
* bean的生命周期:
* bean创建---初始化----销毁的过程
* 容器管理bean的生命周期;
* 我们可以自定义初始化和销毁方法;容器在bean进行到当前生命周期的时候来调用我们自定义的初始化和销毁方法
*
* 构造(对象创建)
* 单实例:在容器启动的时候创建对象
* 多实例:在每次获取的时候创建对象\
*
* BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization
* 初始化:
* 对象创建完成,并赋值好,调用初始化方法。。。
* BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization
* 销毁:
* 单实例:容器关闭的时候
* 多实例:容器不会管理这个bean;容器不会调用销毁方法;
Car.java
package com.dym.bean;
public class Car {
public Car(){
System.out.println("car constructor...");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("car ... init...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("car ... destroy...");
}
}
MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class
package com.dym.config;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import com.dym.bean.Car;
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
//@Scope("prototype")
@Bean(initMethod="init",destroyMethod="destroy")
public Car car(){
return new Car();
}
}
IOCTest_LifeCycle.class
package com.dym.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import com.dym.config.MainConfigOfLifeCycle;
public class IOCTest_LifeCycle {
@Test
public void test01(){
//1、创建ioc容器
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成...");
applicationContext.getBean("car");
//关闭容器
applicationContext.close();
}
}



* 1)、指定初始化和销毁方法;
* 通过@Bean指定init-method和destroy-method;
* 2)、通过让Bean实现InitializingBean(定义初始化逻辑),
* DisposableBean(定义销毁逻辑);
* 3)、可以使用JSR250;
* @PostConstruct:在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成;来执行初始化方法
* @PreDestroy:在容器销毁bean之前通知我们进行清理工作
* 4)、BeanPostProcessor【interface】:bean的后置处理器;
* 在bean初始化前后进行一些处理工作;
* postProcessBeforeInitialization:在初始化之前工作
* postProcessAfterInitialization:在初始化之后工作
Cat.class
package com.dym.bean.dd;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean,DisposableBean {
public Cat(){
System.out.println("cat constructor...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("cat...destroy...");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("cat...afterPropertiesSet...");
}
}

Dog.class
package com.dym.bean.dd;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dog implements ApplicationContextAware {
//@Autowired
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
public Dog() {
System.out.println("dog constructor...");
}
//对象创建并赋值之后调用
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("Dog....@PostConstruct...");
}
//容器移除对象之前
@PreDestroy
public void detory() {
System.out.println("Dog....@PreDestroy...");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}


MyBeanPostProcessor.class
package com.dym.bean.dd;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 后置处理器:初始化前后进行处理工作
* 将后置处理器加入到容器中
*/
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization..."+beanName+"=>"+bean);
return bean;
}
}


BeanPostProcessor原理
* 遍历得到容器中所有的BeanPostProcessor;挨个执行beforeInitialization,
* 一旦返回null,跳出for循环,不会执行后面的BeanPostProcessor.postProcessorsBeforeInitialization
*
* BeanPostProcessor原理
* populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);给bean进行属性赋值
* initializeBean
* {
* applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
* invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);执行自定义初始化
* applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
*}
* Spring底层对 BeanPostProcessor 的使用;
* bean赋值,注入其他组件,@Autowired,生命周期注解功能,@Async,xxx BeanPostProcessor;





















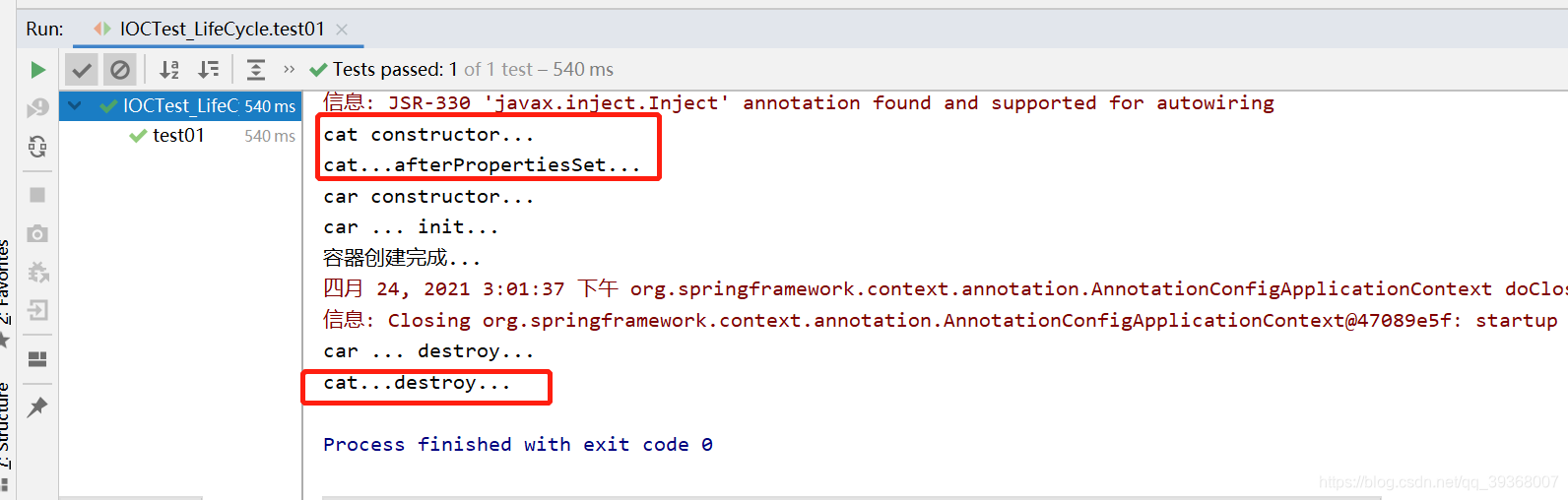
 本文深入探讨了Spring框架中Bean的生命周期,重点介绍了如何使用`init-method`和`destroy-method`进行初始化和销毁操作。同时,通过分析`Car`、`MainConfigOfLifeCycle`、`IOCTest_LifeCycle`、`Cat`、`Dog`及`MyBeanPostProcessor`等类的示例,展示了BeanPostProcessor的工作原理及其在Bean生命周期中的作用。
本文深入探讨了Spring框架中Bean的生命周期,重点介绍了如何使用`init-method`和`destroy-method`进行初始化和销毁操作。同时,通过分析`Car`、`MainConfigOfLifeCycle`、`IOCTest_LifeCycle`、`Cat`、`Dog`及`MyBeanPostProcessor`等类的示例,展示了BeanPostProcessor的工作原理及其在Bean生命周期中的作用。

















 994
994

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








