主要内容:
Tree, Binary Tree, Binary Search Tree
Graph
Tree:
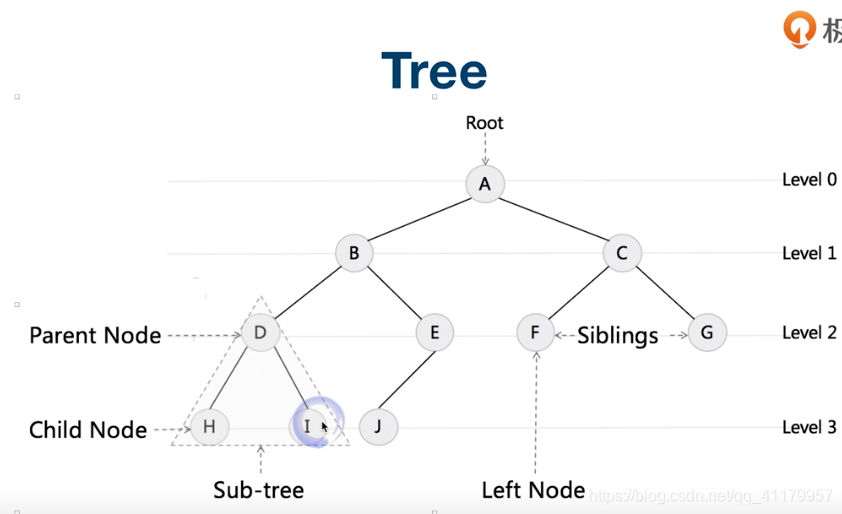
Linked List 就是特殊化的 Tree
Tree 就是特殊化的 Graph
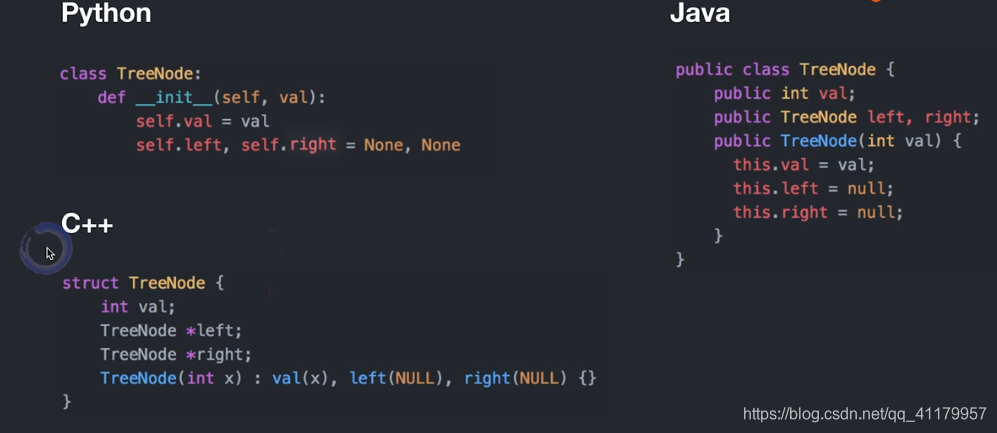
二叉搜索树:

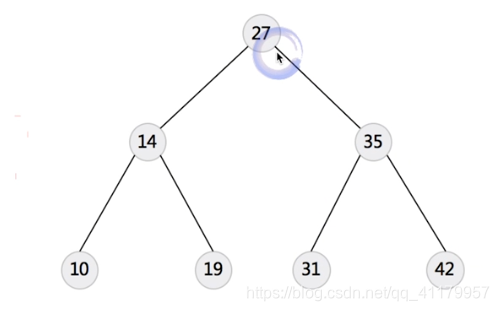
二叉树的遍历: 这里看的是根的位置
Pre-order 前序:根左右
In-order 中序: 左根右
Post-order 后序:左右根

