本系列博客汇总在这里:Java系列_汇总
一、字符集编码概述
-
存储
在计算机中存储字符都是存储的字符所对应的数值,以二进制的形式表示。 -
展示
去相关的编码表中去查找该值(存储的值)所对应的字符。 -
常见的
(1)ASCII表:用7bit来表示存储数据。
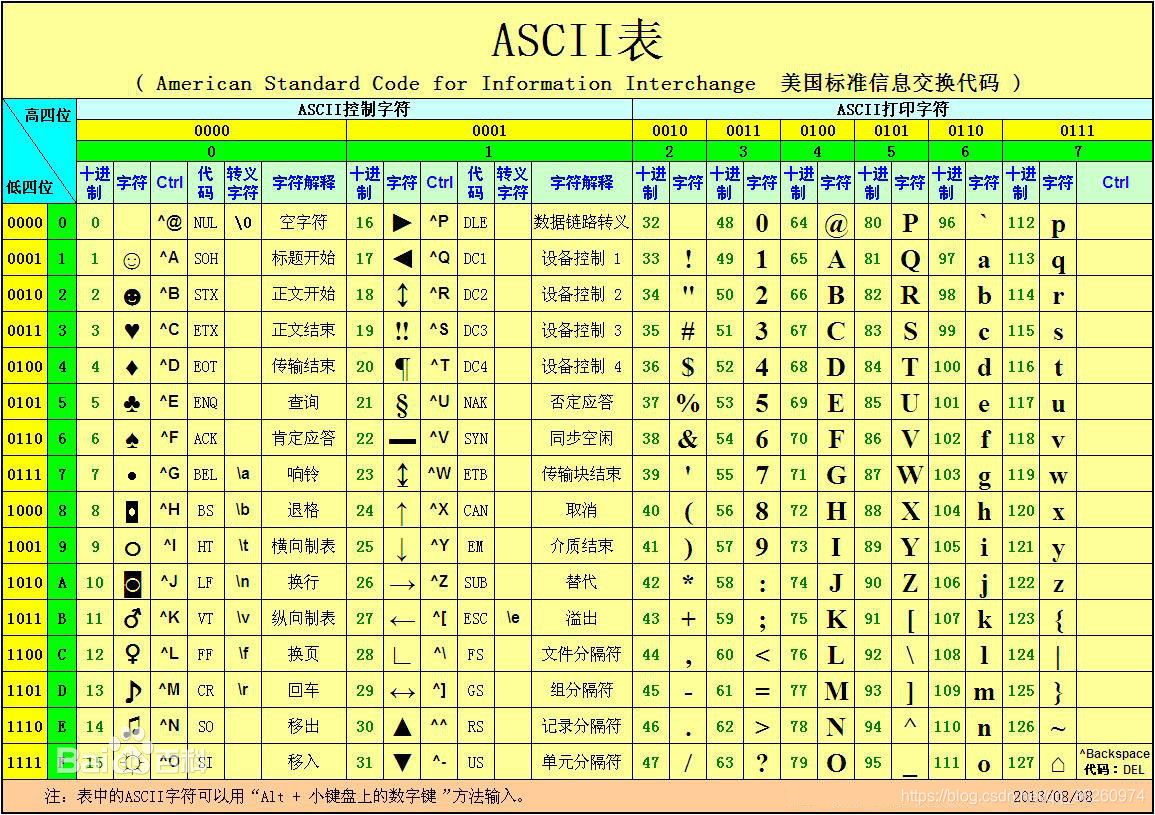 (2)ISO-8859-1(拉丁码表):用 8bit 来表示。
(2)ISO-8859-1(拉丁码表):用 8bit 来表示。
(3)GB2312:简体中文编码(国标码)。
(4)GBK:对 GB2312 做了增强。
(5)GB18030:对 GBK 做了增强。
(6)BIG5:支持繁体。
(7)Unicode:支持多种国家的语言,这是国际标准,用 2 个字节来存储。缺点在于不管是什么字符都用 2 个字节,会有浪费。
(8) UTF-8:支持多种国家的语言,针对不同的字符的范围给出不同的字节表示。- 0,a,A用一个字符存储。
- 中间的范围用二个字节。
- 中文就使用 3 个字节。
- 写入的编码和读取的编码必须要一致,否则会有乱码。
二、使用给定编码方式来写入和读取文件

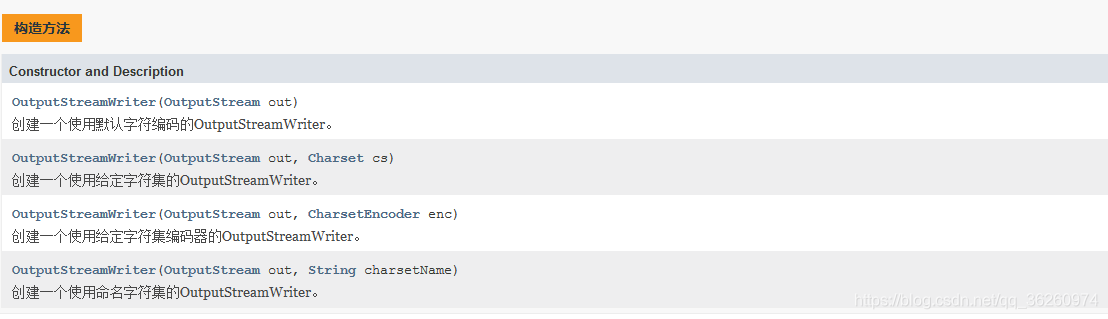
1、写入
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) { PrintWriter pw = null; try { // 默认编码就是 GBK // 把“魏宇轩”转换成字节然后按照 UTF-8 的编码方式存储到文件中 pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("f.txt"), "UTF-8"), true); pw.println("魏宇轩"); } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pw != null) pw.close(); } }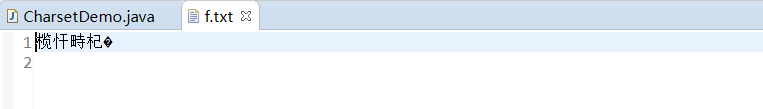
2、读取
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("f.txt"), "UTF-8")); char[] chs = new char[1024]; int len = br.read(chs); System.out.println( new String(chs,0,len)); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (br != null) { try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }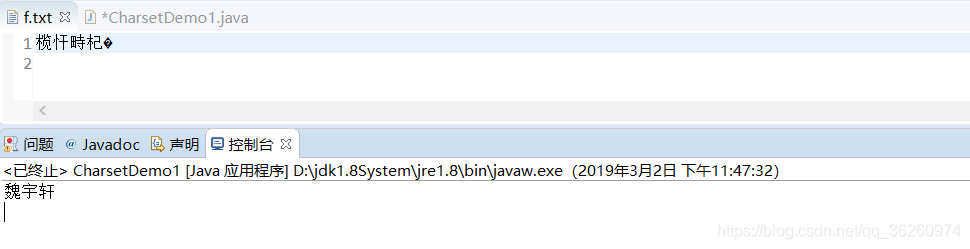
