一、web项目的启动顺序
1、启动一个WEB项目的时候,WEB容器会去读取它的配置文件web.xml,读取<context-param>和<listener>两个结点。
2、紧急着,容创建一个ServletContext(servlet上下文),这个web项目的所有部分都将共享这个上下文。
3、容器将<context-param>转换为键值对,并交给servletContext。
4、容器创建<listener>中的类实例,创建监听器。
5、容器创建<filter>中的类实例,创建过滤器。
最终得出的结论是:ServletContext-> listener ->filter -> servlet
二、加载spring容器相关的bean
ContextLoaderListener
Tomcat在启动web应用的时候,会通过监听器的方式,通知ServletContextListener,web容器开始启动web应用了,ServletContextListener可以自定义初始化逻辑。ContextLoaderListener就是ServletContextListener接口的一个实现类,主要负责加载spring主容器相关的bean,默认加载WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml文件的配置信息。
ContextLoaderListener通过实现ServletContextListener接口,将spring容器融入web容器当中。这个可以分两个角度来理解:
- web项目自身:接收web容器启动web应用的通知,开始自身配置的解析加载,创建bean实例,通过一个WebApplicationContext来维护spring项目的主容器相关的bean,以及其他一些组件。
- web容器:web容器使用ServletContext来维护每一个web应用,ContextLoaderListener将spring容器,即WebApplicationContext,作为ServletContext的一个attribute,key为,保存在ServletContext中,从而web容器和spring项目可以通过ServletContext来交互。
ContextLoaderListener只是作为一个中间层来建立spring容器和web容器的关联关系,而实际完成以上两个角度的工作是通过ContextLoader来进行的,即在ContextLoader中定义以上逻辑,ContextLoaderListener的实现如下:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.context;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
/**
* Bootstrap listener to start up and shut down Spring's root {@link WebApplicationContext}.
* Simply delegates to {@link ContextLoader} as well as to {@link ContextCleanupListener}.
*
* <p>As of Spring 3.1, {@code ContextLoaderListener} supports injecting the root web
* application context via the {@link #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)}
* constructor, allowing for programmatic configuration in Servlet 3.0+ environments.
* See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 17.02.2003
* @see #setContextInitializers
* @see org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer
*/
public class ContextLoaderListener extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener {
/**
* Create a new {@code ContextLoaderListener} that will create a web application
* context based on the "contextClass" and "contextConfigLocation" servlet
* context-params. See {@link ContextLoader} superclass documentation for details on
* default values for each.
* <p>This constructor is typically used when declaring {@code ContextLoaderListener}
* as a {@code <listener>} within {@code web.xml}, where a no-arg constructor is
* required.
* <p>The created application context will be registered into the ServletContext under
* the attribute name {@link WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE}
* and the Spring application context will be closed when the {@link #contextDestroyed}
* lifecycle method is invoked on this listener.
* @see ContextLoader
* @see #ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)
* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)
*/
public ContextLoaderListener() {
}
/**
* Create a new {@code ContextLoaderListener} with the given application context. This
* constructor is useful in Servlet 3.0+ environments where instance-based
* registration of listeners is possible through the {@link javax.servlet.ServletContext#addListener}
* API.
* <p>The context may or may not yet be {@linkplain
* org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh() refreshed}. If it
* (a) is an implementation of {@link ConfigurableWebApplicationContext} and
* (b) has <strong>not</strong> already been refreshed (the recommended approach),
* then the following will occur:
* <ul>
* <li>If the given context has not already been assigned an {@linkplain
* org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#setId id}, one will be assigned to it</li>
* <li>{@code ServletContext} and {@code ServletConfig} objects will be delegated to
* the application context</li>
* <li>{@link #customizeContext} will be called</li>
* <li>Any {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializer org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer ApplicationContextInitializers}
* specified through the "contextInitializerClasses" init-param will be applied.</li>
* <li>{@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh refresh()} will be called</li>
* </ul>
* If the context has already been refreshed or does not implement
* {@code ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}, none of the above will occur under the
* assumption that the user has performed these actions (or not) per his or her
* specific needs.
