一、ETL
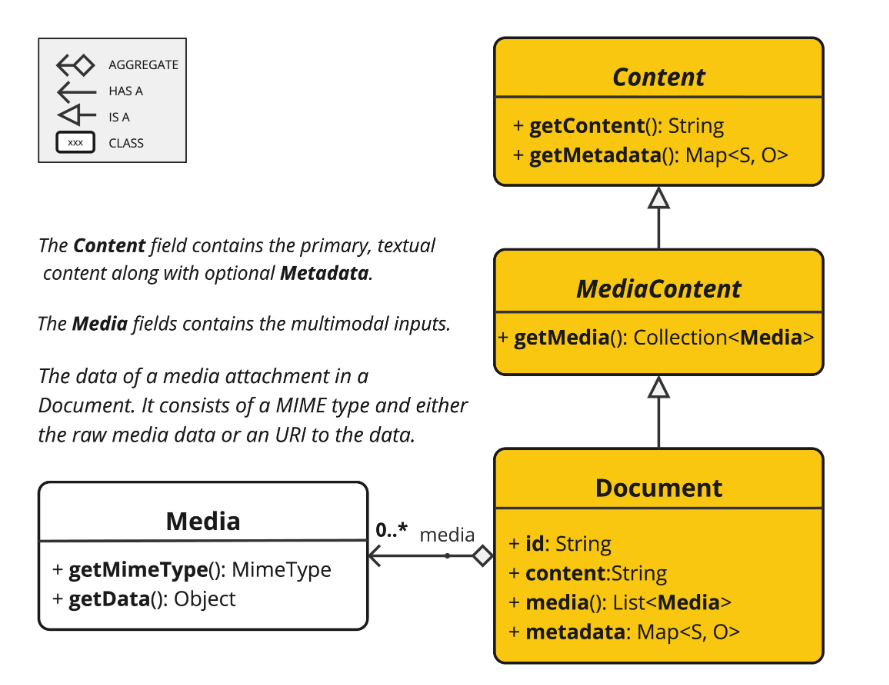
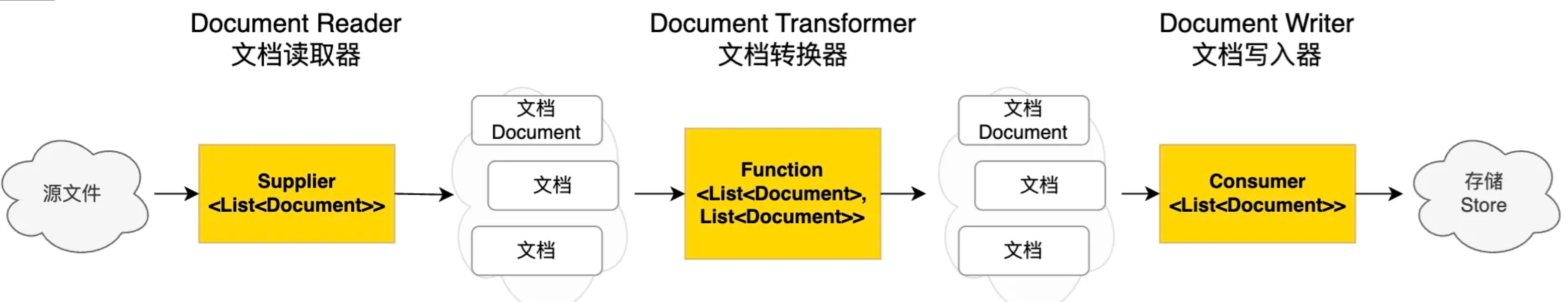
ETL的3大核心组件,按照顺序执行:
- DocumentReader:读取文档,得到文档列表
- DocumentTransformer:转换文档,得到处理后的文档列表
- DocumentWriter:将文档列表保存到存储中(可以是向量数据库,也可以是其他存储)
在Spring AI中,对Document的处理通常遵循以下流程:
- 读取文档
使用DocumentReader组件从数据源(如本地文件、网络资源、数据库等)加载文档。 - 转换文档
通过DocumentTransformer组件将文档转换为适合后续处理的格式,包括:
-
- 去除冗余信息
- 分词处理
- 词性标注等操作
- 写入文档
使用DocumentWriter将处理后的文档保存到指定存储中,支持:
-
- 以嵌入向量形式写入向量数据库
- 以键值对字符串形式保存到Redis等KV存储
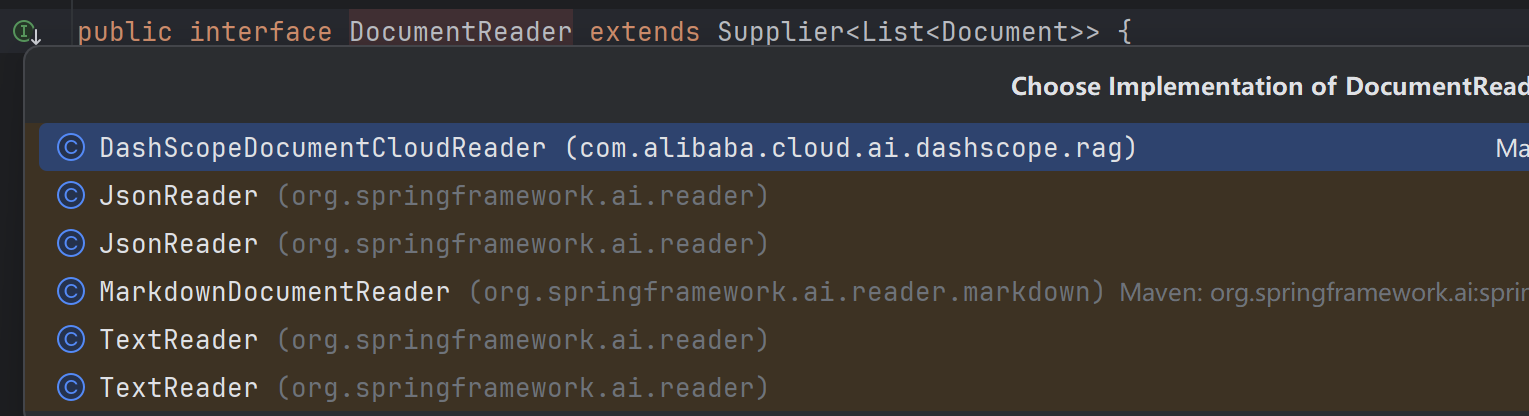
Spring AI目前实现了六个Reader,都是基于Document类进行实现的。
二、VectorStore
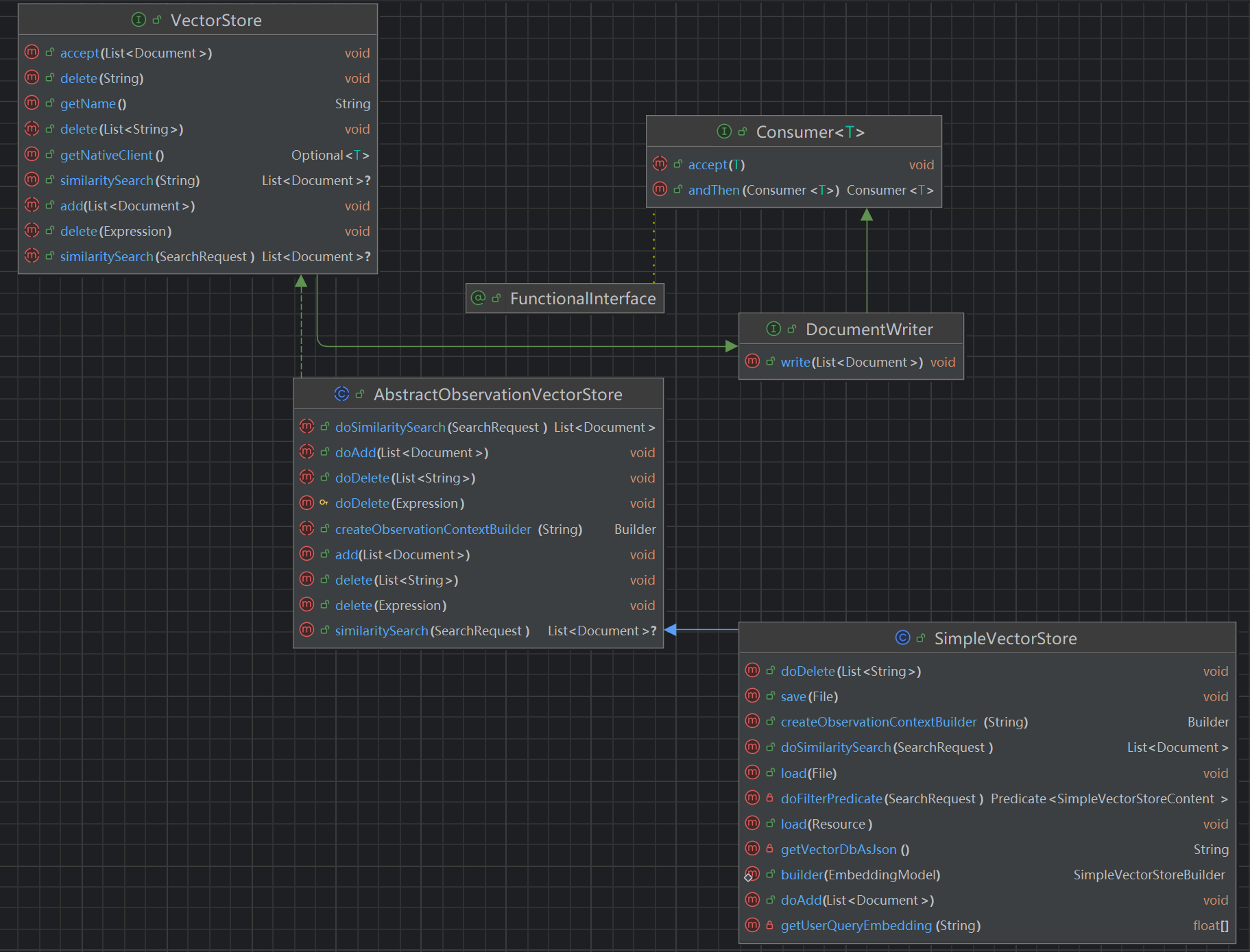
使用 Spring AI 内置的、基于内存读写的向量数据库 SimpleVectorStore 来保存文档。
SimpleVectorStore 实现了 VectorStore 接口,而 VectorStore 接口集成了 DocumentWriter,所以具备文档写入能力。
在将文档写入到数据库前,会先调用Embedding大模型将文档转换为向量,实际保存到数据库中的是向量类型的数据。
public class SimpleVectorStore extends AbstractObservationVectorStore {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SimpleVectorStore.class);
private final ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private final ExpressionParser expressionParser;
private final FilterExpressionConverter filterExpressionConverter;
protected Map<String, SimpleVectorStoreContent> store = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
protected SimpleVectorStore(SimpleVectorStoreBuilder builder) {
super(builder);
this.objectMapper = JsonMapper.builder().addModules(JacksonUtils.instantiateAvailableModules()).build();
this.expressionParser = new SpelExpressionParser();
this.filterExpressionConverter = new SimpleVectorStoreFilterExpressionConverter();
}
......
@Override
public void doAdd(List<Document> documents) {
