我的PAT-ADVANCED代码仓:https://github.com/617076674/PAT-ADVANCED
原题链接:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805361586847744
题目描述:

题目翻译:
1107 社交集群
在社交网络上注册时,总是会要求您指定自己的爱好,以便找到具有相同爱好的潜在朋友。 社交群集是一群拥有共同兴趣爱好的人。 你需要找到所有的集群。
输入格式:
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。在每个测试用例中,第一行有一个正整数N(<= 1000),代表社交网络中的总人数。人的编号为1 ~ N。接下来的N行,每一行以如下格式给出一个人的信息:
Ki: hi[1] hi[2] ... hi[Ki]
其中Ki(> 0)是兴趣总数,hj是兴趣编号,是一个[1, 1000]范围内的整数。
输出格式:
对每个测试用例,在第一行输出社交网络中的集群总数。第二行,以非降序输出各个集群中的人数。一行中的所有的数字由一个空格分隔,行末不得有多余空格。
输入样例:
8
3: 2 7 10
1: 4
2: 5 3
1: 4
1: 3
1: 4
4: 6 8 1 5
1: 4输出样例:
3
4 3 1知识点:并查集
思路:将人的编号填进兴趣编号分组的vector<int>集合里,对每组兴趣编号里的人进行合并操作
题目只要求对人数进行统计,没有涉及人的编号。虽然题目中写了人的编号从1 ~ N,但为了方便,我们从0 ~ N - 1也是完全可以的。
(1)首先建立一个数组int father[1000],代表我们的并查集,初始时father[i] = i,每个人各自成一个集群。
(2)再建立一个兴趣分组vector<int> hoppy[1001],根据人的兴趣将人的编号填进兴趣分组里。
(3)对每个hoppy[i]中的元素,两两进行合并操作,合并过程的父节点可以任意指定
(4)用一个数组int countFather[1000]来统计以i为父节点的人数。
(5)对countFather数组进行非降序排序,再统计非0的个数依次输出即可。
时间复杂度是O(NlogN)。空间复杂度是O(N)。
C++代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int N;
int father[1000]; //并查集,假设人的编号是从0 ~ N - 1的
vector<int> hoppy[1001]; //根据兴趣将人进行分组
int countFather[1000] = {0}; //countFather[i]表示以i为父节点的人数
int change(string s);
int findFather(int x);
void unionTwo(int a, int b);
int main(){
cin >> N;
string count;
int num;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
father[i] = i; //初始时各自成一个节点
cin >> count;
int total = change(count);
for(int j = 0; j < total; j++){
cin >> num;
