Spring版本5.2.12.RELEASE
PostConstruct是bean的初始化方法,PreDestroy是Bean销毁的方法,他们都是Java原生的注解 ,处理这两个注解的类为:org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor该类是注解驱动的spring应用上下文内建的可以查找的依赖
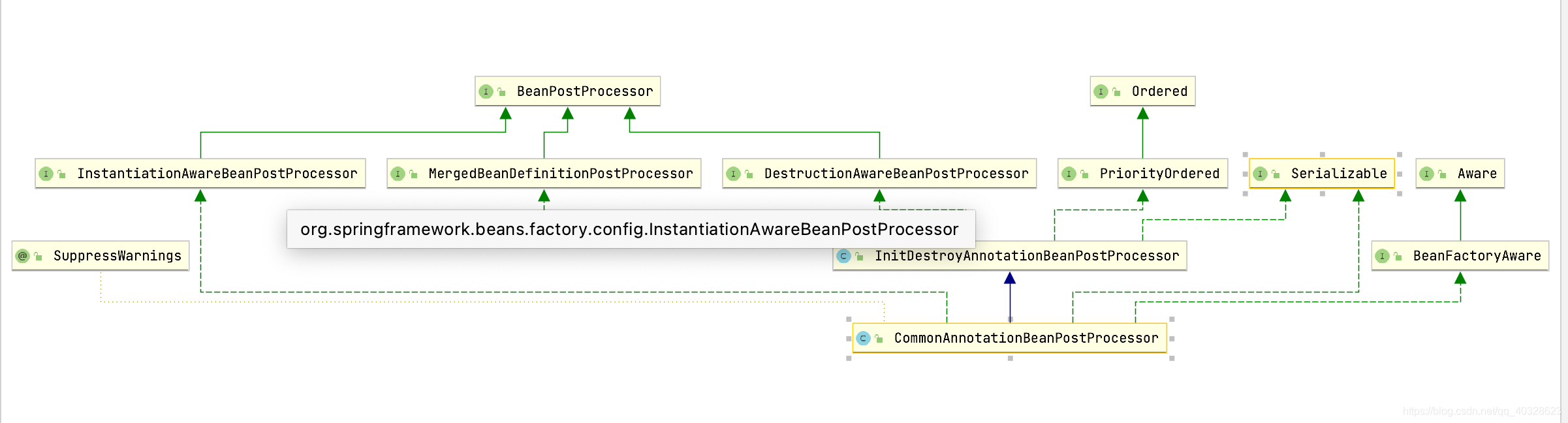
实现原理解析:
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,该类主要是定义初始化的销毁的注解类型,这个类的构造函数中设置了初始化注解类型和销毁的注解类型
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
//设置PostProcessor的优先级
setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3);
//设置初始化方法的注解类型
setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class);
//设置销毁方法的注解类型
setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class);
ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext");
}
处理这两个注解主要是在CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor父类InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,从类的结构图中可以看出,InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor实现类,并且MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor是个Bean的后置处理器,主要是在BeanDefinition合并后进行回调。
注解的处理
1.处理的入口,BeanDefinition合并后的回调方法
//回调方法
public void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName) {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(beanType);
metadata.checkConfigMembers(beanDefinition);
}
- 寻找PostConstruct 和PreDestory的元数据信息核心的方法是buildLifecycleMetadata
private LifecycleMetadata findLifecycleMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (this.lifecycleMetadataCache == null) {
// Happens after deserialization, during destruction...
return buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
}
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
LifecycleMetadata metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
synchronized (this.lifecycleMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.lifecycleMetadataCache.get(clazz);
if (metadata == null) {
metadata = buildLifecycleMetadata(clazz);
//按照key为class value为被注解方法的元数据放入缓存
this.lifecycleMetadataCache.put(clazz, metadata);
}
return metadata;
}
}
return metadata;
}
- 构造元数据信息。
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
//判断当前Class中是否有PostConstruct 和PreDestroy注解的定义,存在一个即返回true
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, Arrays.asList(this.initAnnotationType, this.destroyAnnotationType))) {
return this.emptyLifecycleMetadata;
}
//从这里可看出PostConstruct和PreDestroy 一个类中可定义多个
List<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new ArrayList<>();
List<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new ArrayList<>();
final List<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new ArrayList<>();
//利用反射遍历 bean的class中所有method 是否存在初始化和销毁的注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
if (this.initAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.initAnnotationType)) {
//将方法包装为LifecycleElement
LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method);
currInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
if (this.destroyAnnotationType != null && method.isAnnotationPresent(this.destroyAnnotationType)) {
currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method));
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method);
}
}
});
initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods);
destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods);
//检查父类中的PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解信息
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}// 终结条件-》直到targetClass为Object
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
//将所有的PostConstruct和PreDestroy 包装为LifecycleMetadata
return (initMethods.isEmpty() && destroyMethods.isEmpty() ? this.emptyLifecycleMetadata :
new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods));
}
4.LifecycleElement 是PostConstruct和PreDestroy 包装类
public LifecycleElement(Method method) {
//方法的不能有入参
if (method.getParameterCount() != 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Lifecycle method annotation requires a no-arg method: " + method);
}
this.method = method;
//方法的标识符,如果是修饰符是private则保存全名称,主要是区别子类和父类同名方法
this.identifier = (Modifier.isPrivate(method.getModifiers()) ?
ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(method) : method.getName());
}
//通过反射调用被注解的方法
public void invoke(Object target) throws Throwable {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method);
this.method.invoke(target, (Object[]) null);
}
5.LifecycleMetadata 一个类中所有的PostConstruct和PreDestroy 包装类
private class LifecycleMetadata {
private final Class<?> targetClass;
private final Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethods;
private final Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods;
@Nullable
private volatile Set<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods;
@Nullable
private volatile Set<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods;
public LifecycleMetadata(Class<?> targetClass, Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethods,
Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods) {
this.targetClass = targetClass;
this.initMethods = initMethods;
this.destroyMethods = destroyMethods;
}
//遍历所有的方法对其去重 被private修饰的所有都会执行,被public修饰的只有子类的会被执行,
public void checkConfigMembers(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
Set<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.initMethods.size());
for (LifecycleElement element : this.initMethods) {
String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier)) {
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedInitMethod(methodIdentifier);
checkedInitMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered init method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
Set<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.destroyMethods.size());
for (LifecycleElement element : this.destroyMethods) {
String methodIdentifier = element.getIdentifier();
if (!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier)) {
beanDefinition.registerExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(methodIdentifier);
checkedDestroyMethods.add(element);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered destroy method on class [" + this.targetClass.getName() + "]: " + element);
}
}
}
this.checkedInitMethods = checkedInitMethods;
this.checkedDestroyMethods = checkedDestroyMethods;
}
public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {
Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedInitMethods = this.checkedInitMethods;
Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate =
(checkedInitMethods != null ? checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods);
if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());
}
element.invoke(target);
}
}
}
public void invokeDestroyMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable {
Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = this.checkedDestroyMethods;
Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethodsToUse =
(checkedDestroyMethods != null ? checkedDestroyMethods : this.destroyMethods);
if (!destroyMethodsToUse.isEmpty()) {
for (LifecycleElement element : destroyMethodsToUse) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking destroy method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod());
}
element.invoke(target);
}
}
}
public boolean hasDestroyMethods() {
Collection<LifecycleElement> checkedDestroyMethods = this.checkedDestroyMethods;
Collection<LifecycleElement> destroyMethodsToUse =
(checkedDestroyMethods != null ? checkedDestroyMethods : this.destroyMethods);
return !destroyMethodsToUse.isEmpty();
}
}
PostConstruct和PreDestroy 调用时机
1.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 是MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor实现类,MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor是BeanPostProcessor的子类,
重点实现了bean生命周期方法postProcessBeforeInitialization
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 获取所有的别PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解的方法的元数据信息,从缓存中获取
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
//调用被PostConstruct 注解的方法
metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex);
}
return bean;
}
2.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor的实现类,重点实现了postProcessBeforeDestruction的方法,即bean销毁前的回调(调用原理和PostContruct一样)
public void postProcessBeforeDestruction(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass());
try {
metadata.invokeDestroyMethods(bean, beanName);
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
String msg = "Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception";
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.warn(msg, ex.getTargetException());
}
else {
logger.warn(msg + ": " + ex.getTargetException());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Failed to invoke destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
该方法在调用IOC容器的close方法后回调








 本文介绍了Spring框架中PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解的处理方式,它们分别对应于bean的初始化和销毁阶段。关键处理类是CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,它在BeanDefinition合并后进行回调,通过MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor接口来管理bean的生命周期。文章详细阐述了这两个注解的元数据构建和调用时机。
本文介绍了Spring框架中PostConstruct和PreDestroy注解的处理方式,它们分别对应于bean的初始化和销毁阶段。关键处理类是CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,它在BeanDefinition合并后进行回调,通过MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor接口来管理bean的生命周期。文章详细阐述了这两个注解的元数据构建和调用时机。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








