链表题
注意的问题:
考虑head为空,还有head.next为空的corner case
保证用的变量循环的时候不能是空.next
自己手写练习的时候多写corner case
删除问题:如果会删除第一个节点,那么制造哑节点
160

思路,问题是,两个列表不等长。只需要双指针让他们遍历到同一位置上就行

开始时让pa指向headA, pb指向headB
当pa 指到None时,走过a步,下一步去headB
当pb 指到None时,走过b步, 下一步去headA
这样再之后两指针开始同步,相遇时走的路程都是a+b-c,刚好在none相遇
若没有公共节点,那么他们将遍历完a+b,然后返回None
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
pa = headA
pb = headB
while pa != pb:
if pa == None:
pa = headB
else: pa = pa.next
if pb == None:
pb = headA
else:pb = pb.next
return pa
简洁写法:
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
A, B = headA, headB
while A != B:
A = A.next if A else headB
B = B.next if B else headA
return A

反转链表:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return
prev,cur,nextNode = None,head,head.next
while nextNode:
cur.next = prev
prev = cur
cur = nextNode
nextNode = nextNode.next
cur.next = prev
return cur21.

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
head = ListNode(0)
cur = head
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val<= l2.val:
cur.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
cur.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
cur = cur.next
if l2:
cur.next = l2
else:
cur.next = l1
return head.next
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not l1:return l2
if not l2:return l1
if l1.val<=l2.val:
l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next,l2)
return l1
else:
l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1,l2.next)
return l2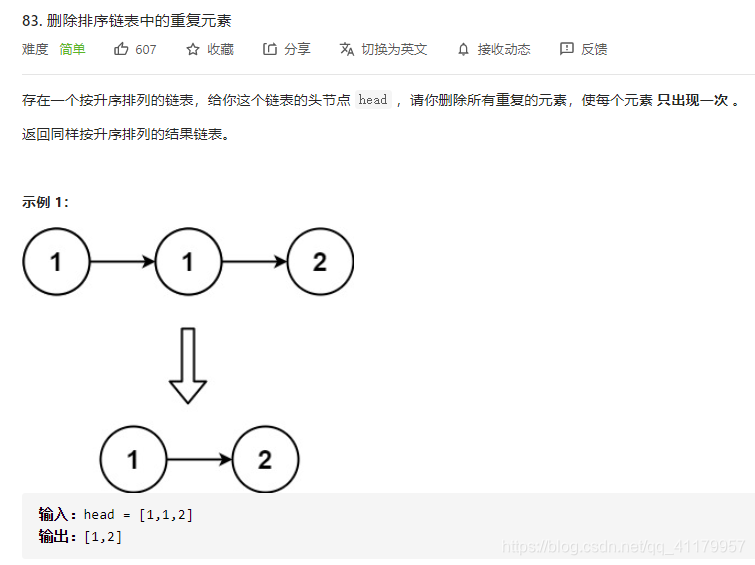 用first和second不停循环两个点:
用first和second不停循环两个点:
注意事项:
当f ==s 的时候, first.next= second.next, seond = first.next 这意味着first这个点不动
当f !=s 的时候,两个点都要往后移动
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
first,second,third = head,head.next,head.next.next
while second:
if first.val == second.val:
first.next = second.next
if first.next:
second = first.next
else:
break
else:
first= second
second = second.next
return head

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
Head = ListNode(0)
Head.next = head
if not head or not head.next:
return
cur1,cur2 = Head,Head
for i in range(n):
cur2 = cur2.next
while cur2.next:
cur1 = cur1.next
cur2 = cur2.next
cur1.next = cur1.next.next
return Head.next24.
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head or not head.next:
return head
Head = ListNode(0)
Head.next = head
f,s,t = Head,head,head.next
while t:
s.next = t.next
t.next = s
f.next = t
if t.next and t.next.next:
f = f.next.next
s = f.next
t = s.next
else:
break
return Head.next
思路:存入栈中,一位一位处理。
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
s1 = []
s2 = []
ans = None
while l1:
s1.append(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
s2.append(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
carry = 0
while s1 or s2 or carry !=0:
a = 0 if not s1 else s1.pop()
b = 0 if not s2 else s2.pop()
cur = a+b+carry
carry = cur // 10
cur = cur%10
curnode = ListNode(cur)
curnode.next = ans
ans = curnode
return ans

翻转列表,数组,字符串等:
return strs == strs[::-1]
begin:end:step 从起点到终点反向输出
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:
strs = ''
cur= head
while cur:
strs= strs+str(cur.val)
cur = cur.next
return strs == strs[::-1]时间和空间复杂度都是O(N)
* 如果要求空间复杂度为O(1),
用快慢指针将链表分为两部分,slow指向中间节点,pre是slow的前节点,用来切开两个链表
然后将链表2倒转, reverse
这之后从链表头到其中一节点为None,判断每个节点val是否相同

# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def splitListToParts(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> List[ListNode]:
n = 0
cur = head
res = []
while cur:
n += 1
cur = cur.next
num = n // k
former = n % k
cur = head
for i in range(k):
res.append(cur)
size = num + (1 if former > 0 else 0)
if cur:
for j in range(size-1):
cur = cur.next
former -= 1
temp = cur.next
cur.next = None
cur = temp
return res

思路:把链表分开分成odd和even.最后把odd.next 连上even.head
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def oddEvenList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if not head:return
evenhead = head.next
odd,even = head,evenhead
while even and even.next:
odd.next = even.next
odd = odd.next
even.next = odd.next
even = even.next
odd.next = evenhead
return head
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








