发送网络数据包概述

具体代码多了一个申请内存操作

lwIP与标准TCP/IP协议栈区别
每个层之间不发生数据拷贝,共用pbuf
|
标准TCP/IP协议 |
lwIP协议栈 |
|
严格分层 |
模糊分层 |
|
数据传输层层拷贝 |
对数据直接操作 |
|
数据包私有 |
数据包共享 |
|
效率低 |
效率高 |
|
数据处理要求低 |
数据处理要求高 |
|
完整的TCP/IP协议栈 |
较完整的TCP/IP协议栈 |
lwIP是一种模糊分层的TCP/IP协议栈,数据传递大大提高
在LWIP(Lightweight IP)中,有以下几种pbuf类型:
PBUF_RAM:这是最常见的pbuf类型,它使用RAM作为存储空间。数据被存储在一个连续的RAM缓冲区中。
PBUF_ROM:这种pbuf类型用于存储只读数据,例如常量字符串。它使用ROM作为存储空间。
PBUF_REF:这种pbuf类型用于引用其他pbuf的数据。它不存储实际的数据,而是引用另一个pbuf的数据。
PBUF_POOL:这是一种特殊的pbuf类型,用于从预先分配的内存池中分配pbuf。它可以提高内存分配和释放的效率
pBUF.h文件
数据的首部偏移量的枚举结构体
typedef enum {
/** Includes spare room for transport layer header, e.g. UDP header.
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like udp_send().
*/
PBUF_TRANSPORT = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN + PBUF_IP_HLEN + PBUF_TRANSPORT_HLEN,//网络层 传输层 应用层的首部 总偏移 偏移54
/** Includes spare room for IP header.
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like raw_send().
*/
PBUF_IP = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN + PBUF_IP_HLEN,//传输层 ip层偏移
/** Includes spare room for link layer header (ethernet header).
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like ethernet_output().
* @see PBUF_LINK_HLEN
*/
PBUF_LINK = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN + PBUF_LINK_HLEN,//链路层
/** Includes spare room for additional encapsulation header before ethernet
* headers (e.g. 802.11).
* Use this if you intend to pass the pbuf to functions like netif->linkoutput().
* @see PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN
*/
PBUF_RAW_TX = PBUF_LINK_ENCAPSULATION_HLEN,//附加封装 应该是pbuf的首部吧
/** Use this for input packets in a netif driver when calling netif->input()
* in the most common case - ethernet-layer netif driver. */
PBUF_RAW = 0
} pbuf_layer;//payload(指向数据) 指针的偏移量
补充
typedef enum
{
PBUF_TRANSPORT = ..., /* 传输层报头的空闲空间(发送数据)*/
PBUF_IP = ..., /* 网络层IP头的空闲空间(ICMP应答)*/
PBUF_LINK = ..., /* 链路层报头(IP分片、ARP数据包)*/
PBUF_RAW_TX = ..., /* 以太网前附加封装头的空闲空间 */
PBUF_RAW = 0 /* 原始层,不预留任何空间 */
}pbuf_layer;
pbuf的结构

pbuf类型枚举
typedef enum {
/** pbuf data is stored in RAM, used for TX mostly, struct pbuf and its payload
are allocated in one piece of contiguous memory (so the first payload byte
can be calculated from struct pbuf).
pbuf_alloc() allocates PBUF_RAM pbufs as unchained pbufs (although that might
change in future versions).
This should be used for all OUTGOING packets (TX).*/
PBUF_RAM = (PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_HEAP), //RAM型
/** pbuf data is stored in ROM, i.e. struct pbuf and its payload are located in
totally different memory areas. Since it points to ROM, payload does not
have to be copied when queued for transmission. */
PBUF_ROM = PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF,
/** pbuf comes from the pbuf pool. Much like PBUF_ROM but payload might change
so it has to be duplicated when queued before transmitting, depending on
who has a 'ref' to it. */
PBUF_REF = (PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_DATA_VOLATILE | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF),//内存堆型
/** pbuf payload refers to RAM. This one comes from a pool and should be used
for RX. Payload can be chained (scatter-gather RX) but like PBUF_RAM, struct
pbuf and its payload are allocated in one piece of contiguous memory (so
the first payload byte can be calculated from struct pbuf).
