所需要的技能
如何将shadertoy上的shader移植到本地OpenGL相信是很多学习OpenGL的同学迈向中高级的一道门槛,这篇教程将会一步步带你使用VSCode和CMake构建代码,使用OpenGL移植iq大神的心型shader到本地OpenGL
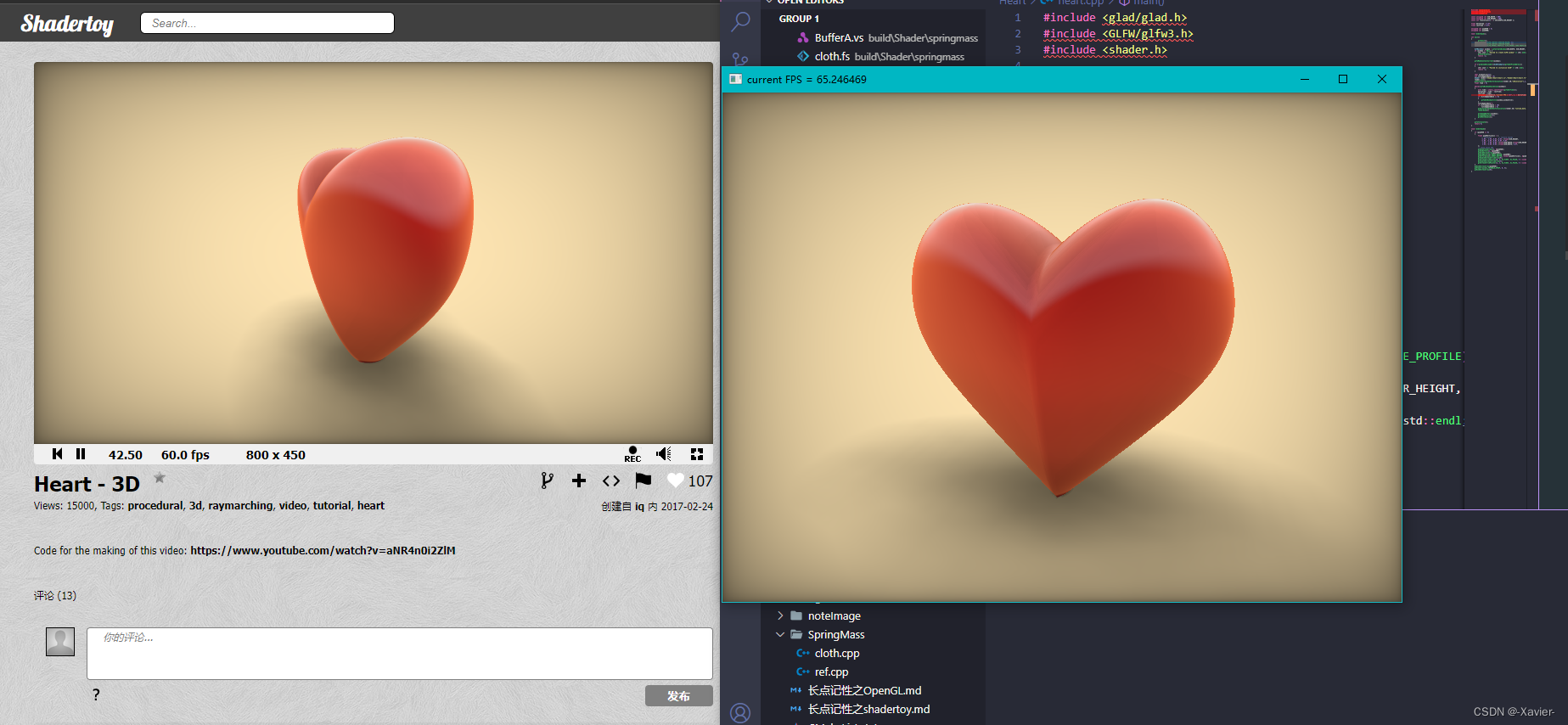
先看下运行效果:
在正式展开这门教程前我需要你有以下基础
基本的OpenGL的使用经验,包括最基本的shader编译和数据传递,最经典的OpenGL教程:https://learnopengl.com/
基本的使用VSCode编写C/C++代码的经验
基本的CMake使用经验以及编译/链接的概念,官方教程:CMake Tutorial — CMake 3.27.0 Documentation
为了使用VSCode有良好的编码体验,我建议首先配置VSCode的C/C++环境,可以参考我安装的插件来配置你的环境,必须要有的插件为C/C++,CMake,GLSL Lint
目录结构
首先配置OpenGL相关库:
需要的组件有glew,glfw,glad,如果你学过LearnOpenGL系列教程,你一定对这些库不陌生
来看看文件结构:
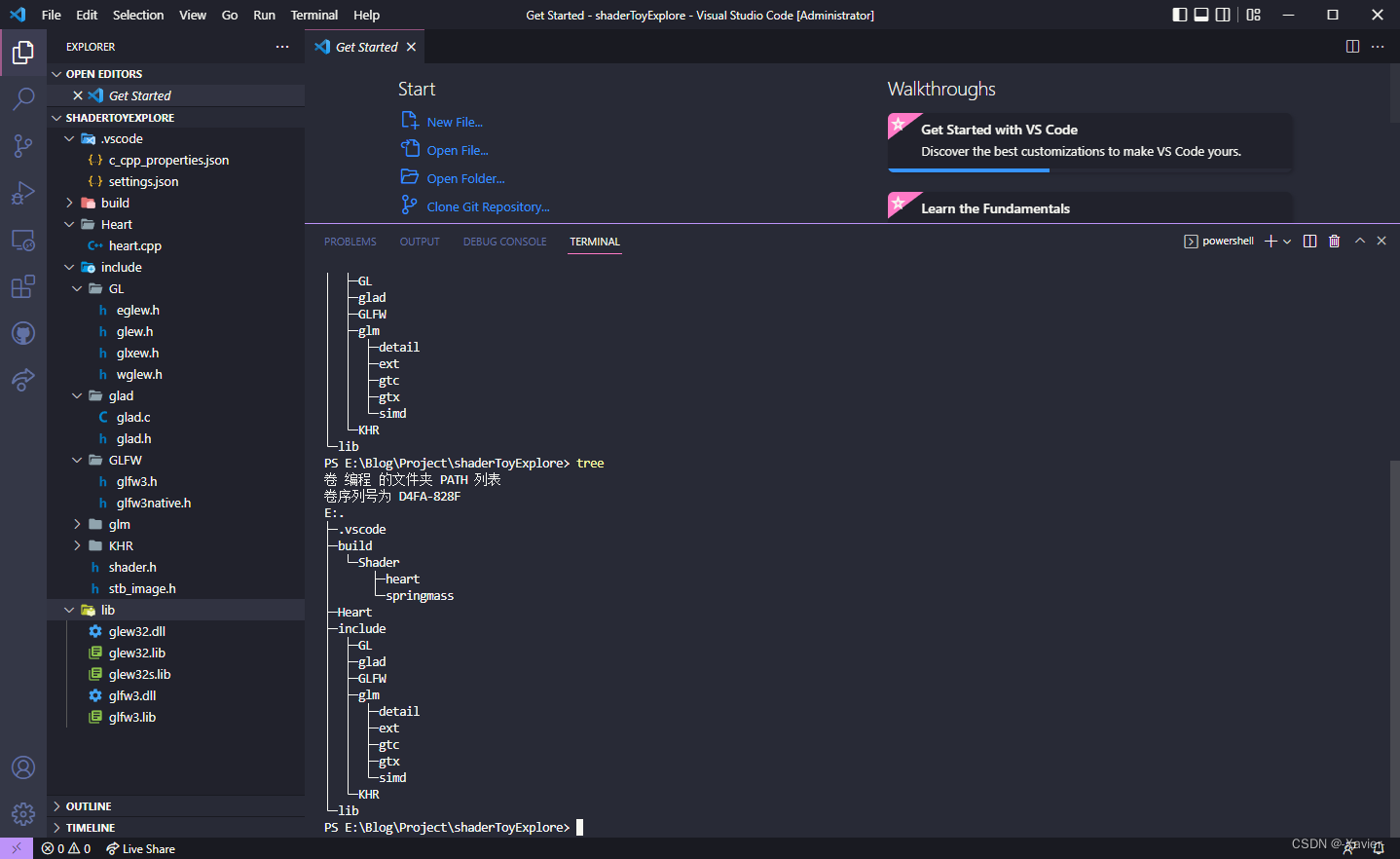
include文件夹用来存放相关的头文件,Lib用来存放需要链接的动态及静态库,Heart文件夹我们用来存放cpp源文件,build文件夹则是CMake用来构建目录的文件夹。
shader.h实际就是LearnOpenGL作者为Shader封装的头文件
#ifndef SHADER_H
#define SHADER_H
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
class Shader
{
public:
unsigned int ID;
// constructor generates the shader on the fly
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
Shader(const char* vertexPath, const char* fragmentPath, const char* geometryPath = nullptr)
{
// 1. retrieve the vertex/fragment source code from filePath
std::string vertexCode;
std::string fragmentCode;
std::string geometryCode;
std::ifstream vShaderFile;
std::ifstream fShaderFile;
std::ifstream gShaderFile;
// ensure ifstream objects can throw exceptions:
vShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
fShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
gShaderFile.exceptions (std::ifstream::failbit | std::ifstream::badbit);
try
{
// open files
vShaderFile.open(vertexPath);
fShaderFile.open(fragmentPath);
std::stringstream vShaderStream, fShaderStream;
// read file's buffer contents into streams
vShaderStream << vShaderFile.rdbuf();
fShaderStream << fShaderFile.rdbuf();
// close file handlers
vShaderFile.close();
fShaderFile.close();
// convert stream into string
vertexCode = vShaderStream.str();
fragmentCode = fShaderStream.str();
// if geometry shader path is present, also load a geometry shader
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
{
gShaderFile.open(geometryPath);
std::stringstream gShaderStream;
gShaderStream << gShaderFile.rdbuf();
gShaderFile.close();
geometryCode = gShaderStream.str();
}
}
catch (std::ifstream::failure& e)
{
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FILE_NOT_SUCCESSFULLY_READ: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
const char* vShaderCode = vertexCode.c_str();
const char * fShaderCode = fragmentCode.c_str();
// 2. compile shaders
unsigned int vertex, fragment;
// vertex shader
vertex = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertex, 1, &vShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertex);
