1. 定义常数
方法一 :开头跟头文件一起,不需要分号
#define Day 7
方法二:函数内部定义
const int day = 7;
2. 数据类型及字节大小

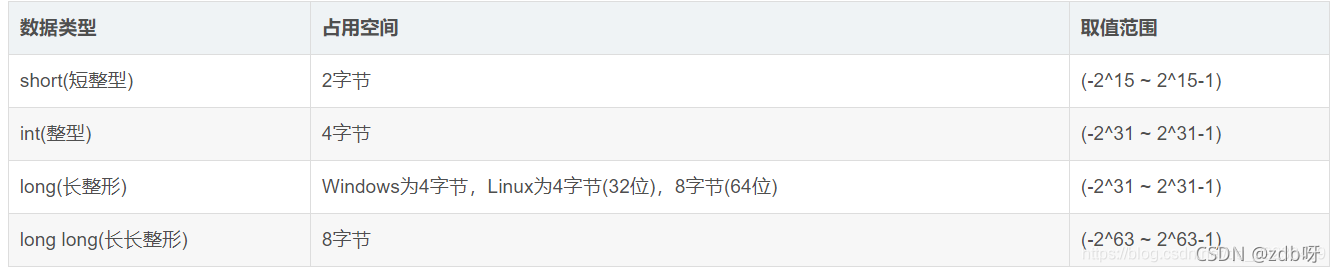
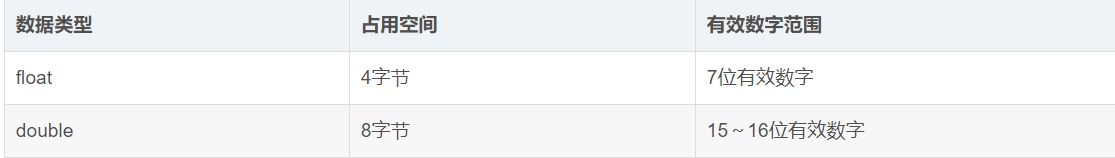
字符型占用1字节
3. 字符串
定义字符串两种方法
方法一:C风格形式
char str1[] = "abc";
方法二:
string str2 = "abc";
4. ++a和a++
++a:前置递增 先让变量+1 然后进行表达式的运算
a++:后置递增 先进行表达式的运算 后让变量+1
5. 三目运算符
语法:表达式1? 结果1 : 结果2
6. 生成随机数和随机数种子
#include <ctime>
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
rand(100)+1; //0~100
8. 指针遍历数组
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int* p = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(arr)/4; i++){ //数组每个元素占4个字节
cout << *p << " ";
p++;
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
9. 结构体和类的区别
10. 栈区和堆区
栈区:由编译器自动分配释放,存放函数的参数值,局部变量等
堆区:由程序员分配和释放,若程序员不释放,程序结束时由操作系统回收。堆区数据利用new关键字进行开辟内存
11. 引用
引用做函数返回值,函数可以作为左值
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//2、函数的调用可以作为左值
int& test02()
{
static int a = 10; //静态变量,存放在全局区,全局区上的数据在程序结束后释放
return a;
}
int main()
{
int aa = test02(); //赋值
int& b = test02(); //又给 test2()取别名 所以现在a b test02()都是同一个东西
test02() = 1000;
cout << "test02():" << test02() << endl;
cout << "aa:" << aa << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
test02():1000
aa:10
b=1000
请按任意键继续. . .
12. 构造函数和析构函数
构造函数:用于初始化数据,构造函数可以重载
析构函数:用于清理工作
13. 深拷贝与浅拷贝
浅拷贝:简单的赋值拷贝操作
深拷贝:在堆区重新申请空间,进行拷贝操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//深拷贝与浅拷贝
class Person {
public:
Person() {
cout << "Person的无参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int age, int height) {
m_Age = age;
m_Height = new int(height); //堆区 手动开辟手动释放
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//自己实现拷贝构造函数 解决浅拷贝带来的问题
Person(const Person& p) {
cout << "Person 拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
//m_Height = p.m_Height; //编译器默认实现就是这行代码,等号复制,即浅拷贝
//深拷贝操作
m_Height = new int(*p.m_Height);
}
~Person() {
//析构代码,将堆区开辟数据做释放操作
if (m_Height != NULL) {
delete m_Height;
m_Height = NULL;
}
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
int* m_Height;
};
void test01() {
Person p1(18, 160);
cout << "p1的年龄:" << p1.m_Age << ";身高为:" <<*p1.m_Height << endl;
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p2的年龄:" << p2.m_Age << ";身高为:" << *p2.m_Height << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
Person的有参构造函数调用
p1的年龄:18;身高为:160
Person 拷贝构造函数调用
p2的年龄:18;身高为:160
Person的析构函数调用
Person的析构函数调用
请按任意键继续. . .
14. 链式编程
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
public:
Person(int age) {
this->age = age;
}
Person& PersonAddAge(Person& p) { //拷贝构造,且取别名,可作为左值
this->age += p.age;
//this指向p2的指针,而*this指向的就是p2这个对象的本体
return *this;
}
int age;
};
//2、返回对象本身用*this
void test02() {
Person p1(10);
Person p2(10);
//链式编程思想
p2.PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1);
cout << "p2的age:" << p2.age << endl;
}
int main() {
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
p2的age:40
请按任意键继续. . .
15. 常函数和常对象
常函数:
- 成员函数后加const后我们称为这个函数为常函数
- 常函数内不可以修改成员属性
- 成员属性声明时加关键字mutable后,在常函数中依然可以修改
常对象:
- 声明对象前加const称该对象为常对象
- 常对象只能调用常函数
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//常函数
class Person {
public:
//this指针的本质 是指针常量 指针的指向是不可以修改的
//在成员函数后面加const,修饰的是this指向,让指针指向的值也不可以修改
void showPerson() const
{
//this->m_A = 100;
this->m_B = 10;
cout << "m_B:" << this->m_B << endl;
//this = NULL; //this指针不可以修改指针的指向的
}
void func() {}
int m_A;
mutable int m_B; //特殊变量,即使在常函数中,也可以修改这个值
};
void test01() {
Person p;
p.showPerson();
}
//常对象
void test02() {
const Person p; //在对象前加const,变为常对象
//p.m_A = 100;
p.m_B = 100; //m_B是特殊值,在常对象下也可以修改
cout << "now,m_B:" << p.m_B << endl;
//常对象只能调用常函数
p.showPerson();
//p.func(); //常对象 不可以调用普通成员函数,因为普通成员函数可以修改属性
}
int main() {
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
16. 纯虚函数
纯虚函数语法:virtual 返回值类型 函数名 (参数列表)= 0 ;
17. 容器
vector<int> v(20) //可以定时直接写上容量大小
v[15] = 1; //可以直接给对应位置等号复制

























 1240
1240

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










