文章目录
布局
- 使用块元素搭建页面框架
- 块元素独占一行空间
- 布局的本质就是让块元素在一行中显示
默认文档流:
默认文档流就是对页面布局不加任何修饰,元素自动的布局方式,其特点如下:
1)元素在页面中的显示顺序与元素在代码中出现的顺序是一致的。
2)块级元素独占一行空间,宽度默认为父级的100%,高度由其内容高度所决定。
3)行内元素与其他元素共享一行空间,宽度由其内容所决定。
默认文档流往往不能满足布局需求,所以可以使用 float、position、display 属性改变默认布局。
1、浮动布局
浮动布局的主要用法是为了让块级元素在一行中显示,或者让文字在图片的周围显示。
float : left / right
浮动布局脱离文档流:
1)宽度高度默认由内容决定
2)原先所在位置就会被其他块元素抢占
3)浮动元素在一行中依次排列,当一行无法容纳的时候会自动换行
2+ 列浮动
给所有的子元素添加浮动,使其排列在一行内,当浏览器视口缩小时,子元素会自动换行。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动布局</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.first {
background-color: lightblue;
}
/*子元素浮动*/
.first > div.one {
background-color: orange;
width: 100px;
height: 320px;
float: left;
/*opacity: 0.4;*/
}
.first > div.two {
background-color: teal;
width: 300px;
height: 130px;
float: left;
}
.first > div.three {
background-color: lightgreen;
width: 500px;
height: 100px;
float: left;
}
/*给父元素添加伪元素,清除浮动*/
.first::after {
content: "";
display: block;
clear: both;
}
.second {
background-color: pink;
height: 400px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="first">
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two"></div>
<div class="three"></div>
<!-- <div class="clear"></div> -->
</div>
<div class="second">
</div>
</body>
</html>



2 列(左侧浮动,右侧不浮动)
给左侧块元素添加浮动,右侧块元素只需添加左外边距,即可使两列块元素在一行显示。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>浮动边框</title>
<style>
.content {
width: 500px;
margin: 0 auto;
background-color: #ededed;
}
.content::after {
display: block;
content: "";
clear: both;
}
/*给左侧块元素添加浮动*/
.content > .left {
width: 238px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid pink;
float: left;
}
/*右侧块元素添加左外边距*/
.content > .right {
margin-left: 240px;
height: 100px;
border: 1px solid lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

2、定位布局
- 作用:
当一个元素悬挂在其他元素之上,优先考虑定位布局
eg: 模态框、下拉菜单、二级菜单、固定宣传栏、网页聊天页面 - 用法:
position : static / relative / absolute / fixed

相对定位 relative
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>相对定位</title>
<style>
.outer {
background-color: #ccc;
}
.outer > div {
height: 100px;
}
.outer > div.one {
background-color: lightblue;
}
/*给two添加相对定位relative*/
.outer > div.two {
background-color: pink;
position: relative;
/*使two在原本的位置向下、向右移动50px*/
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
/*让two显示到最上层*/
z-index: 1;
}
/*给three添加相对定位relative*/
.outer > div.three {
background-color: teal;
position: relative;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two"></div>
<div class="three"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
two 没有脱离文档流,它原来的位置不会被抢占。
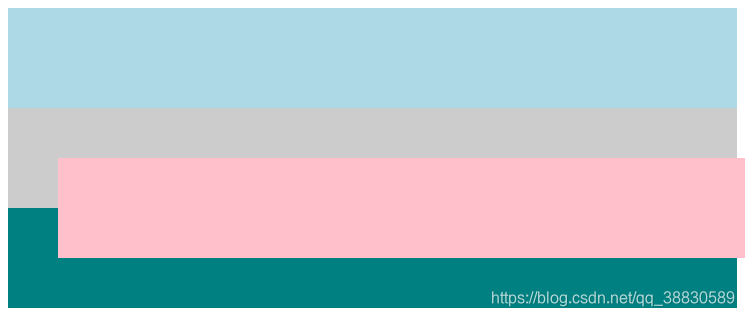
绝对定位 absolute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
body {
}
/*父元素添加相对定位*/
.outer {
background-color: #ccc;
width: 300px;
margin: 100px auto;
position: relative;
}
.outer > div:nth-child(1),
.outer > div:nth-child(3) {
height: 100px;
}
.outer > div.one {
background-color: lightblue;
}
/*子元素添加绝对定位*/
.outer > div.two {
background-color: pink;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
opacity: .5;
}
.outer > div.three {
background-color: teal;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div class="one"></div>
<div class="two"></div>
<div class="three"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
父元素添加了相对定位,子元素参照父元素,two 参照父元素 outer,因此 two 的位置、宽和高均参照父元素的。

固定定位 fixed
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
p {
margin: 0;
}
ul {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
list-style: none;
}
/*固定定位fixed*/
.left-aside {
position: fixed;
left: 0;
top: 200px;
width: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
.left-aside > div {
height: 100px;
line-height: 100px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #fff;
}
.left-aside > div:hover > div{
display: block;
}
/*子元素添加绝对定位absolute,位置参照父元素*/
.left-aside > div > div{
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 100%;
width: 300px;
background-color: #ededed;
display: none;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="left-aside">
<div>
<p>全站</p>
<div>
全站...
</div>
</div>
<div>
<p>居家</p>
<div>
居家....
</div>
</div>
<div>
<p>服饰</p>
<div>
服饰...
</div>
</div>
<div>
<p>美食</p>
<div>
美食...
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
<br>
</body>
</html>
固定定位使元素在浏览器视口的位置不变,参照的是浏览器视口,不会随着浏览器的滚动而滚动。


