我的PAT-ADVANCED代码仓:https://github.com/617076674/PAT-ADVANCED
原题链接:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/1038430130011897856
题目描述:

题目翻译:
1151 二叉树中的最近公共祖先
树中两个节点U和V的最低共同祖先(LCA)是具有U和V作为后代的最深节点。
给定BST中的任何两个节点,你需要找到他们的LCA。
输入格式:
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。对每个测试用例,第一行给出两个正整数:M(<= 1000),代表要测试的节点对的数量;以及N(<= 10000),代表是二叉树中的节点数。在接下来的两行中,每行分别给出N个不同的整数作为二叉树的中序和前序遍历序列。题目保证二叉树可以由输入序列唯一确定。然后是M行,每行包含一对整数键U和V。所有键值都在int范围内。
输出格式:
对任意给定的一组U和V,如果LCA找着了,且其值为A,则在一行中输出“LCA of U and V is A.”。但是如果A和U或V相等,输出“X is an ancestor of Y.”,其中X是A,Y是另一个节点。如果U或V没有在树中找到,则输出“ERROR: U is not found.”或“ERROR: V is not found.”。如果U和V都没有在树中找到,则输出“ERROR: U and V are not found.”。
输入样例:
6 8
7 2 3 4 6 5 1 8
5 3 7 2 6 4 8 1
2 6
8 1
7 9
12 -3
0 8
99 99输出样例:
LCA of 2 and 6 is 3.
8 is an ancestor of 1.
ERROR: 9 is not found.
ERROR: 12 and -3 are not found.
ERROR: 0 is not found.
ERROR: 99 and 99 are not found.知识点:中序遍历和前序遍历区分二叉树的根结点和左右子树、set集合的应用、双指针
思路:由中序遍历和前序遍历区分二叉树的根结点和左右子树
本题和PAT-ADVANCED1143——Lowest Common Ancestor很相似,但本题不是一棵二分搜索树,其中序遍历不是非降序排列,在递归过程中,在中序遍历中寻找根节点时无法用二分查找法。
因此,本题使用左右双指针同时向中间逼近的做法,防止出现根节点太靠后的导致寻找根节点耗时太久的问题,加快寻找到根节点的速度。如果不用左右双指针的做法,测试点4会超时。
时间复杂度是O(h),其中h为树的高度。空间复杂度是O(N)。
C++代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
set<int> numSet; //存储
vector<int> inOrder; //中序遍历序列
vector<int> preOrder; //前序遍历序列
int findLCA(int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight, int num1, int num2);
int main() {
int M, N;
scanf("%d %d", &M, &N);
int num;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%d", &num);
inOrder.push_back(num);
numSet.insert(num); //用set集合存储键值,方便判断某节点是否存在
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
scanf("%d", &num);
preOrder.push_back(num);
}
int num1, num2;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &num1, &num2);
set<int>::iterator it1 = numSet.find(num1);
set<int>::iterator it2 = numSet.find(num2);
if(it1 != numSet.end() && it2 != numSet.end()) {
int lca = findLCA(0, N - 1, 0, N - 1, num1, num2);
if(num1 == lca) {
printf("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n", lca, num2);
} else if(num2 == lca) {
printf("%d is an ancestor of %d.\n", lca, num1);
} else {
printf("LCA of %d and %d is %d.\n", num1, num2, lca);
}
} else if(it1 == numSet.end() && it2 != numSet.end()) {
printf("ERROR: %d is not found.\n", num1);
} else if(it1 != numSet.end() && it2 == numSet.end()) {
printf("ERROR: %d is not found.\n", num2);
} else {
printf("ERROR: %d and %d are not found.\n", num1, num2);
}
}
}
int findLCA(int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight, int num1, int num2) {
int k, countLeft = 0, countRight = 0;
int left, right;