Don't use this for TX, if the pool becomes empty e.g. because of TCP queuing,
you are unable to receive TCP acks! */
PBUF_POOL = (PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_RX | PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS | PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF_POOL)////内存池型
} pbuf_type;//pbuf 类型
RAM ROM 内存堆 内存池型 四个pbuf型
pbuf结构体
/** Main packet buffer struct */
struct pbuf {
/** next pbuf in singly linked pbuf chain */
struct pbuf *next;//指向下一个pbuf
/** pointer to the actual data in the buffer */
void *payload;//指向pbuf 数据区的偏移量 指向数据区域
/**
* total length of this buffer and all next buffers in chain
* belonging to the same packet.
*
* For non-queue packet chains this is the invariant:
* p->tot_len == p->len + (p->next? p->next->tot_len: 0)
*/
u16_t tot_len;// 当前pbuf和剩下的 总长度
/** length of this buffer */
u16_t len;// 当前pbuf的长度
/** a bit field indicating pbuf type and allocation sources
(see PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_*, PBUF_ALLOC_FLAG_* and PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK)
*/
u8_t type_internal;//pbuf类型
/** misc flags */
u8_t flags;//状态位
/**
* the reference count always equals the number of pointers
* that refer to this pbuf. This can be pointers from an application,
* the stack itself, or pbuf->next pointers from a chain.
*/
LWIP_PBUF_REF_T ref;//当前pbuf被引用的次数
/** For incoming packets, this contains the input netif's index */
u8_t if_idx;//包含网卡的索引
/** In case the user needs to store data custom data on a pbuf */
LWIP_PBUF_CUSTOM_DATA//空
};
pbuf块结构图

pbuf.c文件
|
lwIP数据包类型 |
分配方式 |
特点 |
场景 |
|
1、PBUF_RAM |
内存堆,pbuf+数据区域 |
长度不定,耗时,多 |
传递数据、应用程序 |
|
2、PBUF_POOL |
内存池,pbuf+数据区域 |
长度固定,快 |
中断服务程序 |
|
3、PBUF_ROM |
内存池,pbuf |
所指数据都位于ROM中 |
应用程序引用内存区 |
|
4、PBUF_REF |
内存池,pbuf |
所指数据位于RAM中 |
应用程序引用内存区 |

1. pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf 函数 构建pbuf结构体
static void
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(struct pbuf *p, void *payload, u16_t tot_len, u16_t len, pbuf_type type, u8_t flags)
{//设置指向下一pbuf为空 数据区域偏移 剩下的pbuf总大小 当前pbuf大小 pbuf类 被引用次数为1
p->next = NULL;//空
p->payload = payload;
p->tot_len = tot_len;
p->len = len;
p->type_internal = (u8_t)type;
p->flags = flags;
p->ref = 1;
p->if_idx = NETIF_NO_INDEX;
}//设置指向下一pbuf为空 数据区域偏移 剩下的pbuf总大小 当前pbuf大小 pbuf类 被引用次数为1
2.ROM和堆构建pbuf结构体的函数
struct pbuf *
pbuf_alloc_reference(void *payload, u16_t length, pbuf_type type)//
{
struct pbuf *p;
LWIP_ASSERT("invalid pbuf_type", (type == PBUF_REF) || (type == PBUF_ROM));
/* only allocate memory for the pbuf structure */
p = (struct pbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_PBUF);//申请pbuf结构体 大小的控件
if (p == NULL) {//申请的合法性检查
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_SERIOUS,
("pbuf_alloc_reference: Could not allocate MEMP_PBUF for PBUF_%s.\n",
(type == PBUF_ROM) ? "ROM" : "REF"));
return NULL;
}
