实验目的和要求:
1.熟悉类的定义格式和类中成员的访问权限。
2.构造函数与析构函数的调用时机与顺序。
3.掌握对象的定义以及对象的初始化的时机与方法。
实验内容:
1.下面程序sy3-1.cpp中用ERROR标明的语句有错,在不删除和增加代码行的情况下,改正错误语句,使其正确运行。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Aa
{
public:
Aa(int i=0){a=i;cout<<"Constructor"<<a<<endl;}
~Aa(){cout<<"Destructor"<<a<<endl;}
void print(){cout<<a<<endl;}
private:
int a;
};
int main()
{
Aa a1(1),a2(2);
a1.print();
cout<<a2.a<<endl;//ERROR
return 0;
}
错误的运行结果如下图:
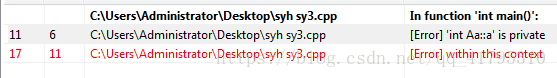
改正后的程序如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Aa
{
public:
Aa(int i=0){a=i;cout<<"Constructor"<<a<<endl;}
~Aa(){cout<<"Destructor"<<a<<endl;}
void print(){cout<<a<<endl;}
private:
int a;
};
int main()
{
Aa a1(1),a2(2);
a1.print();
a2.print();
return 0;
}正确运行结果:
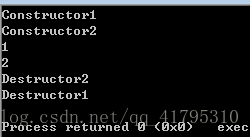
2.调试下列程序:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class TPoint
{
public:
TPoint(int x,int y){X=x,Y=y;}
TPoint(TPoint &p);
~TPoint(){cout<<"Destructor is called\n";}
int getx(){return X;}
int gety(){return Y;}
private:
int X,Y;
};
TPoint::TPoint(TPoint &p)
{
X=p.X;
Y=p.Y;
cout<<"Copy-initialization Constructor is called\n";
}
int main()
{
TPoint p1(4,9);
TPoint p2(p1);
TPoint p3=p2;
TPoint p4,p5(2);
cout<<"p3=("<<p3.getx()<<","<<p3.gety()<<")\n";
return 0;
}在该程序中,将TPoint类的两个带有参数的构造函数进行修改,在函数体内增添下述语句:cout<<"Constructor is called.\n";
修改程序如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class TPoint
{
public:
TPoint(int x,int y){X=x,Y=y;}
TPoint(TPoint &p);
~TPoint(){cout<<"Destructor is called\n";}
int getx(){return X;}
int gety(){return Y;}
private:
int X,Y;
};
TPoint::TPoint(TPoint &p)
{
X=p.X;
Y=p.Y;
cout<<"Copy-initialization Constructor is called\n";
cout<<"Constructor is called\n";
}
int main()
{
TPoint p1(4,9);
TPoint p2(p1);
TPoint p3=p2;
cout<<"p3=("<<p3.getx()<<","<<p3.gety()<<")\n";
return 0;
}结果如下:
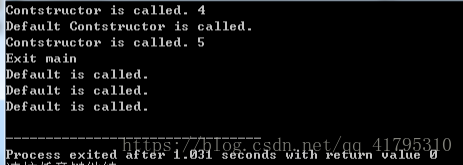
(2)按下列要求进行调试:
在主函数体内,添加下列说明语句:
TPoint P4,P5(2);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class TPoint
{
public:
TPoint(int x,int y){X=x,Y=y;}
TPoint(TPoint &p);
~TPoint(){cout<<"Destructor is called\n";}
int getx(){return X;}
int gety(){return Y;}
private:
int X,Y;
};
TPoint::TPoint(TPoint &p)
{
X=p.X;
Y=p.Y;
cout<<"Copy-initialization Constructor is called\n";
cout<<"Constructor is called\n";
}
int main()
{
TPoint P4,P5(2);
