如果大家对文章内容有疑问或建议,欢迎评论区留言,我们可以一起讨论,共同提高
转载请标明原作者:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/qq_36622751
GCC高效利用cache的方法
cache简介
cache作为承接CPU计算单元和内存的重要通道,能够避免cpu频繁进行效率不高的读写内存操作。然后由于成本和物理空间的关系,cache的大小不能做的很大,差不多是内存千分之一的容量。如何高效利用cache就成为了一个重要的任务。
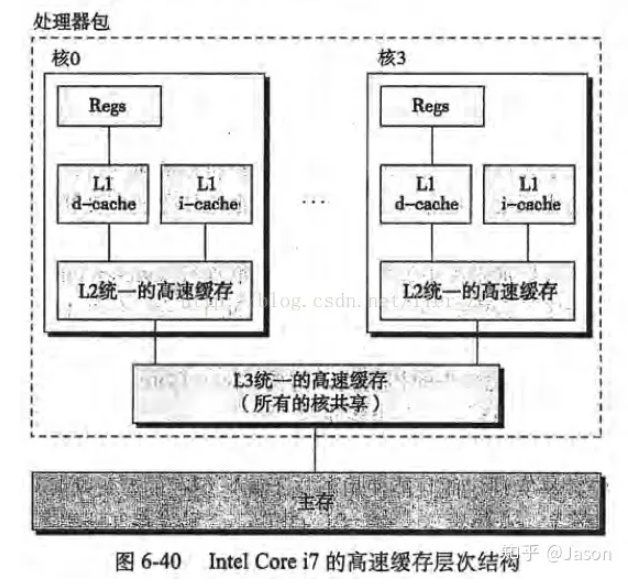
局部性原理是指CPU访问存储器时,无论是存取指令还是存取数据,所访问的存储单元都趋于聚集在一个较小的连续区域中。
- 时间局部性(Temporal Locality):如果一个信息项正在被访问,那么在近期它很可能还会被再次访问。
程序循环、堆栈等是产生时间局部性的原因。 - 空间局部性(Spatial Locality):在最近的将来将用到的信息很可能与正在使用的信息在空间地址上是临近的。
- 顺序局部性(Order Locality):在典型程序中,除转移类指令外,大部分指令是顺序进行的。顺序执行和非顺序执行的比例大致是5:1。此外,对大型数组访问也是顺序的。
指令的顺序执行、数组的连续存放等是产生顺序局部性的原因。
由于局部性原理,cache的利用率实际上还是挺高的。但是由于代码是人工编写的,难免能够充分的利用好局部性原理。因此编译器主动承担了这样一项重要的任务,基本上在开启了-O2或-O3的优化级别后,编译器能够尽可能的使得可执行程序的局部性更好。
本文将介绍gcc编译器中绝大部分为了提高cache命中率而提供了优化选项,并介绍其优化的细节。
这些优化选项基本可以分为三大类:
-
调整数据的访问顺序
一般是由于循环结构,导致有多个数据(如数组,连续分布)在一个很短的时间内都想去占有cache。如访问一个数据的的元素,由于没在cache里面,就从内存中取,但是可能就会把另一个数据刚刚放入cache的部分数据又给挤出去了。这样多个数组都在抢占cache,导致cache频繁的进行更新,cache的命中率也不会很高。这时候应该调整这些数据的访问流程进行调整,包括多个数据访问的拆分和循环逻辑的调整。
-
二进制文件中代码段对齐
因为在程序运行中,cpu得从代码段取出指令,再运行该指令,所以代码段的cache命中率也一样重要。对齐是为了尽量使得部分代码段能集中在一个cache中。当前L1 cache一个单元为64B,即每次可以将64B的内存数据给搬运到cache中。假设有一个代码段(一个函数)的大小正好为64B,如果没有对齐的话,它的数据基本上会放到两个cache中,但是有了对齐后,就只需要占用一个cache。因此gcc通过添加padding的方法,用空间成本换取了时间成本。
-
调整代码块的布局
这里的代码块主要分为两类,一类是函数级别的代码块,这样的代码块相对比较独立,位置可以自由调整,因此根据局部性原理,可以将一些热点函数的代码块放到临近的位置。另一类是函数内的代码块,应该主要指的是以label为分界的代码块,可以在不影响函数正常功能的前提下,进行空间上的调整。在一个更细粒度的程度进行热点代码的聚合。
这里再抽象一个场景,让大家感受一下上面这样做可能带来的好处
假设一个cache的最小分隔单元是64B,有100个这样的单元,而内存大小为64B*100000,这样的话每个cache实际会有1000个内存的单元去抢占它。这里做一个简单的映射 cachePos = memPos % 100;以第0个cache为例,内存中的第0,100,200…的位置是映射的这个位置。对于第一种优化情况,由于同时访问的几个数据在分别内存中连续,因此有可能会存在都去竞争相同cache的情况。第二种优化情况,是让代码段对cache的利用率更高,减少对cache的访问次数,并且降低和其他代码块冲突的概率,如我只占有一个cache单元,冲突肯定小于占有两个的时候。第三种优化的情况,由上述的映射关系可以得知,如果本身代码块之间距离很进,如内存中的100,101,102号位置,那他们映射到cache中也是0,1,2,这些代码块之间不会发生竞争的关系。
调整数据的访问顺序
-ftree-loop-distribution
Perform loop distribution. This flag can improve cache performance on big loop bodies and allow further loop optimizations, like parallelization or vectorization, to take place. For example, the loop执行循环分布。