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(p, payload, length, length, type, 0);//初始刚才申请的内存 初始化位pbuf结构体
return p;
}
3. pbuf_alloc 函数申请pbuf
struct pbuf *
pbuf_alloc(pbuf_layer layer, u16_t length, pbuf_type type)//参1:偏移大小 参2:申请大小 参3:申请类型
{
struct pbuf *p;
u16_t offset = (u16_t)layer;//首部偏移
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_alloc(length=%"U16_F")\n", length));
switch (type) {
case PBUF_REF: /* fall through */
case PBUF_ROM: //两个case 共用这个函数
p = pbuf_alloc_reference(NULL, length, type);// pbuf数据区域偏移为0 申请pbuf的内存长 和规定pbuf的类型
break;
case PBUF_POOL: {
struct pbuf *q, *last;
u16_t rem_len; /* remaining length */
p = NULL;
last = NULL;
rem_len = length;
do {
u16_t qlen;
q = (struct pbuf *)memp_malloc(MEMP_PBUF_POOL);//申请内存池空间 作为pbuf
if (q == NULL) { //合法检查
PBUF_POOL_IS_EMPTY();
/* free chain so far allocated */
if (p) {//第一次是空的
pbuf_free(p);
}
/* bail out unsuccessfully */
return NULL;
}//下一行,如果rem_len 过大 就选择用固定大小的内存池 全用来构建pbuf
qlen = LWIP_MIN(rem_len, (u16_t)(PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE_ALIGNED - LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset)));//需要申请的长 和固定值相比,只取最小的
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(q, LWIP_MEM_ALIGN((void *)((u8_t *)q + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF + offset)),
rem_len, qlen, type, 0);//然后构建初始一个pbuf
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: pbuf q->payload properly aligned",
((mem_ptr_t)q->payload % MEM_ALIGNMENT) == 0);
LWIP_ASSERT("PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE must be bigger than MEM_ALIGNMENT",
(PBUF_POOL_BUFSIZE_ALIGNED - LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset)) > 0 );
if (p == NULL) {//合法性检查 第一次是空的,进这里
/* allocated head of pbuf chain (into p) */
p = q;//p指向 刚才初始构建的pbuf
} else {
/* make previous pbuf point to this pbuf */
last->next = q;//第二次构建进入这里 旧的pbuf 指向新的pbuf ,新建的pbuf的next永远是null
}
last = q;// 把刚构建的记录为旧的
rem_len = (u16_t)(rem_len - qlen);//剩余需要构建的pbuf长
offset = 0;
} while (rem_len > 0);//直到剩余的长构建pbuf完成
break;
}
case PBUF_RAM: {
mem_size_t payload_len = (mem_size_t)(LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(offset) + LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length));//数据内存总长=首部偏移长+申请的长
mem_size_t alloc_len = (mem_size_t)(LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF) + payload_len);// 整个pbuf长=pbuf结构体长+数据内存总长
//RAM的pibuf 没有分块 ,是多长就多长,没有指向下个pbuf
/* bug #50040: Check for integer overflow when calculating alloc_len */
if ((payload_len < LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length)) ||
(alloc_len < LWIP_MEM_ALIGN_SIZE(length))) {
return NULL;//长不能比对齐之后小
}
/* If pbuf is to be allocated in RAM, allocate memory for it. */
p = (struct pbuf *)mem_malloc(alloc_len);//申请整个pbuf空间
if (p == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
pbuf_init_alloced_pbuf(p, LWIP_MEM_ALIGN((void *)((u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF + offset)),
