MySql基础
使用MySql
//选择数据库
use 数据库名称;
//了解数据库和表
show databases;//返回可用数据库的一个列表
show tables;//获得数据库内的表的列表
//显示表列
show columns from 表名;
describe 表名;
检索数据
检索所有列
select * from 表名;
检索不同行(distinct使返回结果都是不同的)
select distinct 列名 from 表名;
限制结果(limit)
select 列名 from 表名 limit 开始位置,检索的行数;
排序检索数据
排序检索
select 列名 from 表名 order by 列名(可以多个列) ;//默认为升序ascend
//降序descend,desc关键字只会应用于直接位于其前面的列名
select 列名 from 表名 order by 列名(可以多个列) desc ;
过滤数据
where子句操作符
//<> != 不等于
//between 在指定的两个值之间
select name
from table_name
where column_name BETWEEN nums AND nums;
空值检查(null)
//过滤数据时一定要验证返回数据中确实给出了被过滤列具有null的行
select name
from table_name
where column_name is null;
AND OR IN (NOT IN)
and操作符优先级高于or,使用时为了表示清楚应使用括号
in操作符用来指定条件范围,范围之中的每个条件都可以匹配
//in
select prod_name,prod_price
from products
where vend_id in (1002,1003)//where vend_id =1002 or vend_id =1003
order by prod_name;
//not in
where vend_id not in (1002,1003)
通配符过滤
like
%表示任意字符出现任意次数
通配符可以在搜索模式的任意位置使用,且可以使用多个
//找到以词jet开头的单词
where name like 'jet%';//告诉MySQL接受jet之后的任意字符,不管有多少字符
//不能匹配null值作为值的行
where name like '%';
_下划线,总是匹配一个字符,不多不少
where name like 'jet_';
正则表达式
用来匹配文本的特殊串(字符集合)
用正则表达式语言建立
regexp----regular expression
//.在正则表达式语言之中可以表示任意一个字符
select prod_name
from products
where prod_name regexp '.000';//正则表达式
like和regexp区别
如果被匹配文本在列值之中出现,以下语句:
like无返回,不会找到它(除非使用通配符)
regexp会找到它
where prod_name like'1000'
where prod_name regexp '1000'
区分大小写binary
where prod_name regexp binary 'JetPack .000';
or匹配
where prod_name regexp '1000|2000|3000';
匹配几个字符之一 [ ]
//匹配1 ton ;2 ton ;3 ton
where prod_name regexp '[123] ton';//where prod_name regexp '[1|2|3] ton';
//匹配 1;2;3 ton
where prod_name regexp '1|2|3 ton';//where prod_name regexp '1|2|(3 ton)';
^ 否定
[^123] 匹配除这些字符之外的任何东西
匹配范围
//[123456789] 相等于[1-9]
//[a-z]匹配任意字母
// .5 ton anvil会被返回 因为5 ton匹配
where prod_name regexp '[1-9] ton';
匹配特殊字符(mysql必知必会p57)
为匹配特殊字符,必须使用\为前导
\\\ 为匹配反斜杠字符本身,需要使用\\\
匹配. \\.
匹配- \\-
匹配字符类(mysql必知必会p58)
[:upper:] = [A-Z]
