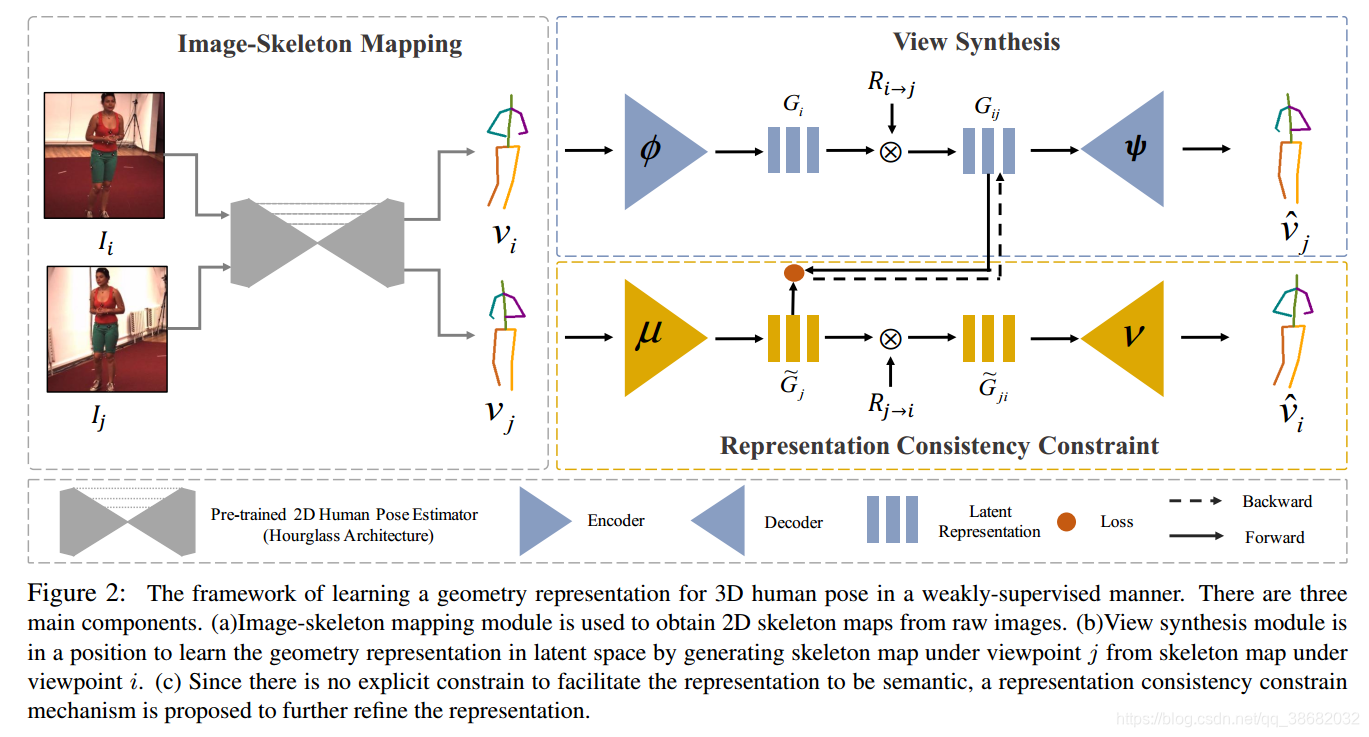
gold:
learn a geometry-aware 3D representation G\mathcal{G}G for the human pose
discover the geometry relation between paired images (Iti,Itj)( I^i_t,I^j_t)(Iti,Itj)
which are acquired from synchronized and calibrated cameras
- i,ji,ji,j:different view point
- ttt:acquiring time acquiring
main components
- image skeleton mapping
- skeleton-based view synthesis
- representation consistency constraint
image-skeleton mapping
input raw image pair (Iti,Itj)( I^i_t,I^j_t)(Iti,Itj) with size of W×HW\times HW×H
- i,ji,ji,j:different view point ,(synchronized and calibrated cameras i,ji,ji,j)
Cti,CtjC^i_t,C^j_tCti,Ctj:KKK keypoint heatmaps from a pre-trained 2D human pose eastimator
We follow previous works [45, 20, 18] to train the 2D estimator on MPII dataset.
constructed 8 pixels width 2D skeleton maps from heatmaps
binary skeleton maps pair (Sti,Stj)( S^i_t,S^j_t)(Sti,Stj),St(⋅)∈{0,1}(K−1)×W×HS_t^{(\cdot)}\in\{0,1\}^{(K-1)\times W \times H}St(⋅)∈{0,1}(K−1)×W×H
Geometry representation via view synthesis
training set T={(Sti,Stj,Ri→j)}\mathcal T = \{(S^i_t,S^j_t,R_{i\to j})\}T={(Sti,Stj,Ri→j)}
- pairs of two views of projection of same 3D skeleton (Sti,Stj)(S^i_t,S^j_t)(Sti,Stj)
- relative rotation matrix Ri→jR_{i\to j}Ri→j from coordinate system of camera iii to jjj
Straightforward way for learning representation in unsupervised/weakly-supervised manner is to utilize auto-encoding mechanism reconstrcting input image.
- no geometry structure information
- nor provides more useful information for 3D pose estimation than 2D coordinates
novel ‘skeleton-based view synthesis’ generate image under a new viewpoint.
Given an image under the known viewpoint as input
source domain : (input image) Si={Sti}i=1V\mathcal S^i = \{S^i_t\}^V_{i=1}Si={Sti}i=1V
- VVV :amount of viewpoints
target domain :generate image Sj={Stj}i=1V\mathcal S^j = \{S^j_t\}^V_{i=1}Sj={Stj}i=1V
- j̸=ij \not=ij̸=i
encoder ϕ:Si→G\phi:\mathcal S^i \to \mathcal Gϕ:Si→G
- source skeleton Sti→SiS^i_t \to \mathcal S^iSti→Si into a latent space Gi∈GG_i\in \mathcal GGi∈G
decoder ψ:Ri→j×G→Si\psi:\mathcal R_{i\to j} \times \mathcal G \to \mathcal S_iψ:Ri→j×G→Si
- ratation matrix Ri→jR_{ i \to j }Ri→j
- GiG_iGi as the set of mmm discrete points on 3η\etaη-dimensional space