length, length, type, 0);//初始化构建pbuf,偏移=申请的地址(偏移首部)+结构体大小+偏移量(头部),就指向了数据
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: pbuf->payload properly aligned",
((mem_ptr_t)p->payload % MEM_ALIGNMENT) == 0);//应该是合法性检查
break;
}
default:
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_alloc: erroneous type", 0);
return NULL;
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_alloc(length=%"U16_F") == %p\n", length, (void *)p));
return p;
}
3.1申请的pbuf为rom类型 /堆类型

3.2申请的pbuf为pool内存池类型

3.3申请的pbuf为RAM类型
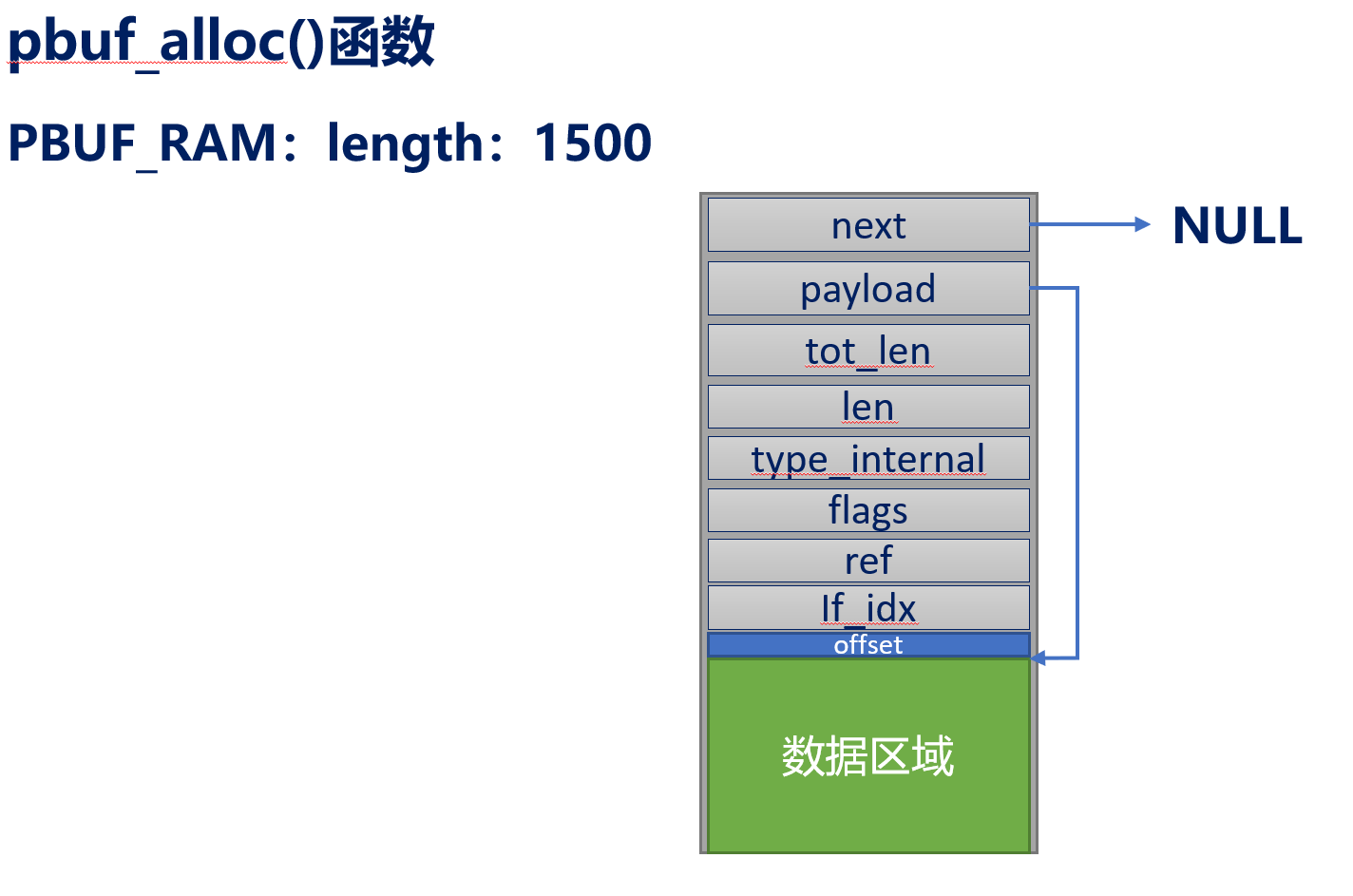
4、pbuf_free函数释放pbuf
u8_t
pbuf_free(struct pbuf *p)
{
u8_t alloc_src;
struct pbuf *q;
u8_t count;
if (p == NULL) {//合法性检查
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
/* if assertions are disabled, proceed with debug output */
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_SERIOUS,
("pbuf_free(p == NULL) was called.\n"));
return 0;
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free(%p)\n", (void *)p));
PERF_START;
count = 0;
/* de-allocate all consecutive pbufs from the head of the chain that
* obtain a zero reference count after decrementing*/
while (p != NULL) {//直到释放到最后一个pbuf
LWIP_PBUF_REF_T ref;//声明一个引用指针
SYS_ARCH_DECL_PROTECT(old_level);//声明一个变量
/* Since decrementing ref cannot be guaranteed to be a single machine operation
* we must protect it. We put the new ref into a local variable to prevent
* further protection. */
SYS_ARCH_PROTECT(old_level);//关中断,保护
/* all pbufs in a chain are referenced at least once */
LWIP_ASSERT("pbuf_free: p->ref > 0", p->ref > 0);//所有引用的pbuf 的数量
/* decrease reference count (number of pointers to pbuf) */
ref = --(p->ref);//pbuf 被引用数量减减
SYS_ARCH_UNPROTECT(old_level);//开中断,解保护
/* this pbuf is no longer referenced to? */
if (ref == 0) {//如果被引用的数为0
/* remember next pbuf in chain for next iteration */
q = p->next;//q为下一个pbuf的地址
LWIP_DEBUGF( PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free: deallocating %p\n", (void *)p));
alloc_src = pbuf_get_allocsrc(p);//pbuf类型,只取低四位
#if LWIP_SUPPORT_CUSTOM_PBUF
/* is this a custom pbuf? */
if ((p->flags & PBUF_FLAG_IS_CUSTOM) != 0) {//这个pbuf是 custom
struct pbuf_custom *pc = (struct pbuf_custom *)p;
LWIP_ASSERT("pc->custom_free_function != NULL", pc->custom_free_function != NULL);
pc->custom_free_function(p);//就调用这个释放
} else
#endif /* LWIP_SUPPORT_CUSTOM_PBUF */
{//不是custom 就按类型释放
/* is this a pbuf from the pool? */
if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF_POOL) {
memp_free(MEMP_PBUF_POOL, p);//内存池释放
/* is this a ROM or RAM referencing pbuf? */
} else if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_MEMP_PBUF) {
memp_free(MEMP_PBUF, p);//堆释放
/* type == PBUF_RAM */
} else if (alloc_src == PBUF_TYPE_ALLOC_SRC_MASK_STD_HEAP) {
mem_free(p);//RAM释放
} else {
/* @todo: support freeing other types */
LWIP_ASSERT("invalid pbuf type", 0);
}
}
count++;//每次释放一次,就计数,直到释放全部pbuf
/* proceed to next pbuf */