for(int i = 0; i <= (inRight - inLeft) / 2; i++) { //双指针两边同时向中间逼近
left = inLeft + i; //left指针从左边开始逼近中间
if(inOrder[left] == preOrder[preLeft]) { //如果left指针找到了preOrder[preLeft]
k = left; //令k = left
break; //跳出循环
}
if(inOrder[left] == num1 || inOrder[left] == num2) { //如果left指针发现了num1或num2
countLeft++; //在左子树中发现的num1或num2的次数加1
}
right = inRight - i; //right指针从右边开始逼近中间
if(inOrder[right] == preOrder[preLeft]){ //如果right指针发现了num1或num2
k = right; //令k = right
break; //跳出循环
}
if(inOrder[right] == num1 || inOrder[right] == num2){ //如果right指针发现了num1或num2
countRight++; //在右子树中发现的num1或num2的次数加1
}
}
int numLeft = k - inLeft; //左子树中的节点个数
if(num1 == preOrder[preLeft] || num2 == preOrder[preLeft]){ //如果num1或num2和当前根节点相等
return preOrder[preLeft]; //当前根节点就是num1和num2的最近公共祖先
}
if(countLeft == 2){ //在左子树中发现num1或num2的次数为2次,说明num1和num2都在左子树中,递归地在左子树中寻找
return findLCA(preLeft + 1, preLeft + numLeft, inLeft, k - 1, num1, num2);
}else if(countLeft == 1){ //在左子树中发现num1或num2的次数为1次
if(countRight == 1){ //在右子树中发现num1或num2的次数为1次
return preOrder[preLeft]; //当前根节点就是num1和num2的最近公共祖先
}else if(countRight == 0){ //在右子树中发现num1或num2的次数为0次
if(k == left){ //如果k == left,说明左子树中确实只包含num1或num2中的一个,另一个在右子树中
return preOrder[preLeft]; //当前根节点就是num1和num2的最近公共祖先
}else if(k == right){ //如果k == right,说明右子树中确实不包含num1或num2,num1和num2都在左子树中
return findLCA(preLeft + 1, preLeft + numLeft, inLeft, k - 1, num1, num2); //说明num1和num2都在左子树中,递归地在左子树中寻找
}
}
}else if(countLeft == 0){ //在左子树中发现num1或num2的次数为0次
if(countRight == 2){ //在右子树中发现num1或num2的次数为2次,说明num1和num2都在右子树中,递归地在右子树中寻找
return findLCA(preLeft + numLeft + 1, preRight, k + 1, inRight, num1, num2);
}else if(countRight == 1){ //在右子树中发现num1或num2的次数为1次
if(k == right){ //如果k == right,说明右子树中确实只包含num1或num2中的一个,另一个在左子树中
return preOrder[preLeft]; //当前根节点就是num1和num2的最近公共祖先
}else if(k == left){ //如果k == left,说明左子树中确实不包含num1或num2,num1和num2都在右子树中
return findLCA(preLeft + numLeft + 1, preRight, k + 1, inRight, num1, num2); //递归地在右子树中寻找
}
}else if(countRight == 0){ //在右子树中发现num1或num2的次数为0次
if(k == right){ //如果k == right,说明右子树中确实不包含num1或num2,num1和num2都在左子树中
return findLCA(preLeft + 1, preLeft + numLeft, inLeft, k - 1, num1, num2);
}else if(k == left){ //如果k == left,说明左子树中确实不包含num1或num2,num1和num2都在右子树中
return findLCA(preLeft + numLeft + 1, preRight, k + 1, inRight, num1, num2);
}
}
}
}C++解题报告:
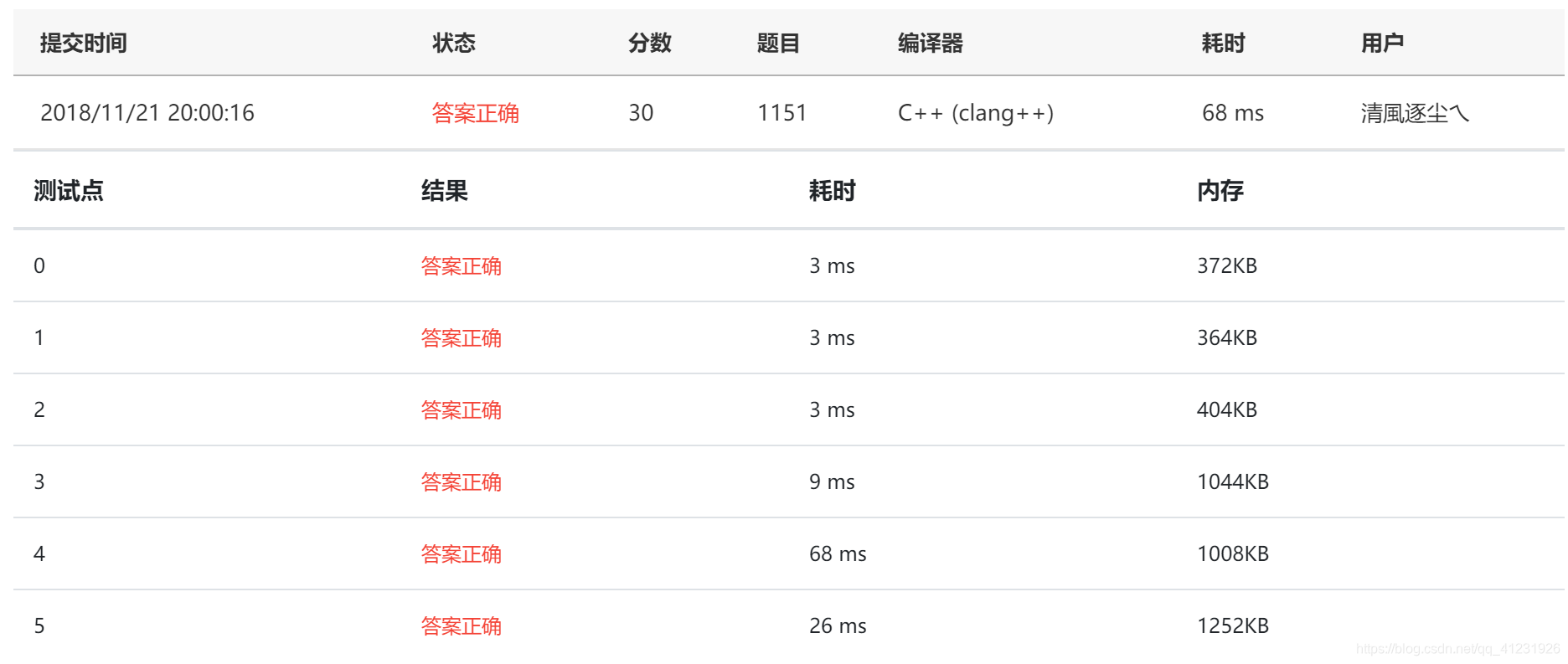





 该博客主要介绍PAT甲级1151题——二叉树中的最近公共祖先(LCA)问题。通过中序遍历和前序遍历来确定二叉树结构,并利用左右双指针来快速找到根节点,解决非二分搜索树中寻找LCA的效率问题。文章提供了C++解题报告和代码实现。
该博客主要介绍PAT甲级1151题——二叉树中的最近公共祖先(LCA)问题。通过中序遍历和前序遍历来确定二叉树结构,并利用左右双指针来快速找到根节点,解决非二分搜索树中寻找LCA的效率问题。文章提供了C++解题报告和代码实现。
















 333
333

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








