<long,ASIZE> c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand();
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
::qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
long* pItem = (long*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}}
运行结果

5.2 Vector
辅助函数
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> //qsort, bsearch, NULL
namespace jj01
{
void test_array()
{
cout << "\ntest_array().......... \n";
array<long,ASIZE> c;
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand();
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
::qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
long* pItem = (long*)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl; //
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
结果:(一部分)

5.3 List
list结构示意:

辅助函数
#include <list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <algorithm> //find()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj03
{
void test_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_list().......... \n";
list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "list.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "list.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(list<MyString>(),list<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
结果(一部分):

5.4 Deque
结构示意:


#include <deque>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj05
{
void test_deque(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_deque().......... \n";
deque<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "deque.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "deque.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "deque.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "deque.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //1073741821
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
test_moveable(deque<MyString>(),deque<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
5.5 forward-list
#include <forward_list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj04
{
void test_forward_list(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_forward_list().......... \n";
forward_list<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "forward_list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //536870911
cout << "forward_list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
结果:

5.6 slist
#include <ext\slist>
//注意, 上一行並沒有引發警告訊息如 #include <ext\hash_set> 所引發者:
//...\4.9.2\include\cpp\backward\backward_warning.h
//[Warning] ...
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj10
{
void test_slist(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_slist().......... \n";
__gnu_cxx::slist<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------
/*
以下測試 hash_multiset, hash_multimap 過程中遇到阻礙:
headers <hash_set> 和 <hash_map> 各有兩個,
分別在 ...\4.9.2\include\cpp\backward 和 ...\4.9.2\include\cpp\ext,
不知要用哪一組!
用 <ext\...> 那一組會有問題
...\4.9.2\include\cpp\backward\hashtable.h
[Error] no match for call to '(const hasher {aka const __gnu_cxx::hash<std::basic_string<char> >}) (const key_type&)'
用 <backward\...> 那一組有相同的問題.
so, 放棄測試 (no insertion or push_back or ...).
*/
5.7 Stack
#include <stack>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj17
{
void test_stack(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_stack().......... \n";
stack<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
{
stack<string, list<string>> c; //以 list 為底層
for(long i=0; i< 10; ++i) {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
}
{
stack<string, vector<string>> c; //以 vector 為底層
for(long i=0; i< 10; ++i) {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
}
{
stack<string, set<string>> c; //以 set 為底層
/*!
for(long i=0; i< 10; ++i) {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
//[Error] 'class std::set<std::basic_string<char> >' has no member named 'push_back'
//[Error] 'class std::set<std::basic_string<char> >' has no member named 'back'
//[Error] 'class std::set<std::basic_string<char> >' has no member named 'pop_back'
*/
}
//!stack<string, map(string>> c5; 以 map 為底層, [Error] template argument 2 is invalid
//!stack<string>::iterator ite1; //[Error] 'iterator' is not a member of 'std::stack<std::basic_string<char> >'
}
}
5.7 multiset
结构示意:

//辅助函数
#include <set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj06
{
void test_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(multiset<MyString>(),multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
结果示意:

5.8 Multimap
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj07
{
void test_multimap(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_multimap().......... \n";
multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 做 insertion
c.insert(pair<long,string>(i,buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
5.9 unordered_multiset
结构示意:
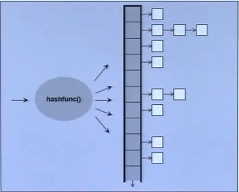

#include <unordered_set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj08
{
void test_unordered_multiset(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl;
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
c.clear();
test_moveable(unordered_multiset<MyString>(),unordered_multiset<MyStrNoMove>(), value);
}
}
结果示意:

5.10 Set
#include <set>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj13
{
void test_set(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_set().......... \n";
set<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "set.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "set.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //214748364
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
}
结果:

5.11 Map
结构示意:

#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> //abort()
#include <cstdio> //snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
namespace jj14
{
void test_map(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_map().......... \n";
map<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c[i] = string(buf);
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "map.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "map.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}
}
结果:

























 160
160

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








