-
第一章
1.const_cast
定义:去除指针和引用的常量性,不能去除变量的常量性
功能:将常量指针转化为非常量的指针,并且仍然指向原来的对象#include <iostream> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; int main() { int a = 10; const int* p = &a; const int ca = 30; int* q; cout << "a的地址:" << &a << "\ta的值:\t" << a << endl; cout << "*p指向的地址:" << p << "\t*p的值:\t" << *p << endl; q = const_cast<int*>(p); // 问:*p = 20报错 // 答:相当于定义了 int * q = &a; // p 还是常指针,不能改变; 而q是与p指向同一地址(&a)的普通指针,可以改变 *q = 20; cout << "a的地址:" << &a << "\ta的值:\t" << a << endl; cout << "*p指向的地址:" << p << "\t*p的值:\t" << *p << endl; cout << "*q指向的地址:" << q << "\t*p的值:\t" << *q << endl; cout << "*************" << endl; p = &ca; return 0; }2.引用作为函数返回值
#include <iostream> #include <typeinfo> using namespace std; int x = 10; int y = 20; int& f(int& x) { return x; //问:return x+1,返回报错原因? //答:&x是x的地址,返回的也是地址,因为不存在 x+1 这个地址,所以报错 // 且引用不能和常量相加 } int main() { f(x) = 30; cout << x << endl; return 0; }- string 对象的成员函数
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string s1 = "c++程序"; s1[0] = "j"; /* 问:报错,单引号正常? 答:定义的"j"是 const char * (类型char的常量指针)类型,而s1[0]是char类型,类型不同不能赋值,如下图报错所示 说明: “j”实际上存储的是 "j\0" 双引号字符相当于数组,s1[0] = "j"[0] ,这样也可以赋值 s1 = "j" 也可以赋值 */ string str; str = str.append("abcdefg"); const char* p = str.c_str(); cout << "*p=" << *p << "\tp=" << p << endl;//*p=a p=abcdefg ? }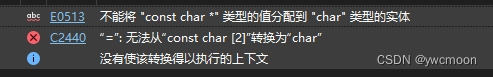
-
第二章
- 写出程序输出结果
#include <iostream>; using namespace std; class MyClassType1{ private: int x, y; public: int getx() { return x; } int gety(); void setx(int x0) { x = x0; } void sety(int y0); void displayx() { cout << "x=" << x << endl; } void displayy() { cout << "y=" << y << endl; } }; int MyClassType1::gety() { return y; } void MyClassType1::sety(int y0) { y = y0; } int main() { MyClassType1 obj1, * p, objArr[10]; obj1.setx(111); cout << obj1.getx() << endl; obj1.displayx(); p = new MyClassType1; //cout << "p\t" << p << endl; (*p).setx(56); p->sety(78); int k = (*p).getx(); int m = p->gety(); cout << "k=" << k << endl; cout << "m=" << m << endl; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { objArr[i].setx(i + 10); objArr[i].sety(i + 20); } p = &objArr[9];// 问题:p没有定义类型;去掉引用未定义 /* cout << "\n"<< endl; cout << "p,&objArr[9]\t"<<p << endl; cout << "&objArr[8]\t" << &objArr[8] << endl; cout << "&objArr[5]\t" << &objArr[5] << endl; */ while (p >= &objArr[5]) { p -> setx(88); p -> sety(99); p--; // 引用地址自减,等于数组键名自减 //cout << p << endl; } //cout << "\n"<< endl; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { cout << objArr[i].getx() << "\t" << objArr[i].gety() << endl; } return 0; }结果如下:

2.套娃指针
#include <iostream>; using namespace std; int main() { int* p1; int** p2 = &p1; int b = 20; p1 = &b; cout << **p2 << endl; // 20 //cout << *p2 <<"\t" << &b << endl; //cout << *p1 << "\t" << &p1<<"\t"<< p1 << endl; return 0; }3.类的静态成员
