一、引用类型
Java通过引用来访问对象,从jdk1.2开始,Java将引用分为以下4种类型,强度依次减弱。
(1)强引用 Strong Reference
日常开发中最经常使用的引用类型,例如Object object = new Object()使用的就是强引用。当一个对象的强引用存在,这个对象用于不会被回收。在Java中没有专门的类与之对应。
(2)软引用 Soft Reference
软引用用来表示有用但不必须的对象。对于一个只有软引用关联着的对象,在内存充足的情况下不会回收,但是内存不充足的情况下会进行回收。SoftReference类用来表示软引用。
(3)弱引用 Weak Reference
弱引用用来表示不必须的对象。对于一个只有弱引用关联的对象,只能生存到下一次垃圾收集之前。WeakReference类用来表示弱引用。WeakReference类用来表示弱引用。
(4)虚引用 Phantom Reference
虚引用不会对对象的生命周期造成任何影响,也无法通过虚引用来获取对象。虚引用的作用是在对象被垃圾收集器收集时得到一个系统通知。PhantomReference类用来表示虚引用。
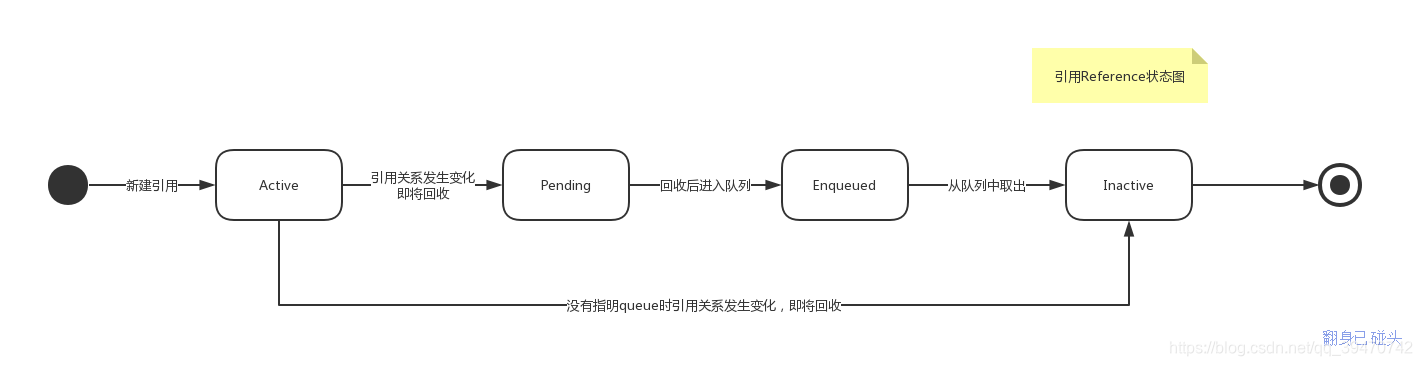
二、引用状态
引用共有4个状态:
(1)Active:起始状态,引用生成时的状态。
(2)Pending:侦测到引用可达性发生变化一段时间后,即将进行回收。
(3)Enqueued:已经加入到引用队列中,对象内存已经回收。
(4)Inactive:终态,引用从队列中取出,不会再变成其它状态。如果引用初始化时没有使用引用队列,那么侦测到引用可达性发生变化一段时间后,状态直接由Active到Inactive。
举一个简单示例:

两条输出语句的输出结果都是true。
三、Reference
Reference表示引用
1. 属性
//引用指向的对象
private T referent; /* Treated specially by GC */
//引用关联的队列,引用被回收时会加入队列
volatile ReferenceQueue<? super T> queue;
/* When active: NULL
* pending: this
* Enqueued: next reference in queue (or this if last)
* Inactive: this
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
//引用队列中下一个将被处理的节点,只有Enqueued状态时引用被加入队列才有意义
volatile Reference next;
/* When active: next element in a discovered reference list maintained by GC (or this if last)
* pending: next element in the pending list (or null if last)
* otherwise: NULL
*/
//pending列表的下一个节点,pending状态时才有意义
transient private Reference<T> discovered; /* used by VM */
/* Object used to synchronize with the garbage collector. The collector
* must acquire this lock at the beginning of each collection cycle. It is
* therefore critical that any code holding this lock complete as quickly
* as possible, allocate no new objects, and avoid calling user code.