用递归解答顺序
一般遍历是:深度优先,广度优先,以及搜索


方法一,先用inorder方式打出来,然后进行对比
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
inorderlist = self.inorder(root)
return inorderlist == list(sorted(set(inorderlist)))
def inorder(self, root:TreeNode):
if root is None:
return []
return self.inorder(root.left) + [root.val] +self.inorder(root.right)
这里用sorted set的原因是,避免
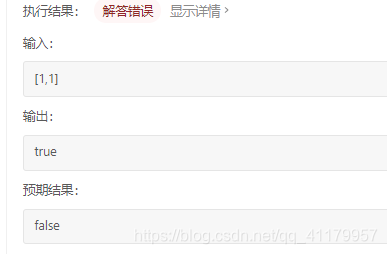
这样的情况。不是树的情况
python 用 +可以拼接list
方法二:先判断这个点是否为中值点。
然后遍历左子树。
然后遍历右子树
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
return self.roothelper(root,-2**32,2**32)
def roothelper(self, root1: TreeNode, min_v:int, max_v:int)-> bool:
if root1 == None:
return True
if root1.val<max_v and root1.val > min_v:
pass
else:
return False
if ( self.roothelper(root1.left,min_v,root1.val))== False:
return False
if (self.roothelper(root1.right,root1.val,max_v)) ==False:
return False
return True
用 ==False, 比 not 会减少运行时间
235:
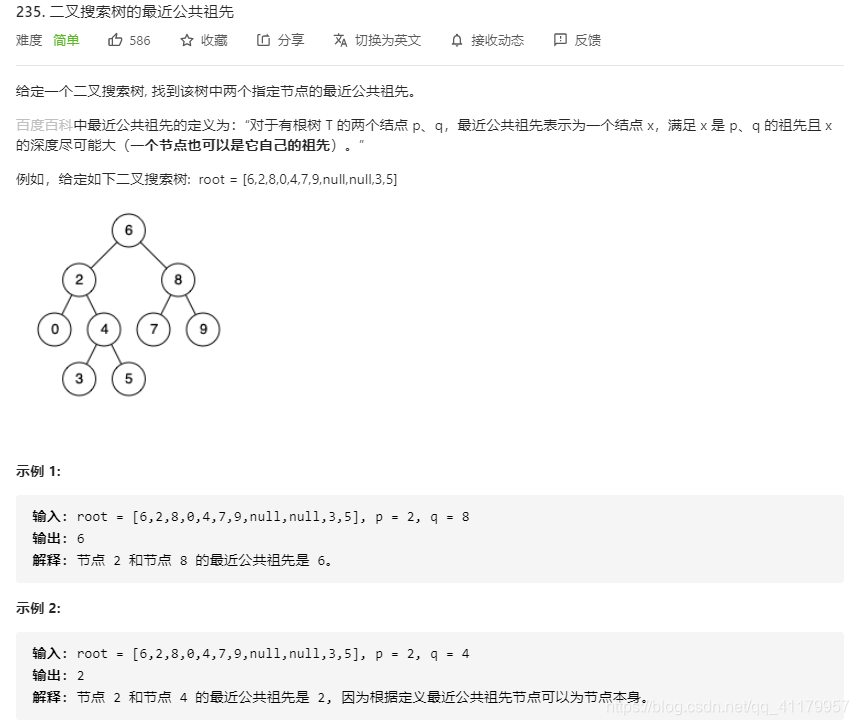
执行用时:100 ms, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了27.95%的用户
内存消耗:18.7 MB, 在所有 Python3 提交中击败了87.82%的用户
解法1: 因为是二叉搜索树,左子树小于中节点,右子树大于中节点
,所以如果pq都小于此节点的值,则向右子树遍历,
如果都大于,向左子树遍历,
如果不是,则是介于其中,就是此节点
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if p.val < root.val and q.val <root.val :
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)
elif p.val > root.val and q.val >root.val:
return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
else:
return root
解法2: copy大佬的思路:
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
while (root.val - p.val) * (root.val - q.val) > 0:
root = (root.left, root.right)[p.val > root.val]
return root
如果root在区间中间,则返回root。
如果不在,说明pq同号。如果p大, 则后面条件满足,为True:[1], 索引元组[1]的位置,root = root.right
反之则为[0], root = root. left
此题思路重点!!抓住在二叉搜索树中公共节点一定是在pq中间。因为左子树小,右子树大的原则
此题思路:
以root为中节点,左右子树去找p和q
在同一回溯级里:
left就是去root的左子树找此节点
right就是去root的右子树找此节点
如果左边没有, 则说明两个都在右边或者 一个为null一个在右边: 此时返回right,要么返回的是存在的那个节点,要么返回的是右边存在的共同父节点
如果右边没有,则同理
如果两边都没有,则返回空
如果两边都有,则返回root,说明p q存在于此root的两边,则root为他们的共同父节点
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if not root:
return None
if root == p or root ==q :
return root
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor( root.right, p, q)
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor( root.left, p,q)
if not right and not left:
return
elif not right and left:
return left
elif not left and right:
return right
else:
return root







 本文介绍二叉搜索树的基本概念,包括二叉树的遍历方法(前序、中序、后序),并详细讲解如何通过递归实现这些遍历。此外,还介绍了两种验证二叉搜索树有效性的方法及寻找二叉搜索树中两个节点的最近公共祖先的有效算法。
本文介绍二叉搜索树的基本概念,包括二叉树的遍历方法(前序、中序、后序),并详细讲解如何通过递归实现这些遍历。此外,还介绍了两种验证二叉搜索树有效性的方法及寻找二叉搜索树中两个节点的最近公共祖先的有效算法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