Objects.requireNonNull(documents, "Documents list cannot be null");
if (documents.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Documents list cannot be empty");
}
for (Document document : documents) {
logger.info("Calling EmbeddingModel for document id = {}", document.getId());
float[] embedding = this.embeddingModel.embed(document);
SimpleVectorStoreContent storeContent = new SimpleVectorStoreContent(document.getId(), document.getText(),
document.getMetadata(), embedding);
this.store.put(document.getId(), storeContent);
}
}
可以看到,将文档存储到向量数据库的流程如下:
- SimpleVectorStore在doAdd方法中,是调用EmbeddingModel对document进行embed
- 将embed后的数据保存为SimpleVectorStoreContent类型
- 最后保存为一个HashMap类型<id, SimpleVectorStoreContent>
SimpleVectorStoreContent的定义如下,包含id,text,metadata(元信息,或者可以理解为文档chunk的标签,还有embedding)
public final class SimpleVectorStoreContent implements Content {
private final String id;
private final String text;
private final Map<String, Object> metadata;
private final float[] embedding;
}
AbstractObservationVectorStore定义了embeddingModel、batchingStrategy、observationRegistry等信息,代码如下:
public abstract class AbstractObservationVectorStore implements VectorStore {
private static final VectorStoreObservationConvention DEFAULT_OBSERVATION_CONVENTION = new DefaultVectorStoreObservationConvention();
private final ObservationRegistry observationRegistry;
@Nullable
private final VectorStoreObservationConvention customObservationConvention;
protected final EmbeddingModel embeddingModel;
protected final BatchingStrategy batchingStrategy;
private AbstractObservationVectorStore(EmbeddingModel embeddingModel, ObservationRegistry observationRegistry,