hoppy[num].push_back(i);
}
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 1000; i++){
int size = hoppy[i].size();
for(int j = 0; j < size - 1; j++){ //直接写成for(int j = 0; j < hoppy[i].size() - 1; j++)会报段错误,不知为何
unionTwo(hoppy[i][j], hoppy[i][j + 1]);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
countFather[findFather(i)]++;
}
sort(countFather, countFather + N);
int clusters;
for(int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(countFather[i] == 0){
clusters = N - 1 - i;
break;
}
}
cout << clusters << endl;
for(int i = N - 1; i > N - 1 - clusters; i--){
cout << countFather[i];
if(i != N - clusters){
cout << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
int change(string s){
s = s.substr(s.length() - 2, 1);
stringstream ss;
ss << s;
int result;
ss >> result;
return result;
}
int findFather(int x){
int a = x;
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
while(a != father[a]){
int z = a;
a = father[a];
father[z] = x;
}
return x;
}
void unionTwo(int a, int b){
int aFather = findFather(a);
int bFather = findFather(b);
if(aFather != bFather){
father[aFather] = bFather;
}
}C++解题报告:
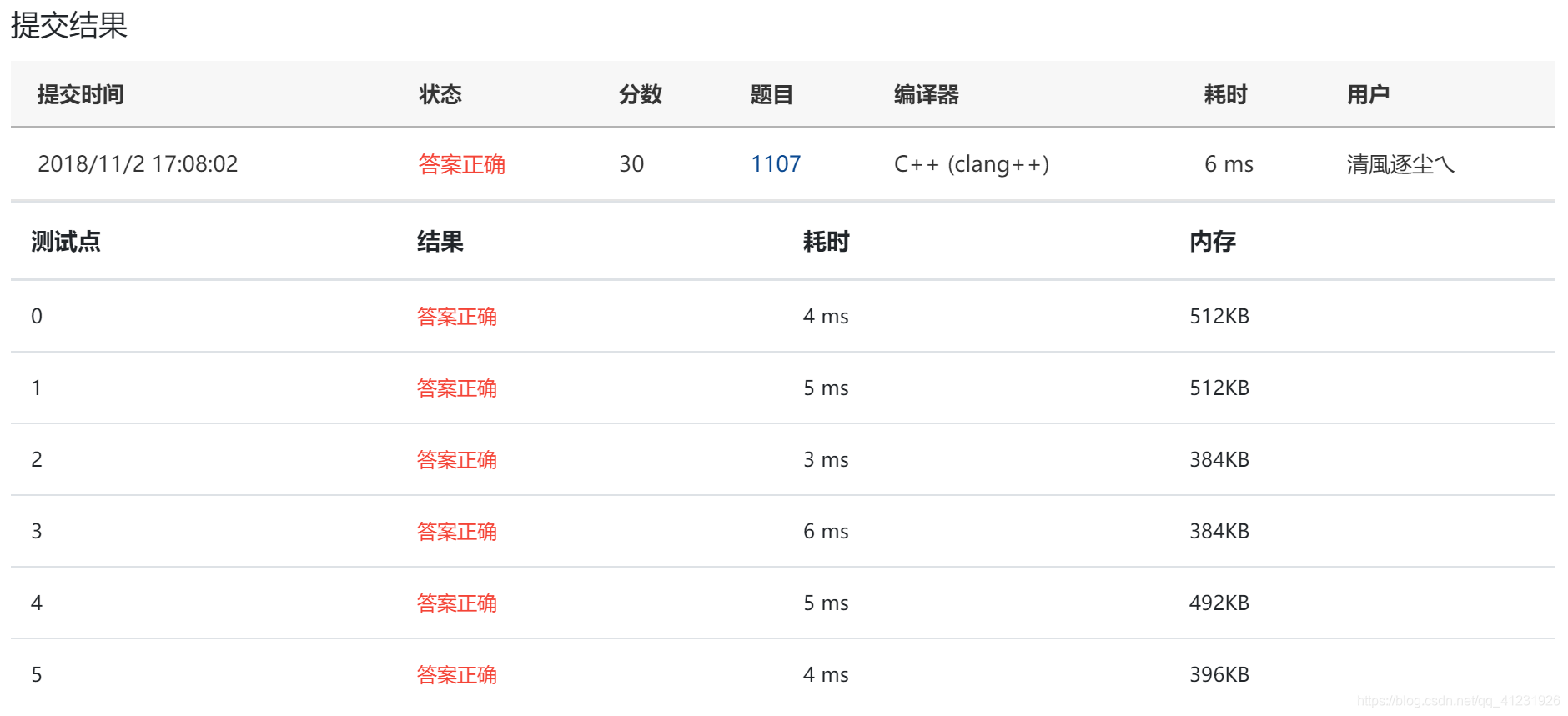








 本文介绍了如何解决PAT甲级1107题——社交集群。通过并查集算法,找到社交网络中具有相同兴趣爱好的集群,并统计每个集群的人数。详细阐述了并查集的实现步骤,包括初始化、兴趣分组、合并操作、计数及排序等,并提供了C++代码实现。
本文介绍了如何解决PAT甲级1107题——社交集群。通过并查集算法,找到社交网络中具有相同兴趣爱好的集群,并统计每个集群的人数。详细阐述了并查集的实现步骤,包括初始化、兴趣分组、合并操作、计数及排序等,并提供了C++代码实现。
















 990
990

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