* <p>See {@link org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer} for usage examples.
* <p>In any case, the given application context will be registered into the
* ServletContext under the attribute name {@link
* WebApplicationContext#ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE} and the Spring
* application context will be closed when the {@link #contextDestroyed} lifecycle
* method is invoked on this listener.
* @param context the application context to manage
* @see #contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent)
* @see #contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent)
*/
public ContextLoaderListener(WebApplicationContext context) {
super(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
/**
* Close the root web application context.
*/
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) {
closeWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
ContextCleanupListener.cleanupAttributes(event.getServletContext());
}
}
servletContext启动后会调用ServletContextListener的contextInitialized方法,所以Spring中的ContextLoaderListener实现了ServletContextListener接口,在contextInitialized方法中进行加载Spring容器bean的相关操作。
ContextLoader
ContextLoader主要负责加载spring主容器,即root ApplicationContext,在设计层面主要定义了contextId,contextConfigLocation,contextClass,contextInitializerClasses。这些参数都可以在配置中指定,如web.xml的context-param标签,或者是基于Java编程方式配置的WebApplicationInitializer中定义。
作用分别为:
- contextId:当前容器的id,主要给底层所使用的BeanFactory,在进行序列化时使用。
- contextConfigLocation:配置文件的位置,默认为WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,可以通过在web.xml使用context-param标签来指定其他位置,其他名字或者用逗号分隔指定多个。在配置文件中通过beans作为主标签来定义bean。这样底层的BeanFactory会解析beans标签以及里面的bean,从而来创建BeanDefinitions集合,即bean的元数据内存数据库。
- contextClass:当前所使用的WebApplicationContext的类型,如果是在WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml中指定beans,则使用XmlWebApplicationContext,如果是通过注解,如@Configuration,@Component等,则是AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext,通过扫描basePackages指定的包来创建bean。
- contextInitializerClasses:ApplicationContextInitializer的实现类,即在调用ApplicationContext的refresh加载beanDefinition和创建bean之前,对WebApplicationContext进行一些初始化。
initWebApplicationContext方法:创建和初始化spring主容器对应的WebApplicationContext,主要完成两个操作:
创建WebApplicationContext对象实例并调用refresh方法完成从contextConfigLocation指定的配置中,加载BeanDefinitions和创建bean实例;核心源码实现如下:
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
//WebApplicationContext存在性的校验
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
// 创建一个WebApplicationContext
// 具体类型如果是指定了contextClass则使用该指定的;
// 默认使用XmlWebApplicationContext
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
// 设置parent WebApplicationContext,
// 对root WebApplicationContext来说,通常为null
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
// 核心方法,完成配置加载,BeanDefinition定义和bean对象创建
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
//将创建好的WebApplicationContext实例作为将创建好的WebApplicationContext实例
//作为一个attribute保存在ServletContext当中
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
从上面的方法中我们可以大概分析WebApplicationContext的创建过程
1、校验WebApplicationContext的的存在性
在配置中只允许声明一次ServletContextListener,多次声明会扰乱Spring的执行逻辑,所以这里首先就是对此验证。在Spring中如果创建了WebApplicationContext实例,会被记录在ServletContext中以方便全局调用,而使用的Key就是WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE,所以这里验证的方式就是通过key判断ServletContext中是否存在。
2、创建WebApplicationContext的实例
验证通过后,创建WebApplicationContext实例的工作交给了createWebApplicationContext方法进行创建,源码如下:
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
//获取webApplicationContext类型
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
return (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
determineContextClass方法负责获取webApplicationContext类型,在其中先通过getInitParameter方法从servletcontext中获取自定义配置,如果自定义配置为空,则选择默认配置类型XmlWebApplicationContext。
源码如下:
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM);
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
/**
* Name of the class path resource (relative to the ContextLoader class)
* that defines ContextLoader's default strategy names.