【程序3-3】自动变量和静态变量的定义和使用#include <iostream>; using namespace std; static int g = 100; void f() { int a = 1; static int fs = 1;// 初始化 //问题:循环为什么没有重新赋值 //答:静态局部变量只执行一次初始化,循环第2次以上时不执行 cout << "a=" << a << "\tfs="<<fs << "\tg=" << g << endl; a += 2; fs += 2; g += 10; cout << "a=" << a << "\tfs=" << fs << "\tg=" << g << endl; } int main() { static int ms = 10; for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) f(); cout << "ms=" << ms<<endl; cout << "g=" << g << endl; }输出
a=1 fs=1 g=100 a=3 fs=3 g=110 a=1 fs=3 g=110 a=3 fs=5 g=120 a=1 fs=5 g=120 a=3 fs=7 g=130 ms=10 g=130 -
第三章
1.【程序3-12】封闭类对象的创建与消亡#include <iostream>; using namespace std; class CTyre { private: int radius; int width; public: CTyre() :radius(16), width(185) { cout<<radius<<"\tCTyre 构造函数" << endl; } CTyre(int r, int w) :radius(r), width(w) { cout<<radius<<"\tCTyre 构造函数" << endl; } ~CTyre() { cout << radius << "\tCTyre 析构函数" << endl; } int getRadius() { return radius; } int getWidth() { return width; } }; class CCar{ private: int price; CTyre tyre; public: CCar(); CCar(int p,int tr,int tw); ~CCar(); int getPrice() { return price; } CTyre getCTyre() { return tyre; } }; CCar::CCar() { price = 50010; CTyre(); // 临时,结束析构 cout << price << "\tCCar 构造函数" << endl; } CCar::CCar(int p, int tr, int tw):price(p),tyre(tr,tw) { cout << price << "\tCCar 构造函数" << endl; } CCar::~CCar() { cout << price << "\tCCar 析构函数" << endl; } int main() { CCar car(48900, 17, 225); cout << "price = " << car.getPrice(); cout <<"\tCTyre.Radius =" << car.getCTyre().getRadius() << "\tCTyre.Width =" << car.getCTyre().getWidth() << endl; // getCTyre()函数内调用tyre类,临时存放,调用结束时析构 【1】 CCar car1; // 默认构造函数,声明的tyre类被初始化,程序结束时析构 【2】 // 调用的tyre类,临时存放,调用结束时析构 【3】 cout << "price = " << car1.getPrice(); cout << "\tCTyre.Radius =" << car1.getCTyre().getRadius() << "\tCTyre.Width =" << car1.getCTyre().getWidth() << endl; return 0; }输出
17 CTyre 构造函数 48900 CCar 构造函数 price = 48900 CTyre.Radius =17 CTyre.Width =225 17 CTyre 析构函数 【1】 17 CTyre 析构函数 【1】 16 CTyre 构造函数 【2】 16 CTyre 构造函数 【3】 16 CTyre 析构函数 【3】 50010 CCar 构造函数 price = 50010 CTyre.Radius =16 CTyre.Width =185 16 CTyre 析构函数 16 CTyre 析构函数 50010 CCar 析构函数 16 CTyre 析构函数 【2】 48900 CCar 析构函数 17 CTyre 析构函数2.以下程序输出3.5,补充完整
#include <iostream>; using namespace std; class point { private: float x,y; public: point(float a,float b) { //f1(float a,float b) x = a; y = b; } point() { x = 0; y = 0; } void getx() { cout << x << endl; } void gety() { cout << y << endl; } friend void print(point& a);//_______ }; void print(point &a) {//(point a) cout << a.x << "," << a.y << endl; } int main() { point a(3.0, 5.0); //point a; a.f1(3.0, 5.0); print(a);//_______ return 0; } -
第六章 多态与虚函数
1.【程序6-4】#include <iostream>; using namespace std; class A { public: int i; virtual void func(){} }; class B :public A { int j; }; int main() { cout << sizeof(A) << "," << sizeof(B); // 本机输出 16,24 return 0; }#include <iostream>; #include <string>; using namespace std; int main() { char ch; int sum = 0, count = 0, x; do { while (cin >> x) { sum += x; count++; } cin.clear(); cin >> ch; } while (toupper(ch)!='Q'); return 0; }
-
第七章 输入输出流