这个标志可以改善大循环体的缓存性能,并允许进一步的循环优化,如并行化或矢量化。例如,循环中的
DO I = 1, N
A(I) = B(I) + C
D(I) = E(I) * F
ENDDO
is transformed to
被转化为
DO I = 1, N
A(I) = B(I) + C
ENDDO
DO I = 1, N
D(I) = E(I) * F
ENDDO
This flag is enabled by default at -O3. It is also enabled by -fprofile-use and -fauto-profile.
这个标志在默认情况下由-O3启用。它也可以由 -fprofile-use 和 -fauto-profile 启用。
-ftree-loop-distribute-patterns
Perform loop distribution of patterns that can be code generated with calls to a library. This flag is enabled by default at -O2 and higher, and by -fprofile-use and -fauto-profile.
对可以通过调用库生成代码的模式进行循环分布。这个标志在-O2和更高版本时默认启用,并由-fprofile-use和-fauto-profile启用。
This pass distributes the initialization loops and generates a call to memset zero. For example, the loop
这个通道分配了初始化循环,并产生了对memset zero的调用。例如,循环中的
DO I = 1, N
A(I) = 0
B(I) = A(I) + I
ENDDO
is transformed to
被转换为
DO I = 1, N
A(I) = 0
ENDDO
DO I = 1, N
B(I) = A(I) + I
ENDDO
and the initialization loop is transformed into a call to memset zero. This flag is enabled by default at -O3. It is also enabled by -fprofile-use and -fauto-profile.
并且初始化循环被转化为对memset zero的调用。这个标志在默认情况下由-O3启用。它也被-fprofile-use和-fauto-profile所启用。
-floop-interchange
Perform loop interchange outside of graphite. This flag can improve cache performance on loop nest and allow further loop optimizations, like vectorization, to take place. For example, the loop
在graphite之外执行循环互换。这个标志可以提高循环嵌套的缓存性能,并允许进一步的循环优化,如矢量化,发生。例如,循环中的
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
c[i][j] = c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j];
is transformed to
被转化为
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
c[i][j] = c[i][j] + a[i][k] * b[k][j];
This flag is enabled by default at -O3. It is also enabled by -fprofile-use and -fauto-profile.
这个标志在默认情况下由-O3启用。它也被-fprofile-use和-fauto-profile所启用。
-floop-unroll-and-jam
Apply unroll and jam transformations on feasible loops. In a loop nest this unrolls the outer loop by some factor and fuses the resulting multiple inner loops. This flag is enabled by default at -O3. It is also enabled by -fprofile-use and -fauto-profile.
