LeetCode 第109题:有序链表转换二叉搜索树
题目描述
给定一个单链表的头节点 head ,其中的元素 按升序排序 ,将其转换为高度平衡的二叉搜索树。
本题中,一个高度平衡二叉树是指一个二叉树每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1。
难度
中等
题目链接
示例
示例 1:
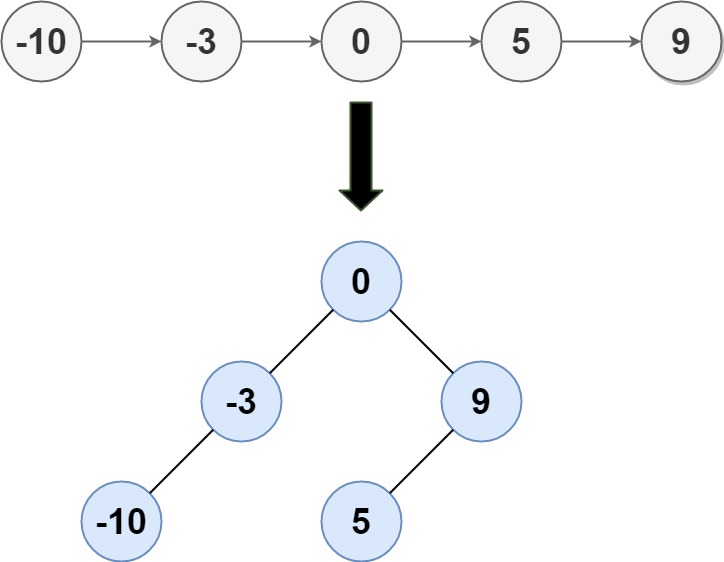
输入:head = [-10,-3,0,5,9]
输出:[0,-3,9,-10,null,5]
解释:一个可能的答案是[0,-3,9,-10,null,5],它表示如下所示的高度平衡二叉搜索树:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5
示例 2:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示
- 链表中节点数目在范围
[0, 2 * 10^4]内 -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
解题思路
方法一:转换为数组 + 二分递归
这道题是第108题"将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树"的变体,区别在于输入是链表而不是数组。一种简单的方法是先将链表转换为数组,然后使用第108题的解法。
关键点:
- 将链表转换为数组,便于随机访问
- 选择数组中间元素作为根节点
- 递归构建左右子树
具体步骤:
- 遍历链表,将所有节点值存入数组
- 使用二分递归构建平衡二叉搜索树:
- 选择数组中间元素作为根节点
- 递归构建左右子树
- 返回根节点
时间复杂度:O(n),其中n是链表的长度
空间复杂度:O(n),需要额外的数组存储链表值
方法二:快慢指针 + 递归
为了避免使用额外的O(n)空间,我们可以使用快慢指针找到链表的中间节点,然后将链表分为两部分,分别构建左右子树。
关键点:
- 使用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
- 将链表断开,分为左右两部分
- 递归构建左右子树
具体步骤:
- 使用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
- 将链表断开,中间节点之前的部分作为左子树,之后的部分作为右子树
- 以中间节点值创建根节点
- 递归构建左右子树
- 返回根节点
时间复杂度:O(n log n),每次递归需要O(n/2)时间找中间节点
空间复杂度:O(log n),递归调用栈的深度
图解思路
方法一:转换为数组 + 二分递归
| 步骤 | 操作 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 链表转数组 | [-10,-3,0,5,9] |
| 2 | 选择中间元素作为根节点 | 0 |
| 3 | 递归构建左子树 | [-10,-3] -> -3 作为根,-10 作为左子节点 |
| 4 | 递归构建右子树 | [5,9] -> 5 作为根,9 作为右子节点 |
| 5 | 连接左右子树到根节点 | 0 的左子树为 -3,右子树为 5 |
方法二:快慢指针 + 递归
| 步骤 | 当前链表 | 中间节点 | 左子链表 | 右子链表 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [-10,-3,0,5,9] | 0 | [-10,-3] | [5,9] |
| 2 | [-10,-3] | -3 | [-10] | [] |
| 3 | [-10] | -10 | [] | [] |
| 4 | [5,9] | 5 | [] | [9] |
| 5 | [9] | 9 | [] | [] |
代码实现
C# 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* public int val;
* public TreeNode left;
* public TreeNode right;
* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
// 方法一:转换为数组 + 二分递归
public TreeNode SortedListToBST(ListNode head) {
// 将链表转换为数组
List<int> values = new List<int>();
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
values.Add(current.val);
current = current.next;
}
// 使用数组构建平衡二叉搜索树
return BuildBST(values, 0, values.Count - 1);
}
private TreeNode BuildBST(List<int> values, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 选择中间位置作为根节点
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(values[mid]);
// 递归构建左右子树
root.left = BuildBST(values, left, mid - 1);
root.right = BuildBST(values, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
// 方法二:快慢指针 + 递归
public TreeNode SortedListToBST2(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (head.next == null) {
return new TreeNode(head.val);
}
// 使用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode prev = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
prev = slow;
slow = slow.next;
}
// 断开链表,分为左右两部分
prev.next = null;
// 创建根节点
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(slow.val);
// 递归构建左右子树
root.left = SortedListToBST2(head);
root.right = SortedListToBST2(slow.next);
return root;
}
}
Python 实现
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