粘滞定位 sticky
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>粘滞定位</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
/*给box添加粘滞定位,当box距离浏览器视口顶端为100px的时候,体现fixed的特点*/
.box {
height: 100px;
width: 100px;
background-color: #ededed;
position: sticky;
top:100px;
float: right;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div style="height: 200px;background-color: pink"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
<div style="height: 1000px;background-color: lightblue;"></div>
</body>
</html>

当 box 距离浏览器视口顶端100px 时,box 固定不再随着浏览器的滚动而滚动。

3、伸缩盒布局
作用:
使得子元素在父元素中分列显示,与 float 的作用类似。一般用于响应式布局(手机 app 中)
用法:
1. 父元素在主轴上一定要有一个固定的宽/高
2. 子元素在交叉轴上默认宽/高占满父元素
如果主轴为 x 轴,那么资源的默认高度占满父元素
如果主轴为 y 轴,那么资源的默认宽度占满父元素
ul 伸缩盒
1)设置父元素为伸缩盒
display : flex ;
2)主轴
默认情况下主轴为 x 轴,交叉轴为 y 轴,元素沿着伸缩盒的主轴排列的
主轴为 x 轴:flex-direction : row
主轴为 y 轴:flex-direction : column
3)伸缩盒自动换行
子元素宽度和大于父元素的时候是否换行
默认值,不换行:flex-wrap : nowrap
换行: flex-wrap : wrap
li 伸缩盒的元素
1)基础值
主轴上元素的基础值(宽/高):flex-basis : 200px ;
2)对盈余空间的分配
flex-grow : 1 ;
3)对亏损空间的贡献
flex-shrink : 2 ;
4)速写
flex : grow shrink basis ;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伸缩盒布局</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
/*给父元素添加flex布局*/
.outer {
display: flex;
/*主轴为x轴*/
flex-direction: row;
/*子元素宽度和大于父元素的时候不换行*/
flex-wrap: nowrap;
background-color: #ededed;
}
.outer > div {
height: 100px;
width: 300px;
}
/*设置子元素对盈余空间和亏损空间的分配与贡献*/
.outer >div:nth-child(1){
background-color: teal;
flex-grow: 1;
flex-shrink: 2;
}
.outer >div:nth-child(2){
background-color: pink;
flex-grow: 2;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
.outer >div:nth-child(3){
background-color: lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="outer">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

当浏览器视口缩小时,按照设置好的 flex-shrink 分配比例,三个块元素会有不同比例的缩小。

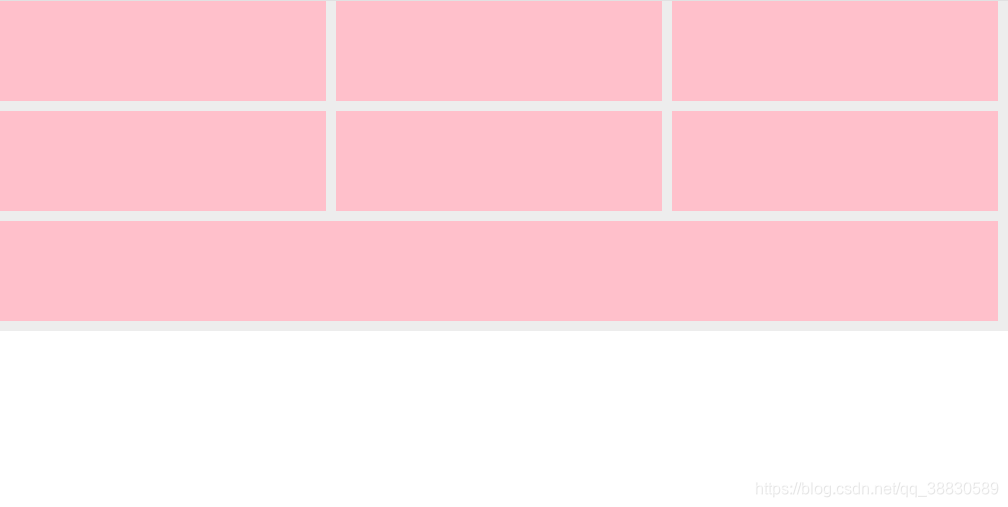
- 当父元素在主轴上满足不了子元素的基础分配需求,换行来满足。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>伸缩盒布局</title>
<style>
body {
margin: 0;
}
.content {
display: flex;
/*x轴,左中右*/
flex-direction: row;
/*当父元素在主轴上满足不了子元素的基础分配需求,换行来满足*/
flex-wrap: wrap;
/*height: 400px;*/
background-color: #ededed;
}
.content > div{
flex-basis: 300px;
flex-grow: 1; /*对于剩余空间分配所占份额*/
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
margin-right: 10px;
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
随着浏览器视口的缩小,每一行溢出的元素自动换到下一行。










 本文详细介绍了CSS布局中的三种主要技术:浮动布局、定位布局和伸缩盒布局。浮动布局用于让元素在一行内显示,定位布局则常用于创建悬停效果和固定元素,而伸缩盒布局适用于响应式设计,让元素根据空间自动调整排列。内容包括各种布局的实现方法及其特性,并提供了实例展示。
本文详细介绍了CSS布局中的三种主要技术:浮动布局、定位布局和伸缩盒布局。浮动布局用于让元素在一行内显示,定位布局则常用于创建悬停效果和固定元素,而伸缩盒布局适用于响应式设计,让元素根据空间自动调整排列。内容包括各种布局的实现方法及其特性,并提供了实例展示。
















 4898
4898

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