in practice: G=[g1,g2,...gM]T,gm=(xm,ym,zm)G = [g_1,g_2,...g_M]^T,g_m = (x_m,y_m,z_m)G=[g1,g2,...gM]T,gm=(xm,ym,zm)
Lℓ2(ϕ⋅ψ,θ)=1NT∑∥ψ(Ri→j×ϕ(Sti))−Stj∥L_{\ell2}(\phi \cdot\psi,\theta)=\frac{1}{N^T}\sum\lVert\psi(R_{i\to j}\times\phi(S^i_t))-S^j_t\rVertLℓ2(ϕ⋅ψ,θ)=NT1∑∥ψ(Ri→j×ϕ(Sti))−Stj∥
Representation consistency constraint
image skeleton mapping + view synthesis (previous two steps)lead to unrealistic generation on target pose when there are large self occlusions in source view
Since there is no explicit constraint on latent space to facilitate G\mathcal GG to be semantic
We assume there exists an inverse mapping (one-to-one) between source domain and target domain, on the condition of the known relative rotation matrix. We could find:
a encoder μ:Sj→G\mu:\mathcal S^j \to \mathcal Gμ:Sj→G
- maps target skeleton StjS^j_tStj to latent space G~j∈G\tilde G_j \in \mathcal GG~j∈G
a decoder ν:Rj→i×G→Sti\nu:R_{j\to i}\times G \to S^i_tν:Rj→i×G→Sti
- maps representation G~j\tilde G_jG~j back to source skeleton StiS^i_tSti
- G~i\tilde G_iG~i and GiG_iGi should be the same shared representation on G\mathcal GG with different rotation-related coefficients ------namely representation consistency
lrc=∑m=1M∥f×Gi−G~i∥2l_{rc}=\sum_{m=1}^M\lVert f \times G_i -\tilde G_i \rVert^2lrc=m=1∑M∥f×Gi−G~i∥2
- f=Ri→jf = R_{i \to j}f=Ri→j rotation-related transformation that map GiG_iGi to G~j\tilde G_jG~j
- a bidirectional encoderdecoder framework
- generator(ϕ,ψ)generator(\phi,\psi)generator(ϕ,ψ),GijG_{ij}Gij:rotated GiG_iGi
- generator(μ,ν)generator(\mu,\nu)generator(μ,ν)
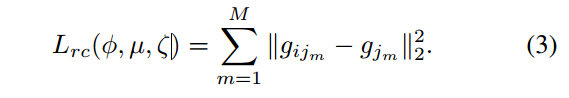
total loss of the bidirectional model
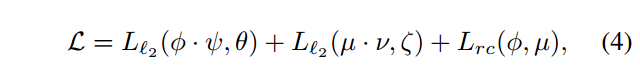
where θ and ζ denotes the parameters of two encode-decoder networks, respectively.
3D human pose estimation by learnt representation
given: monocular image III
goal : b={(xp,yp,zp)}p=1P\bold b = \{(x^p,y^p,z^p)\}^P_{p=1}b={(xp,yp,zp)}p=1P,P body joints,b∈B\bold b \in \mathcal Bb∈B
function F:I→B\mathcal F:\mathcal I \to \mathcal BF:I→B to learn the pose regression
2 fully connect layer





 本文提出了一种基于图像的人体3D姿态估计方法,通过利用不同视角下的图像对,学习几何感知的3D表示。该方法包括图像骨架映射、基于骨架的视图合成以及表示一致性约束等关键步骤。
本文提出了一种基于图像的人体3D姿态估计方法,通过利用不同视角下的图像对,学习几何感知的3D表示。该方法包括图像骨架映射、基于骨架的视图合成以及表示一致性约束等关键步骤。
















 6439
6439

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








