- 排序与检索
sort :对给定区间所有元素进行排序
头文件 :algorithm
语法描述:sort(begin,end,cmp),cmp参数可以没有,如果没有默认非降序排序。
less<数据类型>()//从小到大排序
greater<数据类型>()//从大到小排序
函数lower_bound()
功能:函数lower_bound()在first和last中的前闭后开区间进行二分查找,返回大于或等于val的第一个元素位置。如果所有元素都小于val,则返回last的位置.
注意:如果所有元素都小于val,则返回last的位置,且last的位置是越界的!!
函数upper_bound()
功能:函数upper_bound()返回的在前闭后开区间查找的关键字的上界,返回大于val的第一个元素位置
注意:返回查找元素的最后一个可安插位置,也就是“元素值>查找值”的第一个元素的位置。同样,如果val大于数组中全部元素,返回的是last。(注意:数组下标越界)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5;
int main(){
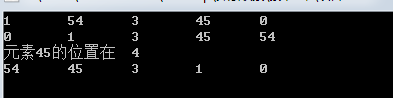
int a[maxn] = {1,54,3,45,0};
//打印出初始序列
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<'\t';
cout<<"\n";
//小到大打印
sort(a,a+maxn);
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<'\t';
cout<<"\n";
//找到元素45的位置
int p = lower_bound(a, a+maxn, 45) - a;
cout<<"元素45的位置在\t"<<p+1<<'\n';
//大到小打印
sort(a, a+maxn, greater<int>());
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
cout<<a[i]<<'\t';
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}
- 最值与绝对值
max(x,y) 和 min(x,y) 分别返回 x y中的最大值和最小值。
abs(x)返回x的绝对值(必须是整数),如果是浮点数需要用math头文件下的fabs函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
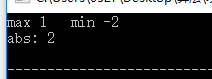
int x = 1, y =- 2;
cout<<"max "<<max(x,y)<<"\tmin "<<min(x,y)<<"\n";
cout<<"abs: "<<abs(y)<<"\n";
return 0;
}
- 交换、反转、填充
swap(x, y)用来交换x和y的值。
reverse(it1, it2)可以将数组指针在[it1 ,it2)之间的元素或迭代器之间的元素进行反转。
fill(it1, it2, x)可以将数组或容器中[it1 ,it2)之间全部赋值为x。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
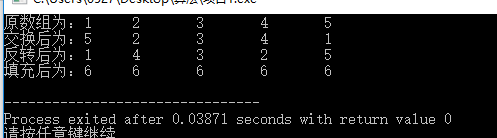
int a[5] = {1,2,3,4,5};
cout<<"原数组为:";
for(int i=0;i<5;++i)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n";
swap(a[0],a[4]);
cout<<"交换后为:";
for(int i=0;i<5;++i)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n";
reverse(a, a+5);
cout<<"反转后为:";
for(int i=0;i<5;++i)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n";
fill(a, a+5, 6);
cout<<"填充后为:";
for(int i=0;i<5;++i)
cout<<a[i]<<"\t";
cout<<"\n";
return 0;
}





 本文深入探讨了C++标准库中的算法,包括排序(sort),检索(lower_bound, upper_bound),最值(max, min),绝对值(abs),交换(swap),反转(reverse)和填充(fill)等实用函数的使用方法及示例代码,帮助读者掌握高效编程技巧。
本文深入探讨了C++标准库中的算法,包括排序(sort),检索(lower_bound, upper_bound),最值(max, min),绝对值(abs),交换(swap),反转(reverse)和填充(fill)等实用函数的使用方法及示例代码,帮助读者掌握高效编程技巧。
















 1232
1232

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