*/
//用于synchronized锁
static private class Lock { }
private static Lock lock = new Lock();
/* List of References waiting to be enqueued. The collector adds
* References to this list, while the Reference-handler thread removes
* them. This list is protected by the above lock object. The
* list uses the discovered field to link its elements.
*/
//静态变量,pending状态的列表的当前节点
private static Reference<Object> pending = null;
可以看到,Reference有有两个链表式结构的属性。
(1)引用队列:内部的元素为Enqueued状态,通过this.next属性访问下一个引用。成员变量,因此每个引用的引用队列可以不一样。
(2)pending列表:由所有Pending状态的引用组成的列表,通过pending.discovered访问下一个引用。静态成员变量,因此每个引用的pending列表一样。
2. 静态代码块
在Refenece类中有一块静态代码块
static {
ThreadGroup tg = Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup();
for (ThreadGroup tgn = tg;
tgn != null;
tg = tgn, tgn = tg.getParent());
Thread handler = new ReferenceHandler(tg, "Reference Handler");
/* If there were a special system-only priority greater than
* MAX_PRIORITY, it would be used here
*/
handler.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
handler.setDaemon(true);
handler.start();
// provide access in SharedSecrets
SharedSecrets.setJavaLangRefAccess(new JavaLangRefAccess() {
@Override
public boolean tryHandlePendingReference() {
return tryHandlePending(false);
}
});
}
在当前线程组的最顶级的父线程组中建立一个最大优先级的后台线程ReferenceHandler,并启动。
3. ReferenceHandler
private static void ensureClassInitialized(Class<?> clazz) {
try {
Class.forName(clazz.getName(), true, clazz.getClassLoader());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw (Error) new NoClassDefFoundError(e.getMessage()).initCause(e);
}
}
static {
// pre-load and initialize InterruptedException and Cleaner classes
// so that we don't get into trouble later in the run loop if there's
// memory shortage while loading/initializing them lazily.
ensureClassInitialized(InterruptedException.class);
ensureClassInitialized(Cleaner.class);
}
ReferenceHandler(ThreadGroup g, String name) {
super(g, name);
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
tryHandlePending(true);
}
}
run方法是一个死循环,无限执行tryHandlePending方法
4. Reference#tryHandlePending(boolean)
static boolean tryHandlePending(boolean waitForNotify) {
Reference<Object> r;
Cleaner c;
try {
synchronized (lock) {
if (pending != null) {
r = pending;
// 'instanceof' might throw OutOfMemoryError sometimes
// so do this before un-linking 'r' from the 'pending' chain...
c = r instanceof Cleaner ? (Cleaner) r : null;
// unlink 'r' from 'pending' chain
pending = r.discovered;
r.discovered = null;
} else {
// The waiting on the lock may cause an OutOfMemoryError
// because it may try to allocate exception objects.
if (waitForNotify) {
lock.wait();
}
// retry if waited
return waitForNotify;
}
}
} catch (OutOfMemoryError x) {
// Give other threads CPU time so they hopefully drop some live references
// and GC reclaims some space.
// Also prevent CPU intensive spinning in case 'r instanceof Cleaner' above
// persistently throws OOME for some time...
