文章目录
Day 11
2019年8月14日。
这是我学习Spring的第十一天。
这一天,我学到了以下的知识。
Dao层简介
对于数据访问层(Dao),无论是 SQL(关系型数据库) 还是 NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理。
Spring Boot 底层都是采用 Spring Data 的方式进行统一处理各种数据库,Spring Data 也是 Spring 中与 Spring Boot、Spring Cloud 等齐名的知名项目。
Sping Data 官网:https://spring.io/projects/spring-data
数据库相关的启动器:官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.7.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter
创建JDBC项目
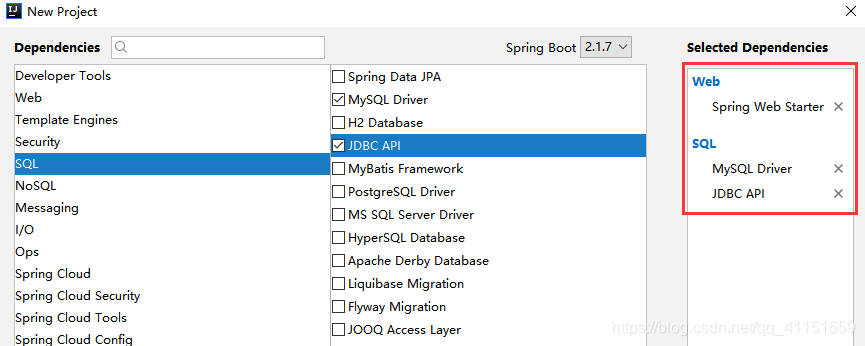
- 新建一个项目,选择Web模块中的Spring Web Starter,SQL中的MySQL Driver和JDBC API,如图所示:
- 创建好项目后,可以发现pom.xml已经自动导入了如下的启动器,代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
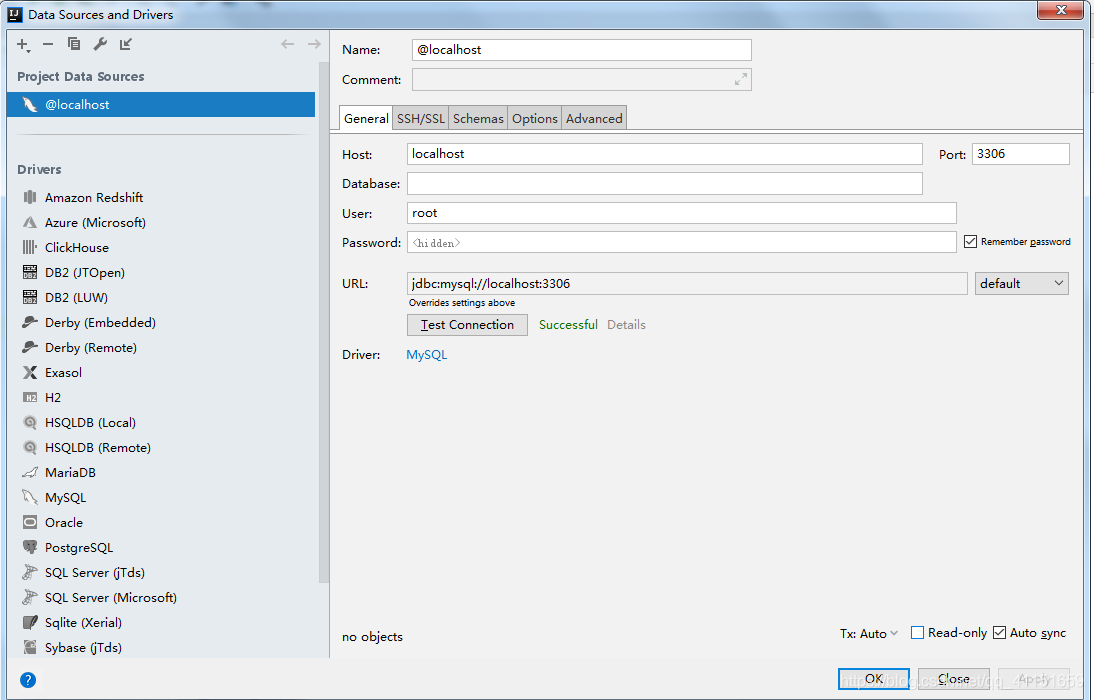
- 连接数据库,如图所示:
- 使用yml来编写application.yml来进行配置,代码如下:
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 配置完毕后,就可以直接去使用了,因为Spring Boot已经默认帮我们进行了自动配置,编写配置类,代码如下:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootDemoDataApplicationTests {
//DI注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
//关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
输出结果:可以看到tSpring Boot默认给我们配置的数据源为 : class com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource , 但是我们并没有手动配置
来全局搜索一下,找到数据源的所有自动配置都在 :DataSourceProperties 文件下;可以在这里来探究下自动配置的原理以及能配置哪些属性;
分析源码,可以看出 Spring Boot 2.1.7 默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource数据源,而以前的版本,如 Spring Boot 1.5,则默认使用 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource 作为数据源;
至今为止,HikariDataSource 号称 Java WEB 当前速度最快的数据源,相比于传统的 C3P0 、DBCP、Tomcat jdbc 等连接池更加优秀;
有了数据库连接,显然就可以使用 CRUD 来操作数据库了。
CRUD操作
具体的CRUD操作步骤如下:
Crud操作
-
有了数据源(com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource),就可以拿到数据库连接(java.sql.Connection),有了连接,就可以使用连接和原生的 JDBC 语句来操作数据库
-
即使不使用第三方第数据库操作框架,如 MyBatis等,Spring 本身也对原生的JDBC 做了轻量级的封装,即 org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
-
数据库操作的所有 CRUD 方法都在 JdbcTemplate 中
-
Spring Boot 不仅提供了默认的数据源,同时默认已经配置好了 JdbcTemplate 放在了容器中,程序员只需自己注入即可使用
-
JdbcTemplate 的自动配置原理是依赖 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc 包下的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration 类
JdbcTemplate主要提供以下几类方法:
-
execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,一般用于执行DDL语句;
-
update方法及batchUpdate方法:update方法用于执行新增、修改、删除等语句;batchUpdate方法用于执行批处理相关语句;
-
query方法及queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关语句;
-