checkCompileErrors(vertex, "VERTEX");
// fragment Shader
fragment = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragment, 1, &fShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragment);
checkCompileErrors(fragment, "FRAGMENT");
// if geometry shader is given, compile geometry shader
unsigned int geometry;
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
{
const char * gShaderCode = geometryCode.c_str();
geometry = glCreateShader(GL_GEOMETRY_SHADER);
glShaderSource(geometry, 1, &gShaderCode, NULL);
glCompileShader(geometry);
checkCompileErrors(geometry, "GEOMETRY");
}
// shader Program
ID = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(ID, vertex);
glAttachShader(ID, fragment);
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
glAttachShader(ID, geometry);
glLinkProgram(ID);
checkCompileErrors(ID, "PROGRAM");
// delete the shaders as they're linked into our program now and no longer necessary
glDeleteShader(vertex);
glDeleteShader(fragment);
if(geometryPath != nullptr)
glDeleteShader(geometry);
}
// activate the shader
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void use()
{
glUseProgram(ID);
}
// utility uniform functions
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setBool(const std::string &name, bool value) const
{
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), (int)value);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setInt(const std::string &name, int value) const
{
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), value);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setFloat(const std::string &name, float value) const
{
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), value);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setVec2(const std::string &name, const glm::vec2 &value) const
{
glUniform2fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, &value[0]);
}
void setVec2(const std::string &name, float x, float y) const
{
glUniform2f(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), x, y);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setVec3(const std::string &name, const glm::vec3 &value) const
{
glUniform3fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, &value[0]);
}
void setVec3(const std::string &name, float x, float y, float z) const
{
glUniform3f(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), x, y, z);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setVec4(const std::string &name, const glm::vec4 &value) const
{
glUniform4fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, &value[0]);
