要实现的功能
1.能够添加key和value的键值对
2.能够根据get方法传入key获取其对应的value
1.HashMap基本原理
JDK1.7的HashMap主要采用的是数组+链表进行存储的,数组存放的是一个类,而这个类中有四个字段,
分别是hashcode(用于存放在数组的指定下标下面)、key、value、next(发生hash冲突时指向下一个类从而形成链表)
put方法基本原理是先将key进行hash运算得到hash值,然后把hash值进行取模数组长度-1,得到一个数
组下标范围内的值,然后判断此下标中是否有值,如果没有值直接创建Entry对象将hashcode、key、value
、next存放在Entry中,然后把Entry对象放在数组对应的下标中,如果此下标中有值,则将创建的Entry挂在
上一个Entry的next上。 例如:第一个key进行hashcode后再取模数组长度后值为1,第二个key进行hashcode
后再取模数组长度后值为4。结果如下图所示
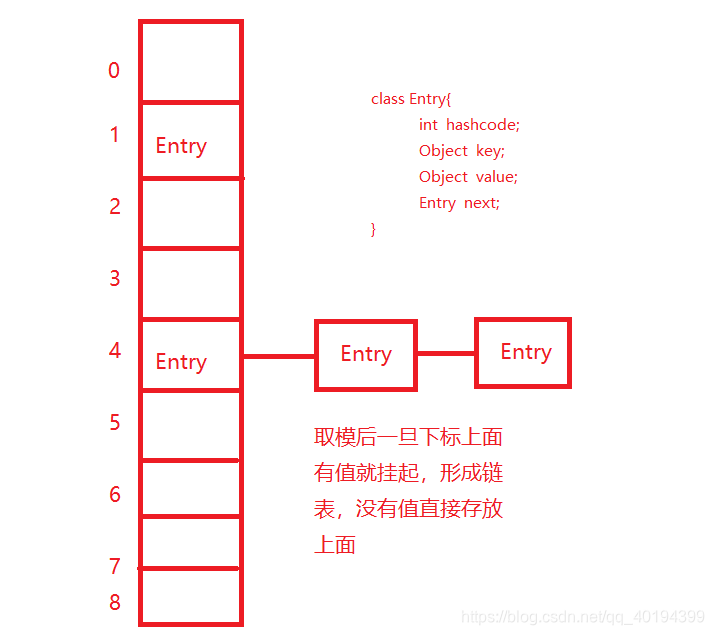
get方法基本原理是先将key进行hash运算得到hash值,然后把hash值进行取模数组长度-1,得到一个数组下标范围内的值,
然后遍历链表通过比对equlas和hashcode是否相等来判断找到对应的Entry从而获取value。
2.手写代码的代码如下
import java.util.Objects;
public class MyHashMap<K,V> {
//初始容量为16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1<<4;
//存放key和value的对象数组
Entry<K,V>[] entrys = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY];
/**
* 添加键值对的方法
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
public void put(K key,V value){
int hash = hash(key);
//判断下标是否已经有值
if (entrys[hash] == null) {
Entry<K, V> entry = new Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);
entrys[hash] = entry;
} else {
Entry<K, V> entry = entrys[hash];
//遍历到最后一个,因为可能挂了多个需要找到最后一个挂在最后一个上面
while(entry.next == null){
if(entry.key.equals(key)){
entry.value = value;
break;
}else {
entry = entry.next;
}
}
entry.next = new Entry<K, V>(hash, key, value, null);
}
}
/**
* 返回hash值,采用取模运算
* @param key 键
* @return hash值
*/
public int hash(K key) {
int hashCode = key.hashCode();
return hashCode % 16-1;
}
/**
*
* @param key 键
* @return 键对应的vlaue值
*/
public V get(K key) {
Entry<K, V> entry = null;
if (key != null) {
int hash = hash(key);
entry =entrys[hash];
while (!entry.key.equals(key)){
entry = entry.next;
}
}
return entry.value;
}
static class Entry<K, V> {
final int hash;
final Object key;
V value;
Entry<K, V> next;
public final Object getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o){
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()){
return false;
}
Entry<K, V> entry = (Entry<K, V>) o;
return hash == entry.hash &&
Objects.equals(key, entry.key) &&
Objects.equals(value, entry.value) &&
Objects.equals(next, entry.next);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(hash, key, value, next);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return key + "=" + value;
}
}
}
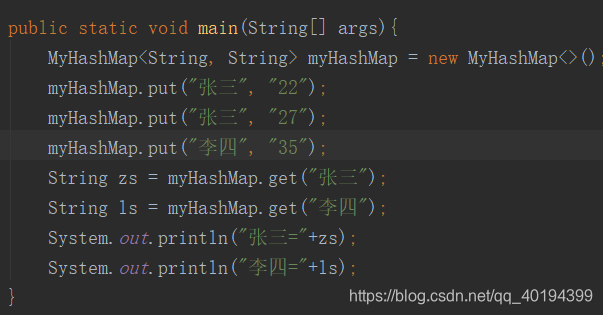
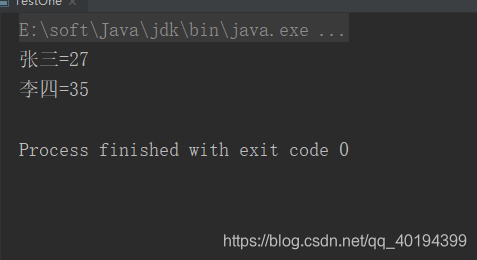
测试代码和测试结果如下








 本文介绍了JDK1.7 HashMap的基本原理,包括其使用数组+链表的数据结构,以及put和get方法的工作流程。通过手写代码,详细解释了如何创建键值对、计算数组下标以及处理哈希冲突的过程。
本文介绍了JDK1.7 HashMap的基本原理,包括其使用数组+链表的数据结构,以及put和get方法的工作流程。通过手写代码,详细解释了如何创建键值对、计算数组下标以及处理哈希冲突的过程。
















 3872
3872

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








