第三章_数组中的问题
文章目录
很多问题都是在 数组中解决一个任务
排序:选择排序;插入排序;归并排序;快速排序
查找:二分查找法
数据结构:栈;队列;堆
3.1 从二分查找法看如何写出正确程序
如何写出一个正确的程序:建立一个基础的框架。
二分查找法(Binary Search):
必须要有序数列,该算法的问题主要在边界的处理上,边界索引的指向。
初始化的初值:[0,n-1],左闭右闭区间内,严格限定l和r两个变量的实际意义。
循环中保证循环不变量,快速排序,归并排序,堆的实现,图论,最短路径,最小生成树,寻找循环不变量,如何控制边界来保证循环不变量。
#include <iostream>
#include <assert.h>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
int BinarySearch(T arr[], int n, int target)//在arr的n个元素,寻找target,找到的元素以int 类型返回
{
int l = 0, r = n - 1; //在[l,r]左闭右闭区间寻找target,初始是[0,n-1]
while (l <= r) //此处又是一个边界问题,由于是左闭右闭区间,l==r时[l,r]仍然有效,所以应该进入循环
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > target)
r = mid - 1; //已经确定了mid不在区间内
else
l = mid + 1;
}
return -1;//没有找到target
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,5,7,11,22,55,77,99 };
int i = 0;
i = BinarySearch(arr, 10, 7);
cout << i;
return 0;
}
输出结果i=4。
3.2 改变变量定义,仍然可以写出正确算法
但是要维护住循环不变量。
template <typename T1>
int BinarySearch(T1 arr[], int n, int target)//在arr的n个元素,寻找target,找到的元素以int 类型返回
{
int l = 0, r = n; //在[l,r)左闭右开区间寻找target,初始是[0,n)
while (l < r) //此处又是一个边界问题,由于是左闭右开区间,l==r时[l,r)无效
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;//注意整型溢出的问题
if (arr[mid] == target)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > target)
r = mid; //[l,mid)
else
l = mid + 1;//[mid+1,r)
}
return -1;//没有找到target
}
发生改变的代码:
1.int l = 0, r = n;//在[l,r)左闭右开区间寻找target,初始的循环不变量改变
2.while (l < r) //左闭右开区间,l==r时[l,r)无效
3.else l = mid + 1;//[mid+1,r]
4.int mid = (l + r) / 2;//注意整型溢出的问题
此处插播循环不变量:
1.初始:[l,r)左闭右开区间寻找target,初始是[0,n),满足。
2.迭代:if (arr[mid] > target) r = mid; //[l,mid)
else l = mid + 1;//[mid+1,r)
3.结束:循环中止条件:while (l < r) //此处又是一个边界问题,l==r时[l,r)无效
如何写出正确的程序:
明确变量的含义
循环不变量
小数据量的调试:考虑空集、边界的情况,耐心寻找bug
大数据量的测试:程序的正确性扩展到一个大的范围,测试性能
3.3 在LeetCode上解决的第一个问题
Move Zeros
对于一个简单的问题可以不断优化。
Q:
Given an array nums, write a function to move all 0’s to the end of it while maintaining the relative order of the non-zero elements.
For example, given nums = [0, 1, 0, 3, 12], after calling your function, nums should be [1, 3, 12, 0, 0].
A1:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
//时间复杂度:O(n)
//空间复杂度:O(n)
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> nonZeroVectors;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i])
nonZeroVectors.push_back(nums[i]);//寻找不为零的数放到一个vector里面
}
for (int i = 0; i < nonZeroVectors.size(); i++) {
nums[i] = nonZeroVectors[i];//把不为零的数复制到原nums,剩下的都是nums
}
for (int i = nonZeroVectors.size(); i < nums.size(); i++) {
nums[i] = 0;//把0填入剩下的
}
}
};
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0,1,0,3,12 };
//由数组创建vector(头指针,尾指针)
vector<int> vec1(arr, arr + sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
Solution().moveZeroes(vec1);
for (int i = 0; i < vec1.size(); i++)
{
cout << vec1[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
该算法:时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n)
3.4 优化思路
优化:时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(1)
class Solution {
public:
//时间复杂度:O(n)
//空间复杂度:O(1)
void moveZeroes(vector<int>& nums) {
int point_k = 0;//[0,k)均为非0元素
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (nums[i])
if (i != point_k) {
swap(nums[i], nums[point_k]);
point_k++;
}
else//整个数组都是非零元素,不用自己和自己交换
point_k++;
}
}
};
课后题:LeetCode 27,26,80
3.5 三路快排 partition
Q:
Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white and blue.
Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue respectively.
Note: You are not suppose to use the library’s sort function for this problem.
click to show follow up.
Follow up: A rather straight forward solution is a two-pass algorithm using counting sort. First, iterate the array counting number of 0’s, 1’s, and 2’s, then overwrite array with total number of 0’s, then 1’s and followed by 2’s.
Could you come up with an one-pass algorithm using only constant space?
A1:
计数排序,统计0,1,2的个数,并放到里面
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
int count[3] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
assert(nums[i] >= 0 && nums[i] <= 2);
count[nums[i]]++;
}
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count[0]; i++)
nums[index++] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count[1]; i++)
nums[index++] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < count[2]; i++)
nums[index++] = 2;
cout << "[";
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
cout << nums[i] << " ";
}
cout << "]";
}
};
**A2:**三路快排
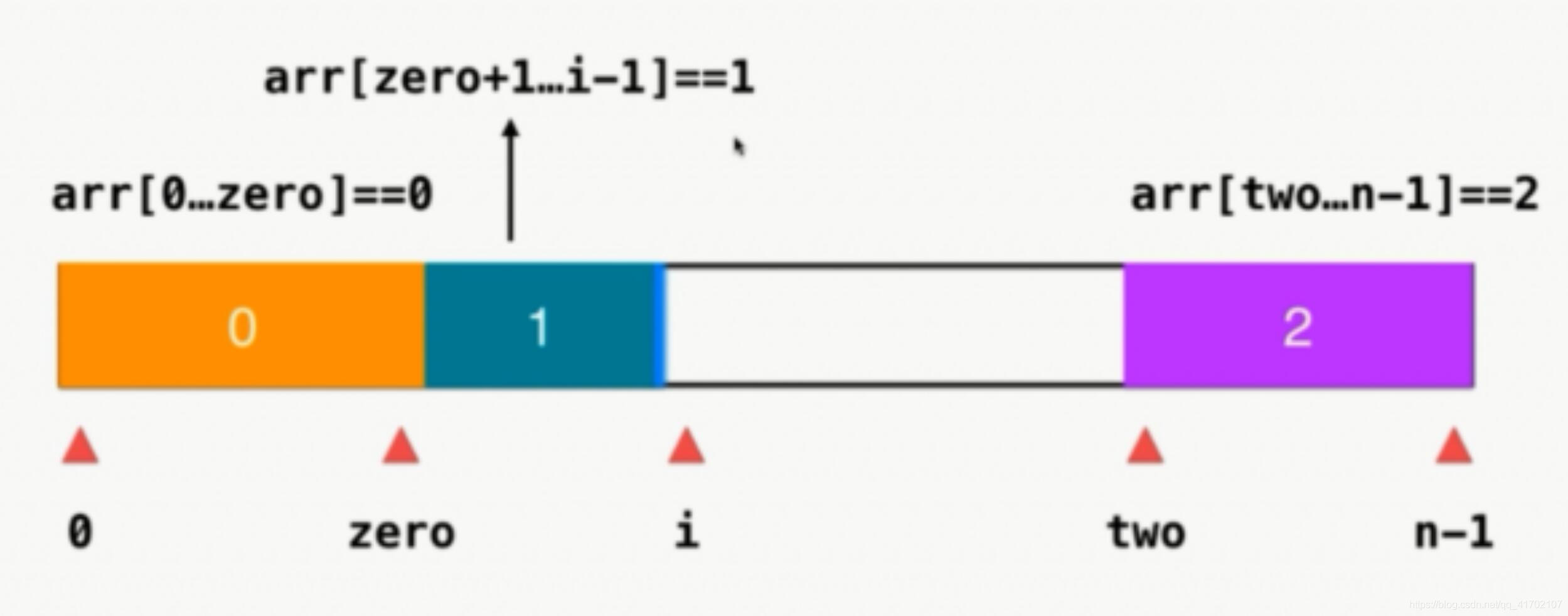
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
//时间复杂度O(n)
//空间复杂度O(1)
//只遍历一次的改进版本
int zero = -1;//在[0,zero]==0
int two = nums.size();//在[two,n-1]==2
for (int i = 0; i < two; i++) {//注意是小于two啊!!!