}
void setVec4(const std::string &name, float x, float y, float z, float w)
{
glUniform4f(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), x, y, z, w);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setMat2(const std::string &name, const glm::mat2 &mat) const
{
glUniformMatrix2fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, GL_FALSE, &mat[0][0]);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setMat3(const std::string &name, const glm::mat3 &mat) const
{
glUniformMatrix3fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, GL_FALSE, &mat[0][0]);
}
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void setMat4(const std::string &name, const glm::mat4 &mat) const
{
glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(ID, name.c_str()), 1, GL_FALSE, &mat[0][0]);
}
private:
// utility function for checking shader compilation/linking errors.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
void checkCompileErrors(GLuint shader, std::string type)
{
GLint success;
GLchar infoLog[1024];
if(type != "PROGRAM")
{
glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(shader, 1024, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER_COMPILATION_ERROR of type: " << type << "\n" << infoLog << "\n -- --------------------------------------------------- -- " << std::endl;
}
}
else
{
glGetProgramiv(shader, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if(!success)
{
glGetProgramInfoLog(shader, 1024, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::PROGRAM_LINKING_ERROR of type: " << type << "\n" << infoLog << "\n -- --------------------------------------------------- -- " << std::endl;
}
}
}
};
#endif将VSCode的配置文件c_cpp_properties.json修改为
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}/**",
"${workspaceFolder}/include",
//参考你自己本机的Windows SDK头文件路径
"C:/Program Files (x86)/Microsoft Visual Studio/2019/Enterprise/VC/Tools/MSVC/14.28.29333/include"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE"
],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.19041.0",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "windows-msvc-x64"
}
],
"version": 4
}将settings.json修改为:
{
"files.associations": {
"fstream": "cpp",
"iostream": "cpp"
},
"clang.cflags": [
"-I${workspaceRoot}/dev"
],
"C_Cpp.errorSquiggles": "enabled"
}我们在工作目录下创建CMakeLists.txt用于编译
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)
project(HEART VERSION 1.0)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 17)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED True)
link_directories(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)//链接阶段寻找库的目录