TPoint p1(4,9);
TPoint p2(p1);
TPoint p3=p2;
cout<<"p3=("<<p3.getx()<<","<<p3.gety()<<")\n";
return 0;
}运行如下:
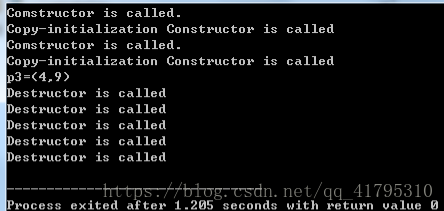
3、对教材中Li3_11.cpp的主函数做如下修改:
(1)将Heapclass *pa1,*pa2 改为Heapclass *pa1,*pa2,*pa3;
(2)在语句pa2=new Heapclass 后增加语句pa3=new Heapclass(5);
(3)将语句 if(!pa1||!pa2) 改为if(!pa1||!pa2||!pa3)
(4)在语句delete pa2 后增加语句delete pa3;
写出程序的输出结果,并解释输出结果。
原程序如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Heapclass
{
public:
Heapclass(int x);
Heapclass();
~Heapclass();
private:
int i;
};
Heapclass::Heapclass(int x)
{
i=x;
cout<<"Contstructor is called."<<i<<endl;
}
Heapclass::Heapclass()
{
cout<<"Default Contstructor is called."<<endl;
}
Heapclass::~Heapclass()
{
cout<<"Default is called."<<endl;
}
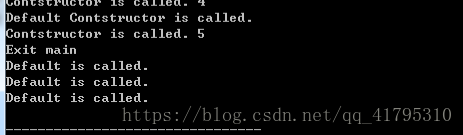
int main()
{
Heapclass *pa1,*pa2,*pa3;
pa1=new Heapclass(4);
pa2=new Heapclass;
pa3=new Heapclass(5);
if(!pa1||!pa2||!pa3);
{
cout<<"Out of Memory!"<<endl;
return 0;
}
cout<<"Exit main"<<endl;
delete pa1;
delete pa2;
delete pa3;
return 0;
}
4、请定义一个矩形类(Rectangle),私有数据成员为矩形长度(len)和宽度(wid),无参构造函数置len和wid为0,有参构造函数置len和wid为对应形参的值,另外还包括求矩形的周长、求矩形的面积、取矩形的长度和宽度、修改矩形的长度和宽度为对应形参的值、输出矩形尺寸等公有成员函数。要求输出矩形尺寸的格式为“length:长度,width:宽度”。(sy3_4.cpp)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Rectangle
{
public:
Rectangle()
{
len=0;
wid=0;
}
Rectangle(double Len,double Wid)
{
len=Len;
wid=Wid;
}
double Circumference()
{
return 2*(len+wid);
}
double Area()
{
return len*wid;
}
double getl()
{
return len;
}
double getw()
{
return wid;
}
void charge(double a,double b)
{
len=a;
wid=b;
}
void s()
{
cout<<"length:"<<len<<" "<<"width:"<<wid<<endl;
}
private:
int len,wid;
};
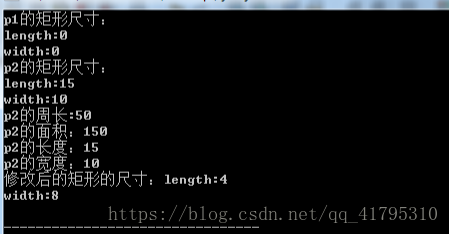
int main()
{
Rectangle q;
Rectangle h(5.0,2.0);
cout<<"q的矩形尺寸:"<<endl;
q.s();
cout<<"h的矩形尺寸:"<<endl;
h.s();
cout<<"h的周长:"<<h.Circumference()<<endl;
cout<<"h的面积:"<<h.Area()<<endl;
cout<<"h的长度:"<<h.getl()<<endl;
cout<<"h的宽度:"<<h.getw()<<endl;
h.charge(8.0,6.0);
cout<<"修改后的矩形的尺寸:"<<endl;
h.s();
return 0;
}
分析与讨论
1、类中私有成员的访问权限;
答:只有类中的函数才能访问类中私有成员。
2、构造函数和析构函数的调用顺序;
答:在对象创建时,先用构造函数对其进行初始化,在程序结束后用析构函数释放由构造函数分配的内存,而且析构函数的执行顺序与构造函数的执行顺序刚好相反。
3、何时进行对象初始化?如何进行?
答: 一般对象:在对象的创建时对其进行初始化,可以用构造函数或者用拷贝构造函数进行初始化。
堆对象:用new进行分配空间,再调用构造函数进行初始化。























 1178
1178

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