在可行的循环上应用解卷和堵塞转换。在一个循环嵌套中,它将外循环按某种系数展开,并将产生的多个内循环融合。这个标志在默认情况下是在-O3下启用的。它也可以由-fprofile-use和-fauto-profile启用。

调整二进制文件中代码段的布局
-falign-functions
-falign-functions=n
-falign-functions=n:m
-falign-functions=n:m:n2
-falign-functions=n:m:n2:m2
Align the start of functions to the next power-of-two greater than or equal to n, skipping up to m-1 bytes. This ensures that at least the first m bytes of the function can be fetched by the CPU without crossing an n-byte alignment boundary.
将函数的开始部分与大于或等于n的下一个2次方对齐,最多跳过m-1字节。这可以确保CPU至少可以获取函数的前m个字节而不跨越n字节的对齐边界。
If m is not specified, it defaults to n.
如果没有指定m,它默认为n。
Examples: -falign-functions=32 aligns functions to the next 32-byte boundary, -falign-functions=24 aligns to the next 32-byte boundary only if this can be done by skipping 23 bytes or less, -falign-functions=32:7 aligns to the next 32-byte boundary only if this can be done by skipping 6 bytes or less.
例子。-falign-functions=32将函数对齐到下一个32字节的边界,-falign-functions=24只有在跳过23个字节或更少时才会对齐到下一个32字节的边界,-falign-functions=32:7只有在跳过6个字节或更少时才会对齐到下一个32字节边界。
The second pair of n2:m2 values allows you to specify a secondary alignment: -falign-functions=64:7:32:3 aligns to the next 64-byte boundary if this can be done by skipping 6 bytes or less, otherwise aligns to the next 32-byte boundary if this can be done by skipping 2 bytes or less. If m2 is not specified, it defaults to n2.
第二对n2:m2值允许你指定二级对齐:-falign-functions=64:7:32:3如果可以跳过6个字节或更少,则对齐到下一个64字节边界,否则如果可以跳过2个字节或更少,则对齐到下一个32字节边界。如果没有指定m2,它默认为n2。
Some assemblers only support this flag when n is a power of two; in that case, it is rounded up.
有些汇编程序只支持n是2的幂时的这个标志;在这种情况下,它被四舍五入。
-fno-align-functions and -falign-functions=1 are equivalent and mean that functions are not aligned.
-fno-align-functions和-falign-functions=1是等同的,意味着函数不被对齐。
If n is not specified or is zero, use a machine-dependent default. The maximum allowed n option value is 65536.
如果没有指定n或为0,则使用与机器相关的默认值。允许的最大n选项值是65536。
Enabled at levels -O2, -O3.
在级别-O2、-O3时启用。
example
// align.c
int f(void) { return 0; }
int g(void) { return 0; }
使用gcc 4.4.5使用默认设置编译时:
align.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <f>:
0: 55 push %rbp
1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
4: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
9: c9 leaveq
a: c3 retq
000000000000000b <g>:
b: 55 push %rbp
c: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
f: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
14: c9 leaveq
15: c3 retq
指定 -falign-functions 给出:
align.o: file format elf64-x86-64
Disassembly of section .text:
0000000000000000 <f>:
0: 55 push %rbp
1: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
4: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
9: c9 leaveq
a: c3 retq
b: eb 03 jmp 10 <g>
d: 90 nop
e: 90 nop
f: 90 nop
0000000000000010 <g>:
10: 55 push %rbp
11: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
14: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
19: c9 leaveq
1a: c3 retq
-flimit-function-alignment
If this option is enabled, the compiler tries to avoid unnecessarily overaligning functions. It attempts to instruct the assembler to align by the amount specified by -falign-functions, but not to skip more bytes than the size of the function.