add_executable(HEART Heart/heart.cpp include/glad/glad.c)
target_include_directories(HEART PUBLIC
"${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include")//指定编译头文件目录
target_link_libraries(HEART glew32.lib glfw3.lib OpenGL32.Lib)//指定链接相关的OpenGL库名称由于Windows的系统环境自带OpenGL32.lib,所以我没有将OpenGL32.lib放在lib目录下,其他平台情况可能有所不同,按照自己的情况进行配置
Dive into code
iq大神的3D心型shader地址在这里:Shader - Shadertoy BETA
我们其实只要控制好cpp文件和Shader的变量传输就可以实现移植shadertoy上的着色器到本地OpenGL
shadertoy内置的输入变量有这些:

由于编译在build目录下进行我们需要把Shader放在build目录下
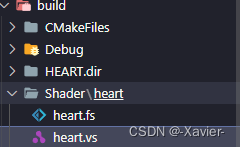
在Shader文件夹下创建heart文件夹,再创建heart.vs作为顶点着色器输入,heart.fs作为片段着色器输入
仔细观察这两个shader,发现iq大神只用了两个shadertoy内置的uniform输入变量,分别为iTime和iResolution,他们分别代表程序运行的时间和程序的像素大小,我们只需要在自己的shader中加入这两个变量并且在源文件中传递这两个变量的值给着色器就可以,当然fragCoord作为mainImage的输入只需要在顶点着色器中传递给片段着色器
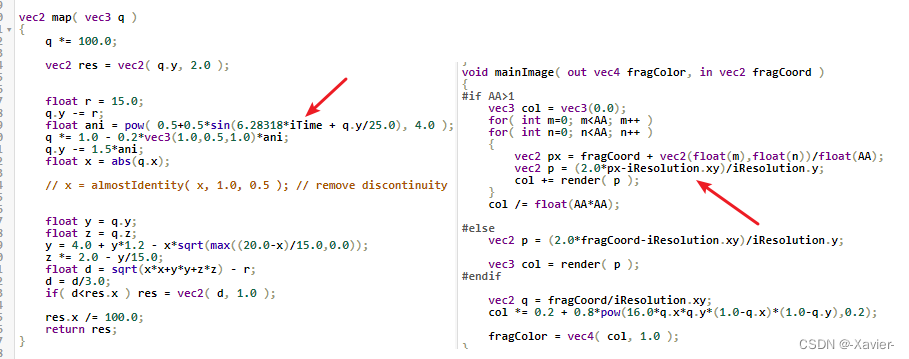
直接上代码:
heart.vs
#version 450 core
layout(location = 0) in vec3 position;
layout(location = 1) in vec2 texlCoord;
out vec2 fragCoord;
void main()
{
fragCoord = texlCoord;
gl_Position = vec4(position,1.0);
}heart.fs
#version 450 core
#if HW_PERFORMANCE==0
#define AA 1
#else
#define AA 2
#endif
out vec4 fragColor;
in vec2 fragCoord;
struct runtime_param
{
//对于其他的shader,这里还可以添加更多的ShaderToy内置Uniform变量
float iTime;
};
uniform runtime_param runtime_data;
uniform ivec2 iResolution;
float hash1(float n)
{
return fract(sin(n) * 43758.5453123);
}
const float PI = 3.1415926535897932384626433832795;
const float PHI = 1.6180339887498948482045868343656;
vec3 forwardSF( float i, float n)
{
float phi = 2.0*PI*fract(i/PHI);
float zi = 1.0 - (2.0*i+1.0)/n;
float sinTheta = sqrt( 1.0 - zi*zi);
return vec3( cos(phi)*sinTheta, sin(phi)*sinTheta, zi);
}
float almostIdentity(float x,float m,float n)
{
if(x>m) return x;
float a = 2.0*n - m;
float b = 2.0*m -3.0*n;
float t = x/m;
return (a*t + b)*t*t + n;
}
#define iTime runtime_data.iTime
vec2 map(vec3 q)
{
q *= 100.0;
vec2 res = vec2(q.y,2.0);
float r = 15.0;
q.y -= r;
float ani = pow(0.5 + 0.5*sin(6.283128*iTime + q.y/25.0),4.0);
q.y -= 1.5*ani;
float x = abs(q.x);
float y = q.y;
float z = q.z;
y = 4.0+y*1.2 - x*sqrt(max((20.0-x)/15.0,0.0));
z *= 2.0 - y/15.0;
float d = sqrt(x*x+y*y+z*z)-r;
d = d/3.0;
if(d<res.x) res = vec2(d,1.0);
res.x /= 100.0;
return res;
}
vec2 intersect(in vec3 ro,in vec3 rd)
{
const float maxd = 1.0;
vec2 res = vec2(0.0);
float t = 0.2;
for(int i=0;i<300;i++)
{
vec2 h = map(ro+rd*t);
if((h.x < 0.0) || (t>maxd)) break;
t+=h.x;
res = vec2(t,h.y);
}
if(t>maxd) res = vec2(-1.0);
return res;
}
vec3 calcNormal(in vec3 pos)
{
vec3 eps = vec3(0.005,0.0,0.0);
return normalize(vec3(
map(pos+eps.xyy).x - map(pos-eps.xyy).x,