[:digit:] = [0-9]
[:lower:] = [a-z]
[:alnum:] 任意字母和数字
[:alpha:] 任意字母
[:digit:] 任意数字
······
匹配多个实例(* + ?{n}等)
* 0个或多个匹配
+ 1个或多个匹配,相当于{1,}
? 1个或0个匹配,相当于{0,1}
{n} 指定数目匹配
{n,} 不少于指定数目匹配
{n,m} 匹配数目范围(m<=255)
where prod_name regexp '\\([0-9] sticks?\\)'
//解释:\\(匹配( \\)匹配)
// [0-9]匹配任意数字
// sticks? 匹配stick或者sticks
// s后的?使得s可选,因为?匹配它前面任何字符的0次或者1次
where prod_name regexp '[[:digit:]]{4}'
where prod_name regexp '[0-9]{4}'
where prod_name regexp '[0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9]'
//{4}要求他前面的字符出现4次
定位符
^ 文本的开始
$ 文本的结束
[[:<:]] 词的开始
[[:>:]] 词的结束
//找出以数或者小数点开始的所有产品
where prod_name regexp '^[0-9\\.]'
//无^是不可行的,因为它将在文本内的任意位置查找匹配
where prod_name regexp '[0-9\\.]'
^的两个用法
在集合之中,用它来否定该集合
否则,用来指串的开始处
创建计算字段
计算字段
计算字段并不实际存在于数据库表中
计算字段是运行时在select语句内创建的
字段基本上和列的意思相同
拼接(concatenate)字段
concat()函数(其他DBMS多使用+或者||)
select Concat(RTrim(vent_name),'(',RTrim(vend_country),')') AS vend_title
from vendors
order by vend_name;
执行算数计算(+ - * /)
select prod_id,
quantity,
item_price,
quantity*item_price AS expanded_price//加操作符
from orderitems
where order_num = 20005;
数据处理函数(可以执行不强)
文本处理函数
left() 返回串左边的字符
length() 返回串的长度
locate() 找出串的一个子串
lower() 将串变为小写
ltrim() 去掉串左边的空格
right()
rtrim()
soundex() 返回串是soundex值
substring() 返回子串的字符
upper()
日期和时间处理函数
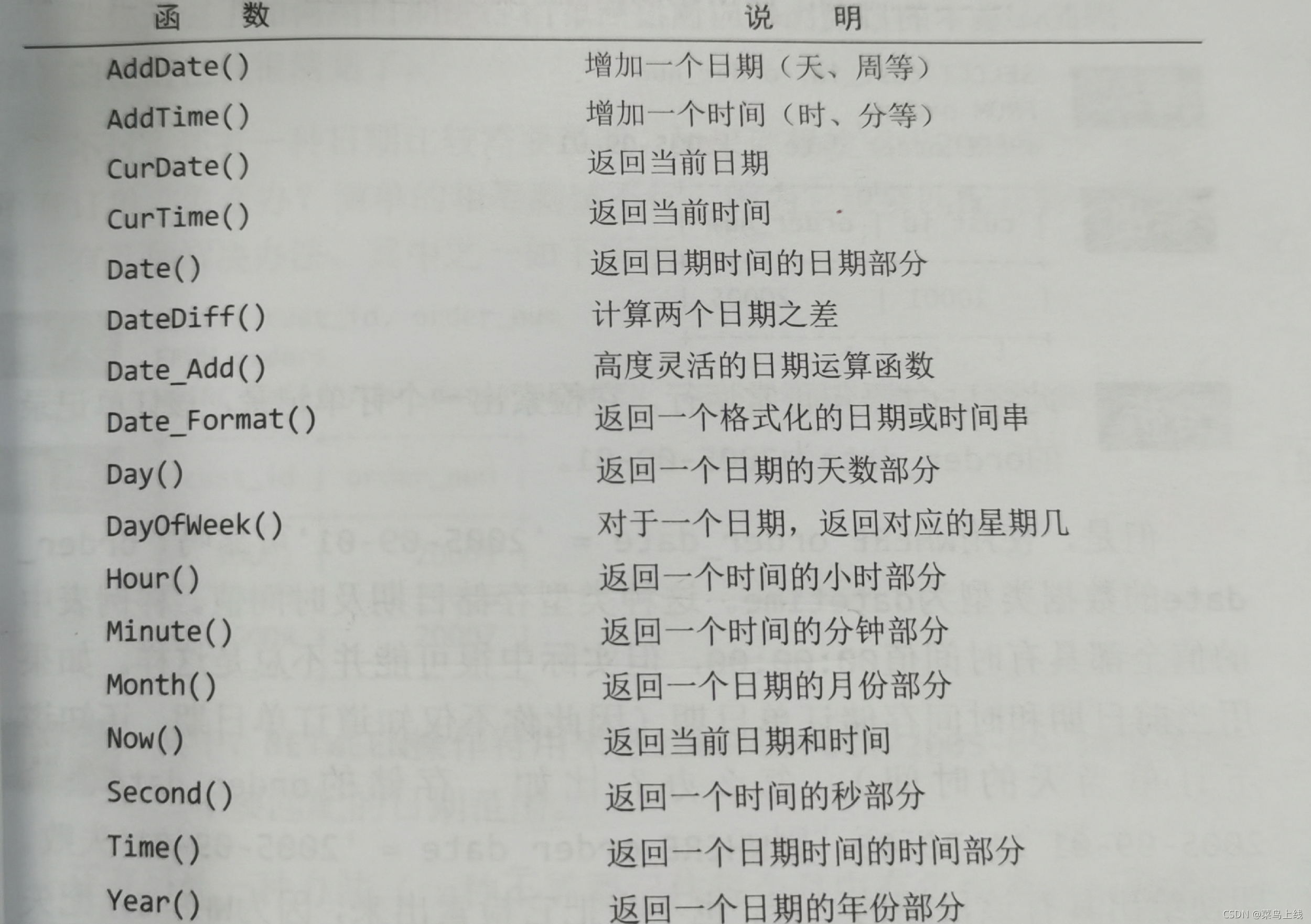
日期使用必须是yyyy-mm-dd
如果想要日期,请使用date(data_date)
数值处理函数
abs() cos() pi() rand() sin() sqrt() tan()
exp() 返回一个数的指数值
mod() 返回除操作的余数
汇总数据
聚集函数
avg() 忽略列值为null的行,必须指定列
count() 返回某列的行数,
count(*) 对表中行的数目统计
count(column) 统计特定列行数,忽略null值
max()
min()
sum()
分组数据
创建分组 group by
使用with rollup可以获得每个分组汇总级别

过滤分组 having
having和where类似
所有类型的where子句都可以用having代替
区别是having过滤分组 where过滤行
having支持所有where操作符

select子句顺序
select
from
where //行级过滤
group by //分组
having //组级过滤
order by //排序
limit //要检索的行数
子查询(嵌套在其他查询之中的查询-从内向外)
- 实际使用时由于性能限制,不可嵌套太多;
- 最常见使用的是在where字句的IN操作符;
- 同一表之中的子查询可使用自联结代替
























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








