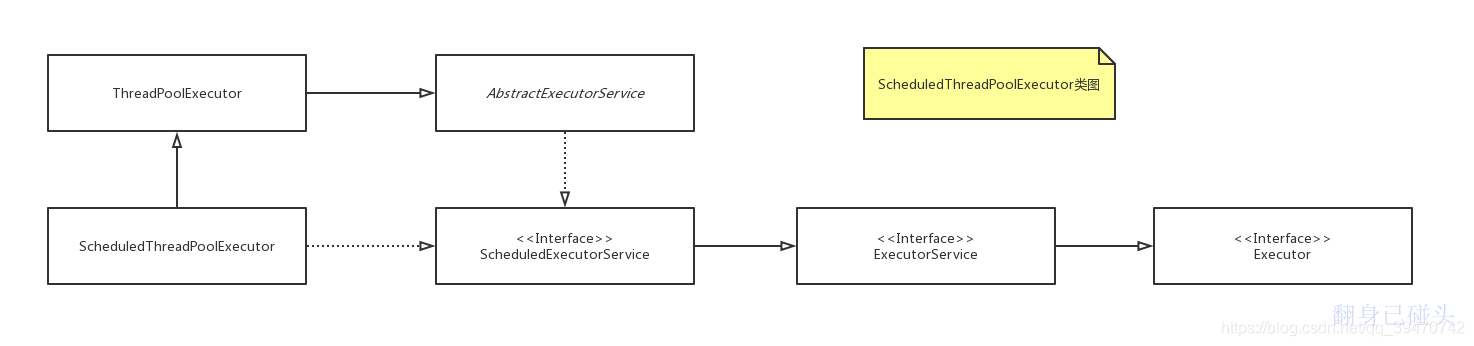
一、简介
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor是ThreadPoolExecutor的子类,继承了父类对线程的管理维护功能,通过还可以执行延迟和定时任务。
/*
* This class specializes ThreadPoolExecutor implementation by
*
* 1. Using a custom task type, ScheduledFutureTask for
* tasks, even those that don't require scheduling (i.e.,
* those submitted using ExecutorService execute, not
* ScheduledExecutorService methods) which are treated as
* delayed tasks with a delay of zero.
*
* 2. Using a custom queue (DelayedWorkQueue), a variant of
* unbounded DelayQueue. The lack of capacity constraint and
* the fact that corePoolSize and maximumPoolSize are
* effectively identical simplifies some execution mechanics
* (see delayedExecute) compared to ThreadPoolExecutor.
*
* 3. Supporting optional run-after-shutdown parameters, which
* leads to overrides of shutdown methods to remove and cancel
* tasks that should NOT be run after shutdown, as well as
* different recheck logic when task (re)submission overlaps
* with a shutdown.
*
* 4. Task decoration methods to allow interception and
* instrumentation, which are needed because subclasses cannot
* otherwise override submit methods to get this effect. These
* don't have any impact on pool control logic though.
*/
根据注释,也可以了解其相对于ThreadPoolExecutor 的变化:
- 使用内部类ScheduledFutureTask封装任务
- 使用内部类DelayedWorkQueue作为线程池队列
- onShutdown方法基于参数配置化去处理shutdown后的任务
- 提供decorateTask方法作为ScheduledFutureTask的修饰方法,以便使用者进行扩展
二、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor属性
/**
* False if should cancel/suppress periodic tasks on shutdown.
*/
//shutdown后是否继续执行定时任务
private volatile boolean continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown;
/**
* False if should cancel non-periodic tasks on shutdown.
*/
//shutdown后是否继续执行延迟任务
private volatile boolean executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown = true;
/**
* True if ScheduledFutureTask.cancel should remove from queue
*/
//cancle方法收费需要将该任务从队列移除
private volatile boolean removeOnCancel = false;
/**
* Sequence number to break scheduling ties, and in turn to
* guarantee FIFO order among tied entries.
*/
//任务的序列号
private static final AtomicLong sequencer = new AtomicLong();
三、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor构造方法
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
与父类的构造方法相比,最大线程数maximumPoolSize固定为Integer.MAX_VALUE,最大活跃时间keepAliveTime固定为0,队列workQueue固定为DelayedWorkQueue。
四、DelayedWorkQueue
DelayedWorkQueue是BlockingQueue的实现类,是专门为了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor设计的队列,队列中的数据结构为最小堆,每个节点的值小于其子节点的值。初始容量为16,节点数量大于数组长度后触发扩容,容量变为原来的1.5倍。
1. 属性
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue =
new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int size = 0;
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
INITIAL_CAPACITY为初始容量,queue数组用于存放节点。lock锁和available用于控制并发和阻塞等待,size表示节点数量。
private Thread leader = null;
leader属性用于表示正在阻塞等待头结点的线程,是一种Leader-Follower模式的变种,可以最小化线程的等待时间。同样通过阻塞方式去获取头结点,那么leader线程的等待时间为头结点的延迟时间,其它线程则会陷入阻塞状态(available.await())。leader线程获取到头结点后需要发送信号唤醒其它线程(available.asignAll())。
2. 插入节点
以DelayedWorkQueue#offer(Runnable)为例,其它插入节点的方法都是通过调用该方法完成
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
//空值校验
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)x;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
//扩容
grow();
size = i + 1;
//插入的是第一个节点
if (i == 0) {
queue[0] = e;
setIndex(e, 0);








 本文深入解析ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,它是ThreadPoolExecutor的子类,用于执行定时和延迟任务。文章介绍了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的属性、构造方法、核心组件DelayedWorkQueue的插入与删除节点机制,以及ScheduledFutureTask的比较、执行逻辑。ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor通过DelayedWorkQueue的阻塞获取头结点来实现任务的延迟执行,ScheduledFutureTask封装任务并根据执行时间和序列号进行排序。文章还详细阐述了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor执行任务的流程,包括schedule、scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay等方法。
本文深入解析ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,它是ThreadPoolExecutor的子类,用于执行定时和延迟任务。文章介绍了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的属性、构造方法、核心组件DelayedWorkQueue的插入与删除节点机制,以及ScheduledFutureTask的比较、执行逻辑。ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor通过DelayedWorkQueue的阻塞获取头结点来实现任务的延迟执行,ScheduledFutureTask封装任务并根据执行时间和序列号进行排序。文章还详细阐述了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor执行任务的流程,包括schedule、scheduleAtFixedRate和scheduleWithFixedDelay等方法。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 5296
5296

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








