链表是有序的列表,但是它在内存中是存储如下(你中有我,我中有你,铁索连环)
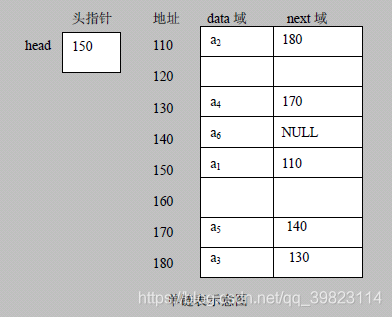
1)链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储.
2)链表分带头节点的链表和没有头节点的链表,根据实际的需求来确定
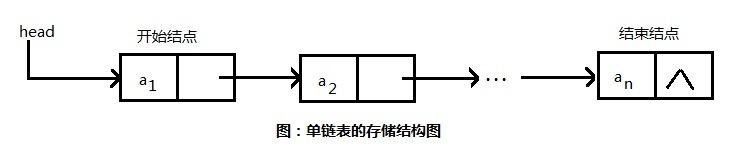
单链表(带头结点) 逻辑结构示意图如下:
3)实现代码:
public class LinkListDemo {
//节点类
public class Node {
protected Node next; //指针域
public int data;//数据域
public Node( int data) {
this. data = data;
}
}
private Node head;//头节点
private Node temp;//临时节点
//初始化链表,生成一个无数据的头节点
LinkListDemo() {
head = new Node();
}
}
//返回头节点
public Node getHead() {
return head;
}
//长度
public int getLength()
{
temp = head;
int length = 0;
while (temp.next!=null)
{
length++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return length;
}
//增加节点
public void add(Node node) {
//因为head节点不能动,因此我们需要一个辅助遍历 temp
Node temp = head;
//遍历链表,找到最后
while(temp.next != null) {
//如果没有找到最后, 将将temp后移
temp = temp.next;
}
//当退出while循环时,temp就指向了链表的最后
//将最后这个节点的next 指向 新的节点
temp.next = node;
}
//删除节点(head 不能动,因此我们需要一个temp辅助节点找到待删除节点的前一个节点)
public void deleteByIndex(int index) {
if (index < 1 || index > getLength()) {
System.out.println("插入的位置不合法。");
return;
}
int count = 1;//记录位置
temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
if (index == count++) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
return;
}
//移动节点位置
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//显示链表[遍历]
public void show() {
if(head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
System.out.print("{" + temp.next.data + "}");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkListDemo list = new LinkListDemo();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
list.add(4);
list.add(5);
list.deleteByIndex(3);
list.show();
System.out.println(list.getLength());
}
4)单链表的常见面试题有如下:
1)求单链表中有效节点的个数
2)查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点 【新浪面试题】
3)单链表的反转【腾讯面试题,有点难度】
4)从尾到头打印单链表 【百度,要求方式1:反向遍历 。 方式2:Stack栈】
5)合并两个有序的单链表,合并之后的链表依然有序
/**
*获取到单链表的节点的个数(如果是带头结点的链表,需求不统计头节点)
* @param head 链表的头节点
* @return 返回的就是有效节点的个数
*/
public static int count(Node head){
if(head.next == null) { //空链表
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
//定义一个辅助的变量, 这里我们没有统计头节点
Node temp = head.next;
while (temp!=null){
count++;
temp = temp.next;
}
return count;
}
System.out.println("有效的节点个数=" +list.count(list.getHead()));
/**
* 查找单链表中的倒数第k个结点 【新浪面试题】
* 思路
* 1. 编写一个方法,接收head节点,同时接收一个index
* 2. k表示是倒数第k个节点
* 3. 先把链表从头到尾遍历,得到链表的总的长度 getLength
* 4. 得到size 后,我们从链表的第一个开始遍历 (size-k)个,就可以得到
* 5. 如果找到了,则返回该节点,否则返回nulll
* @return
*/
public static Node findLastIndexNode(Node head,int k){
//判断如果链表为空,返回null
if(head.next == null) {
return null;
}
//第一个遍历得到链表的长度(节点个数)
int size = count(head);
//先做一个index的校验
if(k <=0 || k > size) {
return null;
}
//定义给辅助变量, for 循环定位到倒数的k
Node temp = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i <(size-k) ; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
System.out.println("倒数第K个节点"+ list.findLastIndexNode(list.getHead(), 3));
//可以利用栈这个数据结构,将各个节点压入到栈中,然后利用栈的先进后出的特点,
// 就实现了逆序打印的效果
public static void reversePrint(Node head) {
if(head.next == null) {
return;//空链表,不能打印
}
//创建要给一个栈,将各个节点压入栈
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>();
Node cur = head.next;
//将链表的所有节点压入栈
while(cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next; //cur后移,这样就可以压入下一个节点
}
//将栈中的节点进行打印,pop 出栈
while (stack.size() > 0) {
System.out.println(stack.pop()); //stack的特点是先进后出
}
}





















 4916
4916

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








