Mybatis环境搭建
1.添加Maven坐标
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.4.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.21</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.建表
3.添加mybatis配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
mybatis中#与$区别
动态 sql 是 mybatis 的主要特性之一,在 mapper 中定义的参数传到 xml 中之后,在查询之前 mybatis 会对其进行动态解析。mybatis 为我们提供了两种支持动态 sql 的语法:#{} 以及 ${}。
在下面的语句中,如果 username 的值为 zhangsan,则两种方式无任何区别:
select * from user where name = #{name};
select * from user where name = ${name};
其解析之后的结果均为
select * from user where name = ‘zhangsan’;
但是 #{} 和 ${} 在预编译中的处理是不一样的。#{} 在预处理时,会把参数部分用一个占位符 ? 代替,变成如下的 sql 语句:
select * from user where name = ?;
而 ${} 则只是简单的字符串替换,在动态解析阶段,该 sql 语句会被解析成
select * from user where name = ‘zhangsan’;
以上,#{} 的参数替换是发生在 DBMS 中,而 ${} 则发生在动态解析过程中。
那么,在使用过程中我们应该使用哪种方式呢?
答案是,优先使用 #{}。因为 ${} 会导致 sql 注入的问题。看下面的例子:
select * from ${tableName} where name = #{name}
在这个例子中,如果表名为
user; delete user; –
则动态解析之后 sql 如下:
select * from user; delete user; – where name = ?;
--之后的语句被注释掉,而原本查询用户的语句变成了查询所有用户信息+删除用户表的语句,会对数据库造成重大损伤,极大可能导致服务器宕机。
但是表名用参数传递进来的时候,只能使用 ${} ,具体原因可以自己做个猜测,去验证。这也提醒我们在这种用法中要小心sql注入的问题。
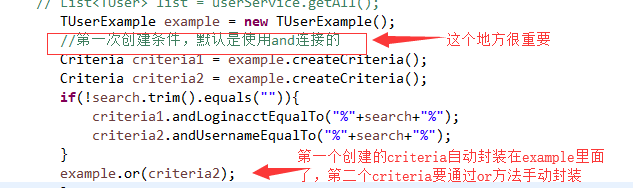
3.mybatis逆向工程中生成的每个pojo会带一个example类,就会涉及到多个criteria的封装问题:见下图解决方案
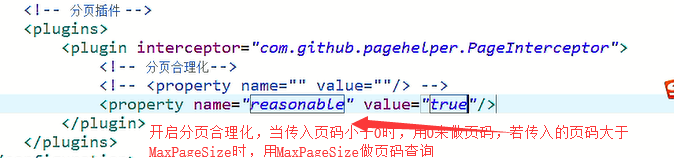
3.pageHelper的总结
4.Mybatis 缓存
一级缓存: Mybatis 的一级缓存的作用域是 session(相当于一次会话),当 openSession()后,如果执行相同的SQL(相同语句和参数),Mybatis 不进行执行 SQL,而是从缓存中命中返回。
二级缓存: Mybatis 的二级缓存的作用域是一个 mapper 的 namespace(同一个namespace里面可能会有多个查询sql,也就是说可能有多个session),同一个 namespace中查询 sql 可以从缓存中命中。二级缓存是可以跨 session 的。

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