#include <iostream> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { float x = 1234.56789; // cout << x << endl; 输出1234.57. double和float 默认保留6位有效数字 cout.width(10); cout.setf(ios::hex | ios::basefield); cout << x << endl;// 调用cout函数,首次默认右对齐,后续没有设置右对齐,则左对齐 cout.setf(ios::left); cout << x << endl; cout.width(15); cout.setf(ios::right, ios::left); cout << x << endl;// 清除left cout.setf(ios::showpos); cout << x << endl; cout.setf(ios::scientific); cout << x << endl; return 0; }输出结果
1234.57 1234.57 1234.57 +1234.57 +1.234568e+032.科学计数法
#include <iostream> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; /* 科学计数法: 保留1位不为0的整数; 6位小数, 不够补0. 小数点右移n位,尾部e - 0n 小数点左移n位,尾部e + 0n */ int main() { float x = 0.1234; cout.setf(ios::scientific); cout << x << endl; //输出 1.234000e-01 return 0; }#include <iostream> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { float x = 1234.56789; cout.width(10); cout << "#"; cout << x << endl; cout.precision(5); cout << x << endl; cout.setf(ios::showpos); cout << x << endl; cout.setf(ios::scientific); cout << x << endl; return 0; }输出结果
#1234.57 1234.6 +1234.6 +1.23457e+03#include <iostream> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; int main() { float x = 1234.56789; cout << setiosflags(ios::fixed | ios::showpos) << x << endl; cout << setw(12) << setiosflags(ios::right) << setprecision(3) << x << endl; cout << resetiosflags(ios::fixed | ios::showpos) << setiosflags(ios::scientific); cout << setprecision(5) << x << endl; return 0; }输出结果
+1234.567871 +1234.568 1.23457e+03
- 第八章 文件操作
1.#include <iostream> #include<fstream> using namespace std; int main() { ofstream outf("tem.dat",ios::trunc); outf << "Hello wold."; outf.close(); ifstream inf("tem.dat"); char str[100]; string k; while (!inf.eof()) { // k += inf.get(); inf >> str; k += str; k += " "; } cout << k << endl; inf.close(); return 0; }
-
第九章 函数模板与类模板
1.【9-3】对象排序程序#include <iostream>; using namespace std; template <typename T> int cp(const T& l, const T& r) { if (l < r) { return -1; } else if (l > r) { return 1; } else { return 0; } } template <class T> void swap1(T& x, T& y) { T temp = x; x = y; y = temp; } int main() { int as[10] = {1,3,2,5,4,8,7,10,6,9}; int j; for (int i = 1; i < 10;i++) { j = i; while (j > 0 && cp(as[j - 1], as[j]) > 0) { // 没搞懂这里怎么排序的,j的值很迷 swap1(as[j], as[j - 1]); j--; } } for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) cout << as[i]<<endl; return 0; } -
其它
1.表达式 ++j*k,其中++和*都是重载的友元运算符operator*(operator++(j),k) // 先执行++,再执行* // ++ 一个参数,*两个参数
-
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { char a = 'h'; char* p = &a; //&p 为指针p的地址 //p为字符串的地址,等于a的地址 }#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int a = 3; int b = a += a -= a * a; // *比赋值号优先级高,赋值的顺序从右到左 cout << b;// -12 }








 本文介绍了C++中const_cast的使用,展示了如何去除指针和引用的常量性。同时,讲解了引用作为函数返回值的规则,并通过示例解释了string对象的成员函数如append和c_str的用法。此外,还涵盖了类的成员函数,包括静态成员和对象的生命周期。最后,探讨了多态和虚函数的概念,以及输入输出流的格式控制。
本文介绍了C++中const_cast的使用,展示了如何去除指针和引用的常量性。同时,讲解了引用作为函数返回值的规则,并通过示例解释了string对象的成员函数如append和c_str的用法。此外,还涵盖了类的成员函数,包括静态成员和对象的生命周期。最后,探讨了多态和虚函数的概念,以及输入输出流的格式控制。
















 413
413

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