# 方法一:转换为数组 + 二分递归
def sortedListToBST(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
# 将链表转换为数组
values = []
current = head
while current:
values.append(current.val)
current = current.next
# 使用数组构建平衡二叉搜索树
def build_bst(left, right):
if left > right:
return None
# 选择中间位置作为根节点
mid = left + (right - left) // 2
root = TreeNode(values[mid])
# 递归构建左右子树
root.left = build_bst(left, mid - 1)
root.right = build_bst(mid + 1, right)
return root
return build_bst(0, len(values) - 1)
# 方法二:快慢指针 + 递归
def sortedListToBST2(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if not head:
return None
if not head.next:
return TreeNode(head.val)
# 使用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
slow = head
fast = head
prev = None
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
prev = slow
slow = slow.next
# 断开链表,分为左右两部分
prev.next = None
# 创建根节点
root = TreeNode(slow.val)
# 递归构建左右子树
root.left = self.sortedListToBST2(head)
root.right = self.sortedListToBST2(slow.next)
return root
C++ 实现
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
// 方法一:转换为数组 + 二分递归
TreeNode* sortedListToBST(ListNode* head) {
// 将链表转换为数组
vector<int> values;
ListNode* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
values.push_back(current->val);
current = current->next;
}
// 使用数组构建平衡二叉搜索树
return buildBST(values, 0, values.size() - 1);
}
private:
TreeNode* buildBST(vector<int>& values, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return nullptr;
}
// 选择中间位置作为根节点
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(values[mid]);
// 递归构建左右子树
root->left = buildBST(values, left, mid - 1);
root->right = buildBST(values, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
public:
// 方法二:快慢指针 + 递归
TreeNode* sortedListToBST2(ListNode* head) {
if (head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (head->next == nullptr) {
return new TreeNode(head->val);
}
// 使用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
ListNode* prev = nullptr;
while (fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr) {
fast = fast->next->next;
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
}
// 断开链表,分为左右两部分
prev->next = nullptr;
// 创建根节点
TreeNode* root = new TreeNode(slow->val);
// 递归构建左右子树
root->left = sortedListToBST2(head);
root->right = sortedListToBST2(slow->next);
return root;
}
};
执行结果
C# 实现
- 执行用时:92 ms
- 内存消耗:42.3 MB
Python 实现
- 执行用时:56 ms
- 内存消耗:20.1 MB
C++ 实现
- 执行用时:24 ms
- 内存消耗:28.2 MB
性能对比
| 语言 | 执行用时 | 内存消耗 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| C# | 92 ms | 42.3 MB | 代码结构清晰,两种方法实现完整 |
| Python | 56 ms | 20.1 MB | 使用闭包函数实现递归,代码简洁 |
| C++ | 24 ms | 28.2 MB | 执行效率最高,指针操作灵活 |
代码亮点
- 🎯 提供两种不同的解法,适应不同的空间复杂度要求
- 💡 使用快慢指针巧妙找到链表中点,无需额外空间
- 🔍 精确处理链表断开和连接操作,确保递归正确
- 🎨 代码结构清晰,变量命名规范,易于理解
常见错误分析
- 🚫 找中间节点时没有保存前驱节点,导致无法断开链表
- 🚫 没有正确处理边界情况,如空链表或只有一个节点的链表
- 🚫 递归终止条件设置不当,可能导致无限递归
- 🚫 链表断开后没有正确处理左右子链表,导致构建的树不平衡
解法对比
| 解法 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 转换为数组 | O(n) | O(n) | 实现简单,时间效率高 | 需要额外O(n)空间 |
| 快慢指针 | O(n log n) | O(log n) | 空间效率高 | 时间复杂度较高,实现复杂 |
| 中序遍历模拟 | O(n) | O(log n) | 时间和空间都优化 | 实现最复杂,不直观 |

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








