Database Fundamentals
File System
characteristic(特点):
- Data are stored in files with interface between programs and files.
- Various access(访问) methods exist (e.g. sequential, indexed, random)
- One file corresponds(对应) to one or several programs.
disadvantages(缺点):
- Separation and isolation data
- Data is isolated in separate files, it is difficult to access data if we require data from more than two files.
- Duplication of data
- Duplication can lead to loss of data integrity(完整性)
- Data dependence
- Changes to an existing file structure can lead to identify all the affected programs, modify them, and then retest them.
- This characteristic of file-based systems is known as program-data dependence
Database Management System
advantage(优点)
- Data constitute an organizational asset (↑Integrated control)
- Reduction of redundancy 减少数据冗余
- Avoidance of inconsistency 避免不一致
- Sharability 共享
- Standards 标准
- Improved security 提高安全性
- Data integrity 数据独立性
- Programmer productivity(↑Data Independence)
- Logical Independence
- Physical Independence
- Invisibility (non-transparency) of the details of conceptual organization, storage structure and access strategy to the users(↑Data Independence)
- Logical
- non-transparency of the conceptual organization
- non-transparency of logical access strategy
- Physical
- non-transparency of the physical storage organization
- non-transparency of physical access paths
- Logical
Data Independence
- Logical Independence
- The logical structure of application and database are independence of each other
- Changes to the logical structure of the database do not affect the application
- Physical Independence
- The data of application and database are independence of each other
- Changes to the physical storage of the database do not affect the application
The Three-level Architecture of DBS
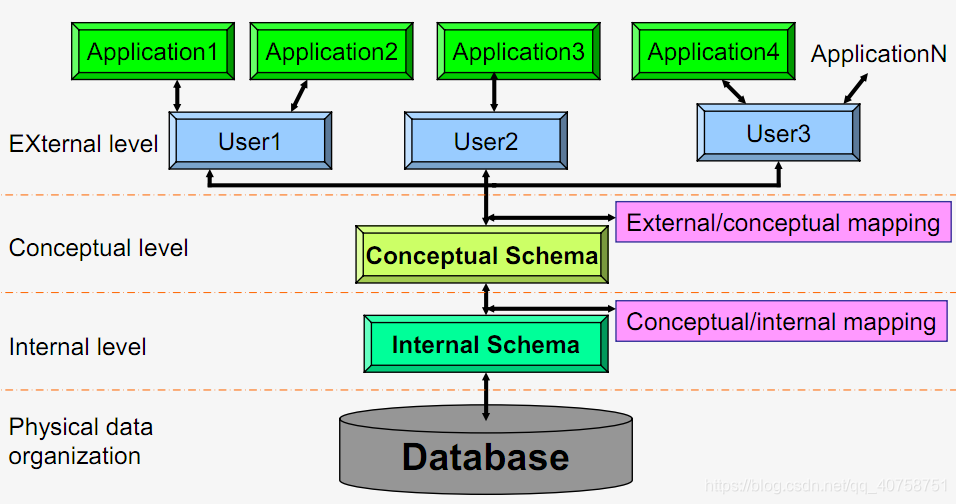
- 三级模式
- External level 外模式
- Conceptual level 模式(概念模式/逻辑模式)
- Internal level 内模式
- 两级映像
- External/conceptual mapping 外模式/模式映像
- Conceptual/internal mapping 模式/内模式映像
The responsibility of Database Administrator
- Defines and manages the conceptual schema(概念模型)
- Defines application and user views
- Monitors(watches 监视) and tunes(调整) DBMS performance
- Loads and reformats(格式化) the Database
- Responsible security and reliability
Relational Database
- Primary key(主键)
- Uniquely identifies a tuple
- Each relationship has only one primary key
- Foreign key(外键)
- The primary key of another relationship
- candidate key(候选键)
relational algebra
并/交/差/笛卡尔积
选择/投影/连接/除
与/或/非
Database Objects
Types and use of Index
- Clustered(聚集) Index
- 特点
- 按照索引项的顺序进行物理排序
- If order of data records is the same as, or close to, order of index data entries, then called clustered index.
- A table can have only one clustered index.
- Cost of search data records through index varies based on whether index is clustered or not!