p = q;//把当前pbuf 记录为上一个pbuf
/* p->ref > 0, this pbuf is still referenced to */
/* (and so the remaining pbufs in chain as well) */
} else {//pbuf 地址不为空
LWIP_DEBUGF( PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_free: %p has ref %"U16_F", ending here.\n", (void *)p, (u16_t)ref));
/* stop walking through the chain */
p = NULL;//直接把地址释放为空,也就是退出while
}
}
PERF_STOP("pbuf_free");
/* return number of de-allocated pbufs */
return count;
}
5、pbuf添加首部地址函数
static u8_t
pbuf_add_header_impl(struct pbuf *p, size_t header_size_increment, u8_t force)
{
u16_t type_internal;
void *payload;
u16_t increment_magnitude;
LWIP_ASSERT("p != NULL", p != NULL);
if ((p == NULL) || (header_size_increment > 0xFFFF)) {
return 1;
}
if (header_size_increment == 0) {
return 0;
}//以上是合法性检查
increment_magnitude = (u16_t)header_size_increment;
/* Do not allow tot_len to wrap as a result. */
if ((u16_t)(increment_magnitude + p->tot_len) < increment_magnitude) {
return 1;
}////以上是合法性检查
type_internal = p->type_internal;
/* pbuf types containing payloads? */
if (type_internal & PBUF_TYPE_FLAG_STRUCT_DATA_CONTIGUOUS) { //包含了payloads 的pbuf
/* set new payload pointer */
payload = (u8_t *)p->payload - header_size_increment;// payload 地址偏移减小 腾出位置加首部
/* boundary check fails? */
if ((u8_t *)payload < (u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF) {//如果偏移到了 pbuf的结构体位置(当前pbuf的描述符) 就不合法
LWIP_DEBUGF( PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE,
("pbuf_add_header: failed as %p < %p (not enough space for new header size)\n",
(void *)payload, (void *)((u8_t *)p + SIZEOF_STRUCT_PBUF)));
/* bail out unsuccessfully */
return 1;
}
/* pbuf types referring to external payloads? */
} else {//ROM 类型和 ref类型的pbuf
/* hide a header in the payload? */
if (force) {
payload = (u8_t *)p->payload - header_size_increment;//pbuf的 payload直接偏移
} else {
/* cannot expand payload to front (yet!)
* bail out unsuccessfully */
return 1;
}
}
LWIP_DEBUGF(PBUF_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("pbuf_add_header: old %p new %p (%"U16_F")\n",
(void *)p->payload, (void *)payload, increment_magnitude));
/* modify pbuf fields */
p->payload = payload;//把偏移好的 ,赋值返回
p->len = (u16_t)(p->len + increment_magnitude);//当前pbuf 的长度加上偏移量
p->tot_len = (u16_t)(p->tot_len + increment_magnitude);//剩余pbuf 的长度加上偏移量 剩余是该pbuf后面所有的pbuf的长度和
return 0;
}
u8_t
pbuf_add_header(struct pbuf *p, size_t header_size_increment)//pbuf,首部类型;
{
return pbuf_add_header_impl(p, header_size_increment, 0);//后面的0是,不选择REF/ROM的pbuf类型
}
pbuf在netconn中的应用
static struct netbuf *sentbuf;//netbuf
sentbuf = netbuf_new();//申请pbuf内存
netbuf_alloc(sentbuf, strlen((char *)g_lwip_demo_sendbuf));//分配内存 首部偏移
memcpy(sentbuf->p->payload, (void *)g_lwip_demo_sendbuf, strlen((char *)g_lwip_demo_sendbuf));//数据复制给payload内存
err = netconn_send(udpconn, sentbuf); /* 将netbuf中的数据发送出去 */

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








