1,什么是异步
异步调用实现一个不需要被等等的方法的返回值;让调用者继续执行(异步执行);在 java 中,简单的讲就是开启另一个线程完成程序计算,使得调用者继续执行,不需要等等计 算的结果,但是调用者任然需要获取线程的计算结果(不需要同步阻塞等待)
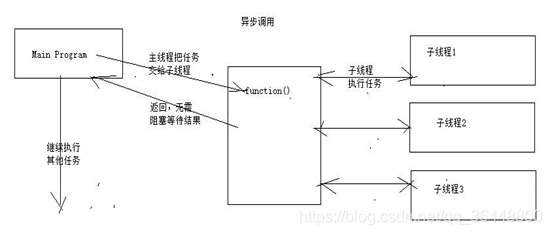
2,Future
Future 也是一个异步计算结果返回接口,目的获取返回值结果。但是 future 在获取返回值结 构的时候,方法必须同步阻塞等待返回值结果。
Get : 获取结果(等待,阻塞)
Get(timeout) : 获取结果,指定等待时间
Cancel : 取消当前任务
isDone : 判断任务是否已经完成 (轮询) futrure 对于结果获取不是很方便,只能通过同步阻塞的方式获取结果,或者是轮询的方式 获取到结果;阻塞的方式获取返回值结果与异步的思想想违背,轮询方式又很占用 cpu 资源, 也不能及时得到我们结果。
3,异步编排
CompletableFuture 可以帮助我们简化异步编程复杂性,提供了函数式编程的能力,可以通 过回调函数的方式处理计算结果。
public class CompletableFuture implements Future, CompletionStage CompletableFuture
具有Future的特性,还实现了CompletionStage接口,具备CompletionStage
接口的特性: 串行执行,并行执行,聚合(AND 聚合,OR 聚合)

1)串行关系执行
串行关系执行: then – 然后,也就是表示下一步,所以通常是一个串行的关系体现,then 后面的单词(比如 run/apply/accept)就是函数是接口中抽象方法名称;
串行关系执行:利用上一步的执行结果,去进行下一步任务执行,任务执行具有先后顺序,因此把这种操作叫做串行关系。
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,Executor executor);
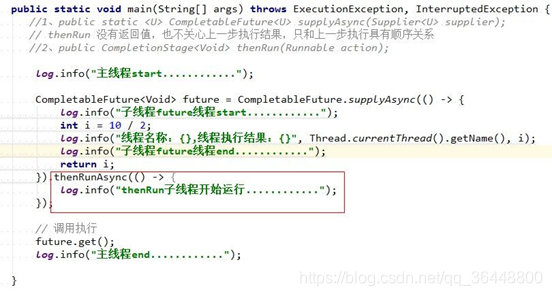
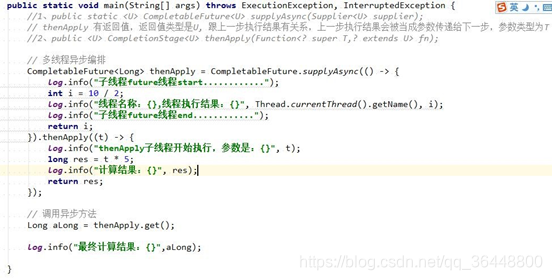
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,Executor executor)
thenApply此方法具有返回值,上一步直接的结果当成传参的传递给thenApply
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor);

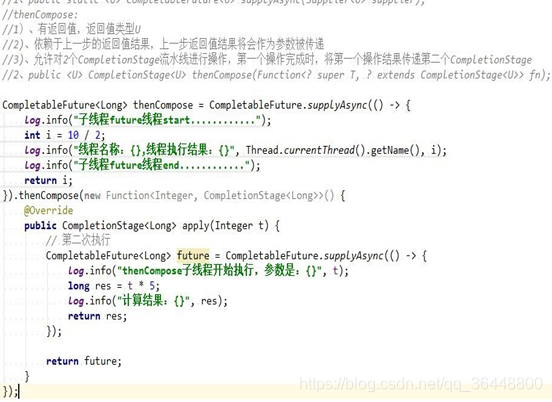
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor);
2)聚合 AND Combine…… with …… 和 both…… and …… 都是要求两者都必须满足,也就是 and 且的关系。
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine (CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync (CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync (CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor)
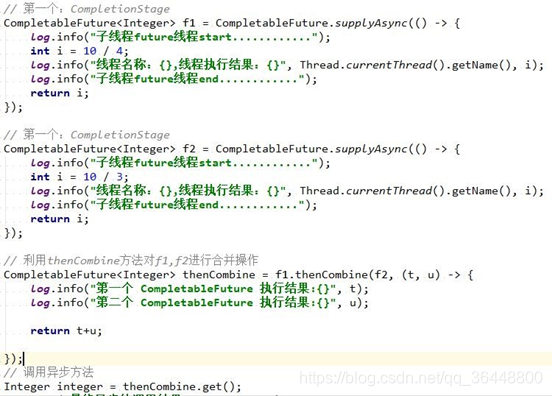
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth (CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
# //1、public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
//thenAcceptBoth: 当 2 个阶段的 CompletionStage 都执行完毕后,把结构
一块交给 thenAcceptBoth 进行执行,没有返回值
//public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth (CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action)