call方法:用于执行存储过程、函数相关语句。
测试
@RestController
public class JdbcController {
//JdbcTemplate 是 core 包的核心类,用于简化 JDBC操作,还能避免一些常见的错误,如忘记关闭数据库连接
//Spring Boot 默认提供了数据源,默认提供了 org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
//JdbcTemplate 中会自己注入数据源,使用起来也不用再自己来关闭数据库连接
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//查询student表中所有数据
//List 中的1个 Map 对应数据库的 1行数据
//Map 中的 key 对应数据库的字段名,value 对应数据库的字段值
@GetMapping("/userList")
public List<Map<String, Object>> userList(){
String sql = "select * from user";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return maps;
}
//新增一个用户
@GetMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(){
//插入语句
String sql = "insert into mybatis.user(id, name, pwd) values (4,'小明','123456')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
//查询
return "addUser-ok";
}
//修改用户信息
@GetMapping("/updateUser/{id}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "update mybatis.user set name=?,pwd=? where id="+id;
//数据
Object[] objects = new Object[2];
objects[0] = "小明2";
objects[1] = "zxcvbn";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,objects);
//查询
return "updateUser-ok";
}
//删除用户
@GetMapping("/delUser/{id}")
public String delUser(@PathVariable("id") int id){
//插入语句
String sql = "delete from user where id=?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
//查询
return "delUser-ok";
}
}
原理探究
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceConfiguration 数据源配置类作用 :根据逻辑判断之后,添加数据源;
SpringBoot默认支持以下数据源
-
com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource (Spring Boot 2.0 以上,默认使用此数据源)
-
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource
-
org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSource
可以使用 spring.datasource.type 指定自定义的数据源类型,值为 要使用的连接池实现的完全限定名。默认情况下,它是从类路径自动检测的。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnMissingBean({DataSource.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(
name = {"spring.datasource.type"}
)
static class Generic {
Generic() {
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource(DataSourceProperties properties) {
return properties.initializeDataSourceBuilder().build();
}
}
自定义数据源 DruidDataSource
这里需要用到阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现:Druid,介绍博客为:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_41151659/article/details/99682243 ,这里不再赘述
引入数据源