map(pos+eps.yxy).x - map(pos-eps.yxy).x,
map(pos+eps.yyx).x - map(pos-eps.yyx).x
));
}
float calcAO( in vec3 pos, in vec3 nor )
{
float ao = 0.0;
for( int i=0; i<64; i++ )
{
vec3 kk;
vec3 ap = forwardSF( float(i), 64.0 );
ap *= sign( dot(ap,nor) ) * hash1(float(i));
ao += clamp( map( pos + nor*0.01 + ap*0.2 ).x*20.0, 0.0, 1.0 );
}
ao /= 64.0;
return clamp( ao, 0.0, 1.0 );
}
vec3 render(in vec2 p)
{
//-------------------------------------
//camera
//-------------------------------------
float an = 1.0*iTime;
vec3 ro = vec3(0.4*sin(an),0.25,0.4*cos(an));
vec3 ta = vec3(0.0,0.15,0.0);
//camera matrix
vec3 ww = normalize(ta-ro);
vec3 uu = normalize(cross(ww,vec3(0.0,1.0,0.0)));
vec3 vv = normalize(cross(uu,ww));
//create view ray
vec3 rd = normalize(p.x*uu + p.y*vv + 1.7*ww);
//--------------------------------------
//render
//--------------------------------------
vec3 col = vec3(1.0,0.9,0.7);
//raymarch
vec3 uvw;
vec2 res = intersect(ro,rd);
float t = res.x;
if( t>0.0 )
{
vec3 pos = ro + t*rd;
vec3 nor = calcNormal(pos);
vec3 ref = reflect( rd, nor );
float fre = clamp( 1.0 + dot(nor,rd), 0.0, 1.0 );
float occ = calcAO( pos, nor ); occ = occ*occ;
if( res.y<1.5 ) // heart
{
col = vec3(0.9,0.02,0.01);
col = col*0.72 + 0.2*fre*vec3(1.0,0.8,0.2);
vec3 lin = 4.0*vec3(0.7,0.80,1.00)*(0.5+0.5*nor.y)*occ;
lin += 0.8*fre*vec3(1.0,1.0,1.00)*(0.6+0.4*occ);
col = col * lin;
col += 4.0*vec3(0.8,0.9,1.00)*smoothstep(0.0,0.4,ref.y)*(0.06+0.94*pow(fre,5.0))*occ;
col = pow(col,vec3(0.4545));
}
else // ground
{
col *= clamp(sqrt(occ*1.8),0.0,1.0);
}
}
col = clamp(col,0.0,1.0);
return col;
}
void main()
{
#if AA>1
vec3 col = vec3(0.0);
for( int m=0; m<AA; m++ )
for( int n=0; n<AA; n++ )
{
vec2 px = fragCoord + vec2(float(m),float(n))/float(AA);
vec2 p = (2.0*px-iResolution.xy)/iResolution.y;
col += render( p );
}
col /= float(AA*AA);
#else
vec2 p = (2.0*fragCoord-iResolution.xy)/iResolution.y;
vec3 col = render( p );
#endif
vec2 q = fragCoord/iResolution.xy;
col *= 0.2 + 0.8*pow(16.0*q.x*q.y*(1.0-q.x)*(1.0-q.y),0.2);
fragColor = vec4( col, 1.0 );
}源文件也非常简单,只需要在进入渲染循环前将固定的画布像素宽高iResolution提交给shader,并在进入渲染循环后每一个渲染阶段提交iTime给shader
heart.cpp:
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <shader.h>
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
const int resolution[2] = { SCR_WIDTH,SCR_HEIGHT };
float deltaTime = 0.0f;
float lastTime = 0.0f;
unsigned int quadVAO = 0;
unsigned int quadVBO;
void renderQuad();
int main()
{
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 2);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL) {
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