如果这个选项被启用,编译器会试图避免不必要地过度对齐函数。它试图指示汇编器按-falign-functions指定的数量对齐,但不会跳过比函数大小更多的字节。
-falign-labels
-falign-labels
-falign-labels=n
-falign-labels=n:m
-falign-labels=n:m:n2
-falign-labels=n:m:n2:m2-
Align all branch targets to a power-of-two boundary.
将所有的分支目标对准一个2次方的边界。
Parameters of this option are analogous to the -falign-functions option. -fno-align-labels and -falign-labels=1 are equivalent and mean that labels are not aligned.
这个选项的参数与-falign-functions选项类似。-fno-align-labels和-falign-labels=1是等同的,意味着标签不被对齐。
If -falign-loops or -falign-jumps are applicable and are greater than this value, then their values are used instead.
如果-falign-loops或-falign-jumps适用并且大于这个值,那么它们的值将被替代使用。
If n is not specified or is zero, use a machine-dependent default which is very likely to be ‘1’, meaning no alignment. The maximum allowed n option value is 65536.
如果没有指定n或者是0,则使用与机器有关的默认值,很可能是’1’,意味着不对齐。允许的最大n选项值是65536。
Enabled at levels -O2, -O3.
在级别-O2、-O3中启用。
-falign-loops
-falign-loops
-falign-loops=n
-falign-loops=n:m
-falign-loops=n:m:n2
-falign-loops=n:m:n2:m2
Align loops to a power-of-two boundary. If the loops are executed many times, this makes up for any execution of the dummy padding instructions.
循环与2的幂的边界对齐。如果循环被多次执行,这就弥补了任何假的填充指令的执行。
If -falign-labels is greater than this value, then its value is used instead.
如果-falign-labels大于这个值,那么就用其值代替。
Parameters of this option are analogous to the -falign-functions option. -fno-align-loops and -falign-loops=1 are equivalent and mean that loops are not aligned. The maximum allowed n option value is 65536.
这个选项的参数与-falign-functions选项类似。-fno-align-loops和-falign-loops=1是等同的,意味着循环不被对齐。允许的最大n选项值是65536。
If n is not specified or is zero, use a machine-dependent default.
如果没有指定n或者为0,则使用与机器有关的默认值。
Enabled at levels -O2, -O3.
在级别-O2、-O3中启用。
-falign-jumps
-falign-jumps
-falign-jumps=n
-falign-jumps=n:m
-falign-jumps=n:m:n2
-falign-jumps=n:m:n2:m2
Align branch targets to a power-of-two boundary, for branch targets where the targets can only be reached by jumping. In this case, no dummy operations need be executed.
对于那些只能通过跳转达到目标的分支目标,将分支目标对准2次方的边界。在这种情况下,不需要执行假操作。
If -falign-labels is greater than this value, then its value is used instead.
如果-falign-labels大于这个值,那么就用它的值代替。
Parameters of this option are analogous to the -falign-functions option. -fno-align-jumps and -falign-jumps=1 are equivalent and mean that loops are not aligned.
这个选项的参数与-falign-functions选项类似。-fno-align-jumps和-falign-jumps=1是等同的,意味着循环不被对齐。
If n is not specified or is zero, use a machine-dependent default. The maximum allowed n option value is 65536.
如果没有指定n或者为0,则使用与机器有关的默认值。允许的最大n选项值是65536。
Enabled at levels -O2, -O3.
在级别-O2, -O3中启用。
调整代码块的布局
-freorder-blocks
Reorder basic blocks in the compiled function in order to reduce number of taken branches and improve code locality.
对编译后的函数中的基本块进行重新排序,以减少所采取的分支数量,提高代码的定位性。
Enabled at levels -O1, -O2, -O3, -Os.
在级别-O1、-O2、-O3、-Os时启用。
-freorder-blocks-algorithm=algorithm
Use the specified algorithm for basic block reordering. The algorithm argument can be ‘simple’, which does not increase code size (except sometimes due to secondary effects like alignment), or ‘stc’, the “software trace cache” algorithm, which tries to put all often executed code together, minimizing the number of branches executed by making extra copies of code.