Thread.yield();
// retry
return true;
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
// retry
return true;
}
// Fast path for cleaners
if (c != null) {
c.clean();
return true;
}
ReferenceQueue<? super Object> q = r.queue;
if (q != ReferenceQueue.NULL) q.enqueue(r);
return true;
}
(1)将pending从pengding列表移除,pengding.discovered作为列表的头结点
(2)使用了引用队列的情况下,pending加入引用队列
JVM会给pengding和discovered进行赋值,所以方法中检查pengding是否为null,null时进行等待。
同时,为了保证线程安全,同时只能有1个对象在执行该方法,所以对静态变量lock加锁。
四、ReferenceQueue
ReferenceQueue表示引用队列
1. 属性
//NULL队列
static ReferenceQueue<Object> NULL = new Null<>();
//表示节点已经加入队列,此时节点的queue属性为ENQUEUED
static ReferenceQueue<Object> ENQUEUED = new Null<>();
//sychronized锁对象
static private class Lock { };
private Lock lock = new Lock();
//头结点
private volatile Reference<? extends T> head = null;
//队列长度
private long queueLength = 0;
2. ReferenceQueue#enqueue(Reference)
加入新节点
boolean enqueue(Reference<? extends T> r) { /* Called only by Reference class */
synchronized (lock) {
// Check that since getting the lock this reference hasn't already been
// enqueued (and even then removed)
ReferenceQueue<?> queue = r.queue;
//校验
if ((queue == NULL) || (queue == ENQUEUED)) {
return false;
}
assert queue == this;
//加入队列后,引用的queue属性采用ENQUEUED表示
r.queue = ENQUEUED;
//尾节点的next执行自身而不是null
r.next = (head == null) ? r : head;
head = r;
queueLength++;
if (r instanceof FinalReference) {
sun.misc.VM.addFinalRefCount(1);
}
lock.notifyAll();
return true;
}
}
3. ReferenceQueue#poll()
获取并移除头结点,非阻塞
public Reference<? extends T> poll() {
if (head == null)
return null;
//移除头结点需要加锁
synchronized (lock) {
return reallyPoll();
}
}
private Reference<? extends T> reallyPoll() { /* Must hold lock */
Reference<? extends T> r = head;
if (r != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Reference<? extends T> rn = r.next;
//是否是尾节点的处理
head = (rn == r) ? null : rn;
//引用从队列移除后,quque属性采用NULL
r.queue = NULL;
r.next = r;
queueLength--;
if (r instanceof FinalReference) {
sun.misc.VM.addFinalRefCount(-1);
}
return r;
}
return null;
}
结合enqueue和poll方法可以看到,ReferenceQueue虽然叫引用队列,实际上是后进先出的。
4. ReferenceQueue#remove
获取并移除头结点,阻塞,两个同名的重载方法
public Reference<? extends T> remove() throws InterruptedException {
return remove(0);
}
public Reference<? extends T> remove(long timeout)
throws IllegalArgumentException, InterruptedException
{
if (timeout < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative timeout value");
}
synchronized (lock) {
Reference<? extends T> r = reallyPoll();
if (r != null) return r;
long start = (timeout == 0) ? 0 : System.nanoTime();
for (;;) {
lock.wait(timeout);
r = reallyPoll();
if (r != null) return r;
if (timeout != 0) {
long end = System.nanoTime();
timeout -= (end - start) / 1000_000;
if (timeout <= 0) return null;
start = end;
}
}
}
}
与poll方法类似,只是在队列中没有节点时阻塞等待








 本文详细介绍了Java中的四种引用类型:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用,以及引用的状态变化。重点讲解了Reference类的属性、静态代码块、ReferenceHandler和tryHandlePending方法,以及ReferenceQueue的属性、enqueue、poll和remove方法,揭示了引用队列的工作原理。
本文详细介绍了Java中的四种引用类型:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用,以及引用的状态变化。重点讲解了Reference类的属性、静态代码块、ReferenceHandler和tryHandlePending方法,以及ReferenceQueue的属性、enqueue、poll和remove方法,揭示了引用队列的工作原理。
















 513
513

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