char windowTile[32];
int titleUpdateRate = 0;
Shader render("Shader/Heart/heart.vs","Shader/Heart/heart.fs");
render.use();
glUniform2iv(glGetUniformLocation(render.ID,"iResolution"),1,&resolution[0]);
float Time = 0;
while(!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
auto time = static_cast<float>(glfwGetTime());
deltaTime = time - lastTime;
lastTime = time;
sprintf_s(windowTile,"current FPS = %2f", 1. / deltaTime);
if (titleUpdateRate == 0)
{
glfwSetWindowTitle(window,windowTile);
}
titleUpdateRate++;
if (titleUpdateRate > 10)
titleUpdateRate = 0;
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(render.ID,"runtime_data.iTime"),time);
renderQuad();
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwSwapInterval(1);
glfwPollEvents();
}
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
void renderQuad()
{
if (quadVAO == 0)
{
float quadVertices[] = {
// positions // texture Coords
-1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_HEIGHT,
-1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_WIDTH,(float)SCR_HEIGHT,
1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_WIDTH, 0.0f,
};
// setup plane VAO
glGenVertexArrays(1, &quadVAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &quadVBO);
glBindVertexArray(quadVAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, quadVBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(quadVertices), &quadVertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 5 * sizeof(float), (void*)(3 * sizeof(float)));
}
glBindVertexArray(quadVAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, 4);
glBindVertexArray(0);
}值得注意的是shadertoy的fragCoord并非像OpenGL一样标准化到[0,1],而是画布实际的像素位置,因此在shadertoy中常用fragCoord.xy / iResolution.xy来表示纹理的归一化坐标
我们在源文件中提交时的纹理坐标应保持和Shadertoy的意义一致
float quadVertices[] = {
// positions // texture Coords
-1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_HEIGHT,
-1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f,
1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_WIDTH,(float)SCR_HEIGHT,
1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, (float)SCR_WIDTH, 0.0f,
};最后 打开VSCode 的Terminal(请确保cmake已添加到环境变量):
cd build
cmake ..
cmake --build .
.\Debug\HEART.exe把这款编译好的3D心型shader打包发送给你的女朋友,让她感受一下数学的浪漫吧~










 教程详细介绍了如何使用VSCode和CMake将Shadertoy上的Shader移植到本地OpenGL环境,包括设置基础环境、配置项目结构、编译链接库,以及处理Shader的输入输出变量。读者需要具备基本的OpenGL、VSCode和CMake知识。
教程详细介绍了如何使用VSCode和CMake将Shadertoy上的Shader移植到本地OpenGL环境,包括设置基础环境、配置项目结构、编译链接库,以及处理Shader的输入输出变量。读者需要具备基本的OpenGL、VSCode和CMake知识。
















 609
609

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