- 叶级节点存放数据
- 适用于
- 包含大量非重复列
- 经常被用来排序/分组的列
- 经常被用作连接的列
- 返回大型结果集的查询
- 不适用于
- 频繁更改的列
- 不利于排序的宽键或若干列组合
- 特点
- Unclustered Index
- 特点
- 数据不按非聚集索引关键字值的顺序排序和存储
- A table can have multiple unclustered indexes.
- 叶级节点不存放数据
- 适用于
- 包含大量非重复列
- 经常被用来连接/分组条件的列
- 经常被用作查询条件的列
- 不返回大型结果集的列
- 特点
- Unique Index
- Unique indexes are necessary on column(s) that must be unique
- Composite(组合) Index
- 组合索引(复合索引)是一个包含多个字段的索引
- 组合索引应该根据实际的查询语句来建立
- 建立组合索引时应将最有可能在where子句中使用的列,并且也是选择性最高的字段放在第一位
- 对于组合索引在索引中添加额外的列不会显著的提高选择性,添加额外的列反而会造成更高的消耗
- Reverse Key Index
- 被索引的每个数据列中的数据都是反向存储的,但仍然保持原来数据列的次序
- 可以高效地打散正常的索引键值在索引叶块中的分布位置,降低索引叶子块的争用,有时会提高系统性能
- 通过在创建索引时指定“REVERSE”关键字,可以创建反向关键字索引
- Bitmap Index(位图索引)
- 对于一些基数很小的列来说,一般的B树索引并不能显著提高查询的速度,位图索引适合建立在有大量重复值的列上
- 当创建位图索引时,Oracle会扫描整张表,并为索引列的每个取值建立一个位图
- Function-Based Indexes(函数索引)
- 对包含有列的函数或表达式创建索引
- 经常访问一些函数或表达式时,可以将其存储在索引中
- 函数索引既可以使用B树索引,也可以使用位图索引,可以根据函数或表达式的结果的基数大小来进行选择
索引的好处
- reduce sort operation
- Ensure uniqueness of key values
- Reduce the number of pages read
Views vs Tables
- 视图是一个虚表
- 视图是由数据库基本表选出来数据构成的
- 是基本表部分行列的组合
- 基本表数据的变化会直接影响视图
- 本质是一组查询语句
- 数据库只存视图的定义,不存数据
Why use Views?
- To restrict(限制) data access
- To make complex queries easy
- To provide data independence
- To present(表示) different views of the same data
Why use triggers?
- monitor user’s operation
- control data integrity
- create complex constraint
- imporve security
Benefits of Stored Procedures
- imrove performance
- ensure security
- reduce traffic
how to use triggers? ECA rule
- Event
- Condition
- Action
Database Design
Why Normalization?
To solve:
- Redundant(冗余) storage of data
- Slow Insertion, Delet and Update operations
- Insertion anomaly
- Deletion anomaly
- Update anomaly
Normal Form
1NF
a relation table that must not contain repeating groups
二维表,不包含非原子结构。
2NF
a 1NF table that every non-key attribute is fully functionally dependent on the primary key.
非主属性完全依赖于主键
3NF
a 2NF table that eliminate transfer dependency
消除传递依赖
BCNF
a 3NF table that eliminate function dependencies on the primary key
消除对主码的函数依赖
4NF
a relation table that Eliminate multi-value dependencies
消除多值依赖
Transaction
Transaction characteristics
- Atomicity
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability
logging
- 先写日志策略





 本文围绕数据库展开,介绍了文件系统的特点与缺点,阐述数据库管理系统的优点、数据独立性及三级模式架构。还讲解了关系数据库的主键、外键等概念,数据库对象中索引的类型与使用,视图和触发器的作用,数据库设计的规范化,以及事务的特性和日志策略。
本文围绕数据库展开,介绍了文件系统的特点与缺点,阐述数据库管理系统的优点、数据独立性及三级模式架构。还讲解了关系数据库的主键、外键等概念,数据库对象中索引的类型与使用,视图和触发器的作用,数据库设计的规范化,以及事务的特性和日志策略。
















 148
148