@Nullable VectorStoreObservationConvention customObservationConvention, BatchingStrategy batchingStrategy) {
this.embeddingModel = embeddingModel;
this.observationRegistry = observationRegistry;
this.customObservationConvention = customObservationConvention;
this.batchingStrategy = batchingStrategy;
}
三、查询增强
Spring AI的RAG功能说明:
- 核心特性:
-
- 通过Advisor特性提供开箱即用的RAG(检索增强生成)功能
- 提供两种拦截器:
-
-
QuestionAnswerAdvisor:简单易用的问答拦截器RetrievalAugmentationAdvisor:更灵活强大的检索增强拦截器
-
- 查询增强原理:
-
- 向量数据库存储AI模型未知的外部数据
- 用户提问时:
a)QuestionAnswerAdvisor自动查询向量数据库
b) 获取与问题相关的文档
c) 将检索结果附加到用户原始问题中
d) 为AI模型提供上下文辅助生成回答
QuestionAnswerAdvisor源码如下,其实就是让模型去根据存储的向量和输入的文本进行比对,根据提示词来控制输出:
public class QuestionAnswerAdvisor implements CallAroundAdvisor, StreamAroundAdvisor {
public static final String RETRIEVED_DOCUMENTS = "qa_retrieved_documents";
public static final String FILTER_EXPRESSION = "qa_filter_expression";
private static final String DEFAULT_USER_TEXT_ADVISE = """
Context information is below, surrounded by ---------------------
---------------------
{question_answer_context}
---------------------
Given the context and provided history information and not prior knowledge,
reply to the user comment. If the answer is not in the context, inform
the user that you can't answer the question.
""";
}
RetrievalAugmentationAdvisor的主要代码如下:
@Override
public AdvisedRequest before(AdvisedRequest request) {
Map<String, Object> context = new HashMap<>(request.adviseContext());
// 0. Create a query from the user text, parameters, and conversation history.
Query originalQuery = Query.builder()
.text(new PromptTemplate(request.userText(), request.userParams()).render())