使用指定的算法进行基本块重排。算法参数可以是 “simple”,它不增加代码大小(除了有时由于对齐等次要影响),或者是 “stc”,即 "软件跟踪缓存 "算法,它试图将所有经常执行的代码放在一起,通过制作额外的代码副本来最小化执行的分支数量。
The default is ‘simple’ at levels -O1, -Os, and ‘stc’ at levels -O2, -O3.
默认情况下,在-O1、-O级别上为’simple’,在-O2、-O3级别上为’stc’。
-freorder-blocks-and-partition
In addition to reordering basic blocks in the compiled function, in order to reduce number of taken branches, partitions hot and cold basic blocks into separate sections of the assembly and .o files, to improve paging and cache locality performance.
除了在编译的函数中重新排序基本块,以减少所采取的分支数量,将热的和冷的基本块划分到汇编和.o文件的不同部分,以改善分页和缓存定位的性能。
This optimization is automatically turned off in the presence of exception handling or unwind tables (on targets using setjump/longjump or target specific scheme), for linkonce sections, for functions with a user-defined section attribute and on any architecture that does not support named sections. When -fsplit-stack is used this option is not enabled by default (to avoid linker errors), but may be enabled explicitly (if using a working linker).
在存在异常处理或解卷表的情况下(在使用setjump/longjump或目标特定方案的目标上),对于linkonce部分,对于具有用户定义的部分属性的函数,以及在任何不支持命名部分的架构上,这种优化会自动关闭。当使用-fsplit-stack时,该选项默认不启用(以避免链接器错误),但可以显式启用(如果使用工作链接器)。
Enabled for x86 at levels -O2, -O3, -Os.
对于x86来说,在-O2、-O3、-Os级别上启用。
-freorder-functions
Reorder functions in the object file in order to improve code locality. This is implemented by using special subsections .text.hot for most frequently executed functions and .text.unlikely for unlikely executed functions. Reordering is done by the linker so object file format must support named sections and linker must place them in a reasonable way.
在对象文件中重新排列函数,以提高代码的定位性。这是通过使用特殊的子段.text.hot和.text.unlikely来实现的,前者用于最常执行的函数,后者用于不常执行的函数。重新排序是由链接器完成的,所以对象文件格式必须支持命名的部分,链接器必须以合理的方式放置它们。
This option isn’t effective unless you either provide profile feedback (see -fprofile-arcs for details) or manually annotate functions with hot or cold attributes (see Common Function Attributes).
这个选项是无效的,除非你提供配置文件反馈(详见-fprofile-arcs)或用热或冷属性手动注释函数(详见常用函数属性)。
Enabled at levels -O2, -O3, -Os.
在级别-O2、-O3、-Os时启用。
others
-fprefetch-loop-arrays
If supported by the target machine, generate instructions to prefetch memory to improve the performance of loops that access large arrays.
如果目标机器支持,生成预取内存的指令,以提高访问大数组的循环的性能。
This option may generate better or worse code; results are highly dependent on the structure of loops within the source code.
这个选项可能产生更好或更差的代码;结果在很大程度上取决于源代码中的循环结构。
Disabled at level -Os.
在-Os级时被禁用。
彩蛋
不知道deepl是咋学习的




 本文介绍了GCC编译器如何通过调整数据访问顺序、代码段对齐和代码块布局来提高cache命中率,从而提升程序性能。主要优化选项包括:-ftree-loop-distribution、-falign-functions、-freorder-blocks等。这些优化有助于减少内存访问次数,充分利用局部性原理,改善代码执行效率。
本文介绍了GCC编译器如何通过调整数据访问顺序、代码段对齐和代码块布局来提高cache命中率,从而提升程序性能。主要优化选项包括:-ftree-loop-distribution、-falign-functions、-freorder-blocks等。这些优化有助于减少内存访问次数,充分利用局部性原理,改善代码执行效率。
















 2917
2917

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