- 应用的 pom.xml 文件中添加上 Druid 数据源依赖,而这个依赖可以从 Maven 仓库官网 Maven Repository 中获取,代码如下:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.12</version>
</dependency>
- 查看项目依赖,导入成功,如图所示:

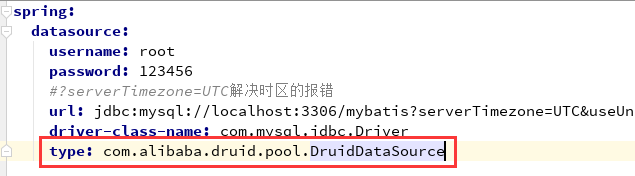
- 切换数据源。之前已经说过 Spring Boot 2.0 以上默认使用 com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource 数据源,但可以 通过 修改yml配置里的spring.datasource.type来指定数据源,如图所示:
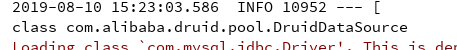
- 数据源切换后,,同理可以注入 DataSource,然后获取到它,输出一看便知是否成功切换,如图所示:
- 数据源切换成功!既然切换成功,就可以设置数据源连接初始化大小、最大连接数、等待时间、最小连接数等设置项,代码如下:
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址: https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
- 添加log4j日志依赖,代码如下:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
- 现在需要程序员自己为 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 绑定全局配置文件中的参数,再添加到容器中,而不能再使用 Spring Boot 的自动生成了;现在添加 DruidDataSource 组件到容器中,并绑定属性,代码如下;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
}
- 编写测试类,查看设置是否成功,代码如下:
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootDemoDataApplicationTests {
//注入数据源
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource;
@Test
public void contextLoads() throws SQLException {
//看一下默认数据源
System.out.println(dataSource.getClass());
//获得连接
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = (DruidDataSource) dataSource;
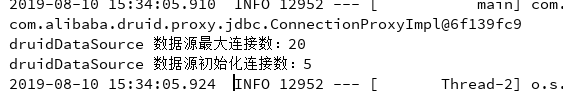
System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源最大连接数:" + druidDataSource.getMaxActive());
System.out.println("druidDataSource 数据源初始化连接数:" + druidDataSource.getInitialSize());
//关闭连接
connection.close();
}
}
- 输出结果,可见配置参数已经生效,如图所示:
配置Druid数据源监控
Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看,类似安装 路由器 时,同样也提供了一个默认的 web 页面。
- 设置 Druid 的后台管理页面,比如 登录账号、密码 等;配置后台管理,代码如下:
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servler 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号
initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//后台允许谁可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
initParams.put("allow", "");
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
//这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
}
}
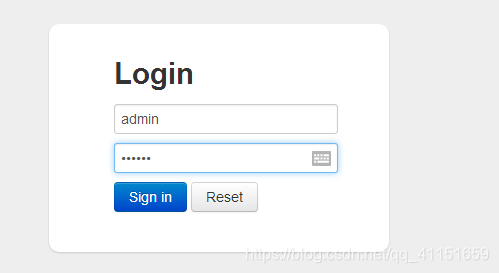
- 访问 : http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html ,显示登录弹窗。输入我们设定好的账户(admin,123456),如图所示:
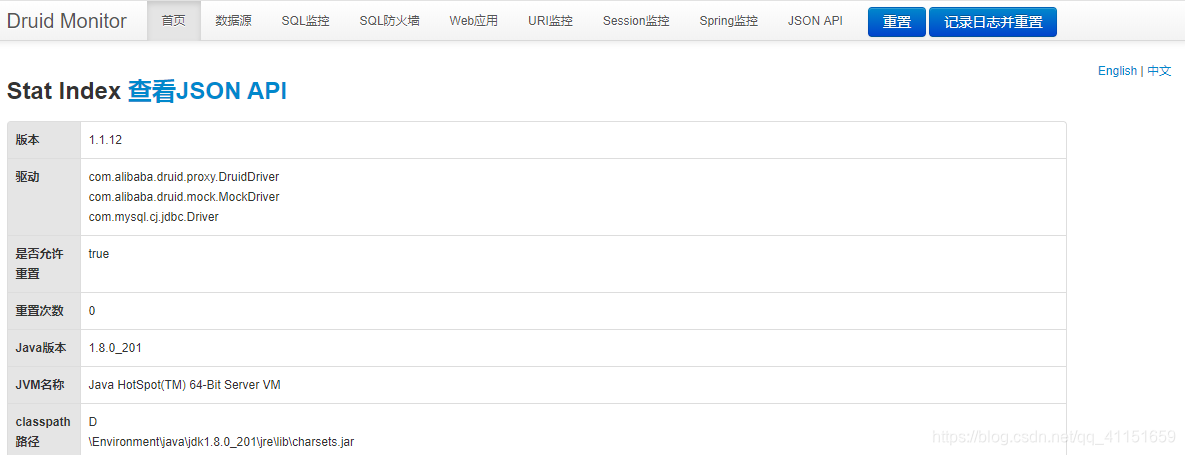
- 进入之后的页面如图缩回:
配置 Druid web 监控 filter