*/
private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
private static final Properties defaultStrategies;
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
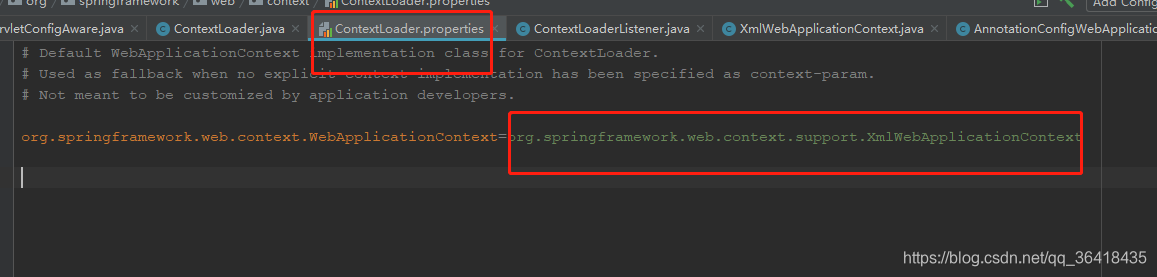
综合以上代码分析
在初始化过程中,程序首先会读取自定义配置的webApplicationContext的实现类,如果不存在,则读取ContextLoader类同目录下的属性文件ContextLoader.properties,获取其中实现webApplicationContext的实现类XmlWebApplicationContext,并根据这个实现类通过反射的方式创建WebApplicationContext。
3、将webApplicationContext实例设置在ServletContext中
4、映射当前的类加载器与创建的实例到全局变量currentContextPerThread中
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext
在initWebApplicationContext初始化方法中的核心是configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法,通过调用这个方法完成配置加载。
1、先从上下文获取自定义contextID和configLocation,不存在,则使用默认配置。
源码如下:
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
//从上下文,获取自定义context_id
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
//生成默认context_id
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
//从上下文,获取自定义配置文件地址
//默认是默认为WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//加载配置文件
wac.refresh();
}
2、调用initPropertySources方法,分别获取上下文初始化参数和servlet初始化参数
public static void initServletPropertySources(MutablePropertySources sources,
@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
Assert.notNull(sources, "'propertySources' must not be null");
//获取上下文初始化参数
String name = StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (servletContext != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
sources.replace(name, new ServletContextPropertySource(name, servletContext));
}
//获取servlet初始化参数
name = StandardServletEnvironment.SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (servletConfig != null && sources.contains(name) && sources.get(name) instanceof StubPropertySource) {
sources.replace(name, new ServletConfigPropertySource(name, servletConfig));
}
}
3、调用refresh方法加载配置文件
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
其中onRefresh方法是FrameworkServlet提供的模板方法在其子类DispatcherServlet中进行重写,主要用于实现Spring在web中所使用的全局变量的初始化。
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);
initLocaleResolver(context);
initThemeResolver(context);
initHandlerMappings(context);
initHandlerAdapters(context);
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
initViewResolvers(context);
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
这里主要介绍启动的准备工作,所以对DispatcherServlet并没有深入分析,这个类用过Spring框架的应该不会陌生,下一篇在详细介绍DispatcherServlet,分析Spring的请求处理。








 本文详细剖析了Spring在web项目启动过程中的顺序,包括web.xml的解析、ServletContext的创建、监听器与过滤器的初始化。接着,重点讲解了ContextLoaderListener如何加载Spring主容器,以及ContextLoader在创建和初始化WebApplicationContext时的角色,包括contextId、contextConfigLocation、contextClass和contextInitializerClasses的作用。最后,概述了WebApplicationContext的创建过程,涉及校验、实例化、设置到ServletContext及配置加载等步骤。
本文详细剖析了Spring在web项目启动过程中的顺序,包括web.xml的解析、ServletContext的创建、监听器与过滤器的初始化。接着,重点讲解了ContextLoaderListener如何加载Spring主容器,以及ContextLoader在创建和初始化WebApplicationContext时的角色,包括contextId、contextConfigLocation、contextClass和contextInitializerClasses的作用。最后,概述了WebApplicationContext的创建过程,涉及校验、实例化、设置到ServletContext及配置加载等步骤。
















 40万+
40万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