.history(request.messages())
.build();
// 1. Transform original user query based on a chain of query transformers.
Query transformedQuery = originalQuery;
for (var queryTransformer : this.queryTransformers) {
transformedQuery = queryTransformer.apply(transformedQuery);
}
// 2. Expand query into one or multiple queries.
List<Query> expandedQueries = this.queryExpander != null ? this.queryExpander.expand(transformedQuery)
: List.of(transformedQuery);
// 3. Get similar documents for each query.
Map<Query, List<List<Document>>> documentsForQuery = expandedQueries.stream()
.map(query -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> getDocumentsForQuery(query), this.taskExecutor))
.toList()
.stream()
.map(CompletableFuture::join)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(Map.Entry::getKey, entry -> List.of(entry.getValue())));
// 4. Combine documents retrieved based on multiple queries and from multiple data
// sources.
List<Document> documents = this.documentJoiner.join(documentsForQuery);
context.put(DOCUMENT_CONTEXT, documents);
// 5. Augment user query with the document contextual data.
Query augmentedQuery = this.queryAugmenter.augment(originalQuery, documents);
// 6. Update advised request with augmented prompt.
return AdvisedRequest.from(request).userText(augmentedQuery.text()).adviseContext(context).build();
}
主要步骤为:
- 根据用户输入的文本、参数和对话历史创建查询请求
- 通过一系列查询转换器对原始用户查询进行转换
- 将查询扩展为一个或多个子查询
- 为每个子查询获取相似度匹配的文档
- 合并来自多查询和多数据源检索到的文档
- 用检索到的文档上下文数据增强用户原始查询
- 使用增强后的提示更新最终建议请求






















 746
746

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