这个过滤器的作用就是统计 web 应用请求中所有的数据库信息,例如:发出的 sql 语句,sql 执行的时间、请求次数、请求的 url 地址、以及seesion 监控、数据库表的访问次数 等,编写相关代码,如下所示:
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servler 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin"); //后台管理界面的登录账号
initParams.put("loginPassword", "123456"); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//后台允许谁可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
initParams.put("allow", "");
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
//这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
}
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter
//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
//exclusions:设置哪些请求进行过滤排除掉,从而不进行统计
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("exclusions", "*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
//"/*" 表示过滤所有请求
bean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
return bean;
}
}
配置完毕后,我们可以启动来进行测试
发送一条sql语句,然后来看一下后台的消息,,如图所示: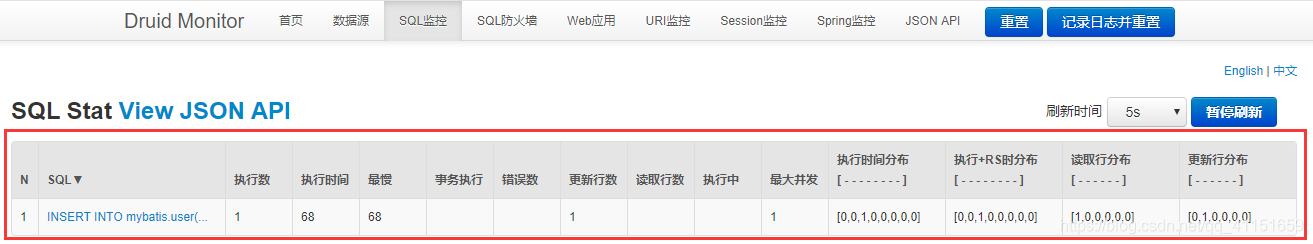
Spring Boot 整合mybatis
- 在pom.xml文件中导入mybatis所需要的依赖,代码如下:
<!-- 引入 myBatis,这是 MyBatis官方提供的适配 Spring Boot 的,而不是Spring Boot自己的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0</version>
</dependency>
- 配置数据库连接信息,代码如下:
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 编写实体类,代码如下:
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- 编写接口,代码如下:
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.util.List;
//@Mapper : 表示本类是一个 MyBatis 的 Mapper,等价于以前 Spring 整合 MyBatis 时的 Mapper 接口
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
//选择全部用户
List<User> selectUser();
//根据id选择用户
User selectUserById(int id);
//添加一个用户
int addUser(User user);
//修改一个用户
int updateUser(User user);
//根据id删除用户
int deleteUser(int id);
}
- 编写Mapper映射文件,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.mybatis.pojo.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="selectUser" resultType="User">
select * from user
</select>
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="User">
insert into user (id,name,pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="User">
update user set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
- 将Mybatis与Spring Boot整合,
以前 MyBatis 未与 spring 整合时,配置数据源、事务、连接数据库的账号、密码等都是在 myBatis 核心配置文件中进行的
myBatis 与 spring 整合后,配置数据源、事务、连接数据库的账号、密码等就交由 spring 管理。因此,在这里我们即使不使用mybatis配置文件,也完全可以。
