5.属性选择器
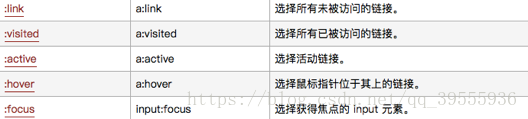

1)^表示以val开头,att表示属性[比如title,class之类的]
2)$表示以val结尾的
3) *表示含有val字符串的
例如;
a[class^="column"]{
background:red;
}
a[href$="doc"]{
background:green;
}
a[title*="box"]{
background:blue;
}
6.root伪类选择器
:root选择器相当于对html修改
即:
“:root”选择器等同于<html>元素,简单点说:
:root{background:orange}
html {background:orange;}
7.not伪类选择器
选择除某个元素外其余的元素
格式:某元素节点:not([其属性节点=“xx”])
就form而言,想给除submit以外的input元素加上红色,css可以写成
form {
width: 200px;
margin: 20px auto;
}
div {
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
input:not([type="submit"]){
border:1px solid red;
}
在例如:
除页脚”div#footer”之外的所有div设置橙色背景色。
div:not([id="footer"]){
background: orange;
}
原html代码:
<div id="header">页头</div>
<div id="page">页体</div>
<div id="footer">页脚</div>
8.伪类选择器:empty
用来选择没有内容的元素,这里指一个内容都没有,哪怕是一个空格
例如:你的文档中有三个段落p元素,你想把没有任何内容的P元素隐藏起来。我们就可以使用“:empty”选择器来控制。
HTML代码:
<p>我是一个段落</p>
<p> </p>
<p></p>
CSS代码:
p{
background: orange;
min-height: 30px;
}
p:empty {
display: none;
}
9.伪类选择器:target
成为目标选择器,用来匹配文档(页面)的url的某个标志符
例如:
HTML代码:
<h2><a href="#brand">Brand</a></h2>
<div class="menuSection" id="brand">
content for Brand
</div>
CSS代码:
.menuSection{
display: none;
}
:target{/*这里的:target就是指id="brand"的div对象*/
display:block;
}
再例如:
<h2><a href="#brand">Brand</a></h2>
<div class="menuSection" id="brand">
content for Brand
</div>
<h2><a href="#jake">Brand</a></h2>
<div class="menuSection" id="jake">
content for jake
</div>
<h2><a href="#aron">Brand</a></h2>
<div class="menuSection" id="aron">
content for aron
</div>
css代码:
#brand:target {
background: orange;
color: #fff;
}
#jake:target {
background: blue;
color: #fff;
}
#aron:target {
background: red;
color: #fff;
}
#brand与后面的id="brand"是对应的,当同一个页面上有很多的url的时候你可以取不同的名字,只要#号后对的名称与id=""中的名称对应就可以了。
可以用来表示点击链接后的变化
即:点击a标签的href对应容器的id名称相同,可使对应容器发生变化
例如:点之前

点brand之后

上例的html:
<div class="menuSection" id="brand">
<h2><a href="#brand">Brand</a></h2>
<p>content for Brand</p>
</div>
css:
#brand:target p {
background: orange;
color: #fff;
}
10伪类选择器--:first-child
表示选择父元素的第一个子元素(其实就是选择元素的第一个子元素而不是后代元素)
例如:
html
<ol>
<li><a href="##">Link1</a></li>
<li><a href="##">Link2</a></li>
<li><a href="##">link3</a></li>
</ol>
css
ol > li{
font-size:20px;
font-weight: bold;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}(表示只能是li直接子元素不能是a孙元素)
ol a {
font-size: 16px;
font-weight: normal;
}(表示可以是孙元素)
ol > li:first-child{
color: red;
}
11伪类选择器--last-child
与first-child类似,不同的是 这是指元素的最后一个子元素
12伪类选择器--nth-child(n)
定位父元素的一个或多个子元素,参数从1开始数
其中的n可以是
1)整数1,2,3,4
2)表达式2n+1,5-n
3)关键字odd,even
但是当n是一个表达式时,从0开始计算,当表达式为0或者小于0不选择任何一个元素
13伪类选择器—nth-last-child(n)
类似于上一个nth-child(n)但是这个是从后面开始计算
14.fist-of-type选择器
类似于first-child选择器,不同的是指定了元素类型,定位父元素某个类型的第一个子元素
例如:
.wrapper > div:first-of-type {
background: orange;
}
其中div不一定是父元素的第一个子元素
15.last-of-type选择器
与first-of-type相似
只是选择父元素下的最后一个指定元素类型的子元素
16.nth-of-type(n)选择器
与nth-child(n)类似,只是指定了元素类型
17.nth-last-of-type(n)选择器
类似于nth-of-type(n),只是从最后一个元素开始数起
18.only-child选择器
选择父元素只有一个子元素,而且是唯一一个子元素
19.only-of-type选择器
表示一个元素有很多子元素,只有一种类型的子元素是唯一的,only-of-type可以选中这个唯一一个类型的子元素
例如:
<div class="wrapper">
<p>我是一个段落</p>
<p>我是一个段落</p>
<p>我是一个段落</p>
</div>
<div class="wrapper">
<p>我是一个段落</p>
</div>
<div class="wrapper">
<div>我是一个Div元素</div>
<p>我是一个段落</p>
<div>我是一个Div元素</div>
</div>
.wrapper p:only-of-type{
background: orange;
}
表示


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