public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor)

3)OR 聚合
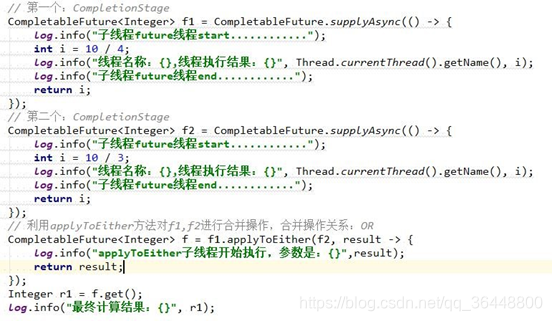
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action,Executor executor);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync (CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync (CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor)
4)异常处理
public CompletionStage<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
public CompletionStage<T> whenComplete (BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action)
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync (BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync (BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle (BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync (BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync (BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor);
4 异步开启
CompletableFuture 提供了 4 个静态的方法,来创建一个异步操作(异步开启: 从这 4 个静 态的方法开发即可)
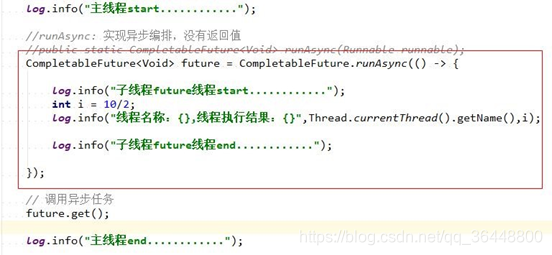
runAsync: 没有返回值的方法,不关注返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,Executor executor);
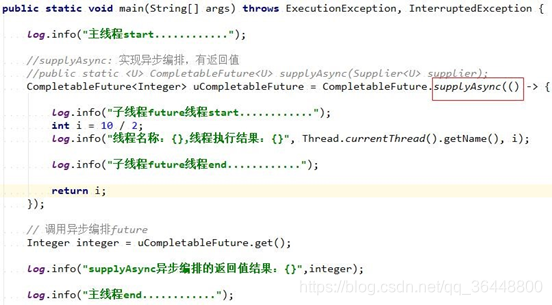
# supplyAsync : 有返回值,关注返回值的。
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor)
1)RunAsync : 没有使用自定义线程池,默认使用的线程池 ForkJoinPool.commonPool
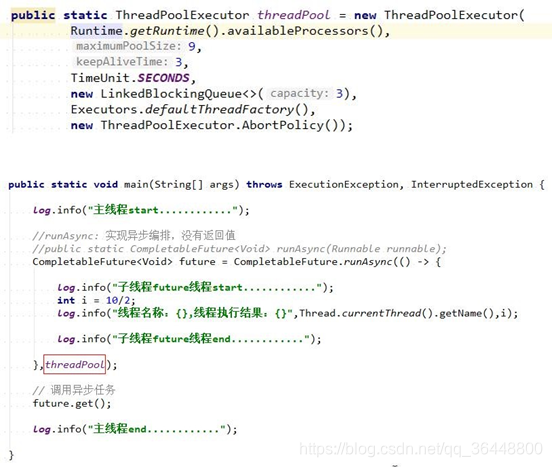
2)RunAsync 使用自己的线程
3)supplyAsync:有返回值的,关注返回值








 本文介绍Java中的异步编程概念,包括异步调用、Future接口的使用及其局限性,重点讲解了CompletableFuture如何简化异步编程,提供串行、并行及聚合操作,并给出异步开启方法。
本文介绍Java中的异步编程概念,包括异步调用、Future接口的使用及其局限性,重点讲解了CompletableFuture如何简化异步编程,提供串行、并行及聚合操作,并给出异步开启方法。
















 1408
1408

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