既然已经提供了 mybatis 的映射配置文件,自然要告诉 spring boot 这些文件的位置
#指定myBatis的核心配置文件与Mapper映射文件
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
# 注意:对应实体类的路径
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.kuang.mybatis.pojo
- 查看配置文件
Spring boot 官方并没有提供 mybaits 的启动器,是 mybatis 官方提供的开发包来适配的 spring boot,从 pom.xml 文件中的依赖包名也能看出来,并非是以 spring-boot 开头的
同理,上面全局配置文件中的这两行配置也是以 mybatis 开头,而非 spring 开头,也充分说明这些都是 mybatis 官方提供的
可以从 org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisProperties 中查看所有配置项
ConfigurationProperties(
prefix = "mybatis"
)
public class MybatisProperties {
public static final String MYBATIS_PREFIX = "mybatis";
private static final ResourcePatternResolver resourceResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
private String configLocation;
private String[] mapperLocations;
private String typeAliasesPackage;
private Class<?> typeAliasesSuperType;
private String typeHandlersPackage;
private boolean checkConfigLocation = false;
private ExecutorType executorType;
private Class<? extends LanguageDriver> defaultScriptingLanguageDriver;
private Properties configurationProperties;
@NestedConfigurationProperty
private Configuration configuration;
- 编写Controller,代码如下:
import com.kuang.mybatis.pojo.User;
import com.kuang.mybatis.pojo.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
//选择全部用户
@GetMapping("/selectUser")
public String selectUser(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectUser();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
return "ok";
}
//根据id选择用户
@GetMapping("/selectUserById")
public String selectUserById(){
User user = userMapper.selectUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
return "ok";
}
//添加一个用户
@GetMapping("/addUser")
public String addUser(){
userMapper.addUser(new User(5,"阿毛","456789"));
return "ok";
}
//修改一个用户
@GetMapping("/updateUser")
public String updateUser(){
userMapper.updateUser(new User(5,"阿毛","421319"));
return "ok";
}
//根据id删除用户
@GetMapping("/deleteUser")
public String deleteUser(){
userMapper.deleteUser(5);
return "ok";
}
}





 本文详细介绍了如何在SpringBoot项目中整合MyBatis,包括创建JDBC项目、配置数据源、CRUD操作、引入Druid数据源、监控配置、以及SpringBoot与MyBatis的整合步骤。
本文详细介绍了如何在SpringBoot项目中整合MyBatis,包括创建JDBC项目、配置数据源、CRUD操作、引入Druid数据源、监控配置、以及SpringBoot与MyBatis的整合步骤。

















 809
809

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