if (nums[i] == 0)
swap(nums[i], nums[++zero]);
if(nums[i] == 2)
swap(nums[i--], nums[--two]);//注意这里,还要重新检查i整个位置,因为此处换完以后是之前的--two位置的不知名的数
}
}
};
练习题:88号,215号
3.6 对撞指针
**Q167:**给定一个有序整型数组和一个整数target,在其中寻找两个元素,使其和为target。返回这两个数的索引。
如numbers = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,返回数字2,7的索引1, 2 (索引从1开始计算)
**明确细节:**如果没有解?如果有多解?
**A1:**暴力解法 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
**A2:**遍历,并在剩下的数中进行二分搜索
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& numbers, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = numbers.size() - 1;
vector<int> vec;
while (i < j) {
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] == target) {
vec.push_back(i+1);
vec.push_back(j+1);
return vec;
}
else if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] > target) {
j--;
}
else {
i++;
}
}
throw invalid_argument("the input has no solution");
}
};
错误处理:throw invalid_argument("the input has no solution");
课后题:Q125,Q344,Q345,Q11
3.7 双索引计数——滑动窗口
Q209:
Minimum Size Subarray Sum:给定一个整型数组和一个数字s,找到数组中最短的一个连续子数组,使得连续子数组的数字和sum >= s,返回这个最短的连续子数组的长度值如,给定数组[2, 3, 1, 2, 4, 3], s = 7答案为[4, 3],返回2。
细节:
什么是子数组?连续还是不连续?
如果没有解怎么办?返回0
有多个解怎么做?
**A:**滑动窗口不断往前行进

class Solution {
public:
int minSubArrayLen(int s, vector<int>& nums) {
int l = 0, r = -1;//[l,r]区间为滑动窗口
//注意r初始为-1,初始不包含任何元素
int sum = 0;
int win = nums.size() + 1;
while (l < nums.size()) {//左边界还能取值,还存在有可能有的滑动窗口
if(r+1<nums.size()&&sum < s) {//右边界已经不能再加了
sum += nums[++r];
}
else {
sum = sum - nums[l++];
}
if(sum>=s){
win = min(r - l + 1, win);
}
}
if (win == nums.size() + 1)
return 0;
return win;
}
};
3.8 在滑动窗口中做记录
**Q3:**在一个字符串中寻找没有重复字母的最长子串,返回其长度。
如”abcabcbb”,则结果为”abc”,长度为3;如”bbbbb”,则结果为”b”,长度为1;如”pwwkew”,则结果为”wke”,长度为3
细节:
字符集?只有字母,数字+字母,ASCII
大小写是否敏感?
class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
int freq[256] = { 0 };
int l = 0, r = -1;
int win = 0;
while (l < s.size()) {
if (r + 1 < s.size() && freq[s[r + 1]] == 0) {
freq[s[++r]]++;
}
else
freq[s[l++]]--;
win = max(win, r - l + 1);
}
return win;
}
};
练习题:Q438,Q76





 本文深入探讨数组中的各类问题,包括排序、查找、数据结构等核心算法。通过具体案例,如二分查找、三路快排、对撞指针等,解析算法设计与优化技巧。同时,介绍了在LeetCode上解决实际问题的方法,如MoveZeros、MinimumSizeSubarraySum等,涵盖从小数据调试到大数据测试的全过程。
本文深入探讨数组中的各类问题,包括排序、查找、数据结构等核心算法。通过具体案例,如二分查找、三路快排、对撞指针等,解析算法设计与优化技巧。同时,介绍了在LeetCode上解决实际问题的方法,如MoveZeros、MinimumSizeSubarraySum等,涵盖从小数据调试到大数据测试的全过程。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