注意:写入和读取的字符编码务必一致,否则会出现乱码!
三、字符串编码解析
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String str = "魏宇轩"; // 使用GBK编码方式把字符串编码为字节 byte[] bs = str.getBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < bs.length; i++) { System.out.print(bs[i] + "\t"); } System.out.println("\n------------------------------解码-------------------------------"); // 使用 GBK 编码方式解码 String str1 = new String(bs, "GBK"); System.out.println("\n"+str1); System.out.println("\n\n"); // 使用UTF-8编码方式把字符串编码为字节 byte[] bs1 = str.getBytes("UTF-8"); for (int i = 0; i < bs1.length; i++) { System.out.print(bs1[i] + "\t"); } System.out.println("\n-------------------------------解码-------------------------------"); // 使用 UTF-8 编码方式解码 String str2 = new String(bs1, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("\n"+str2); }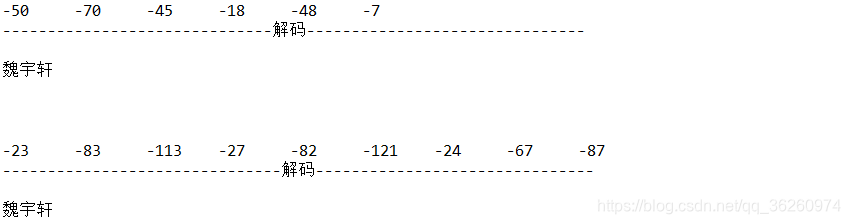
如有错误,欢迎指正!
 Java字符集编码详解
Java字符集编码详解








 本文深入探讨了字符集编码的概念,包括ASCII、ISO-8859-1、GB2312、GBK、GB18030、BIG5、Unicode及UTF-8等常见编码方式,并通过实例演示了如何在Java中使用指定编码读写文件以及字符串编码的解析过程。
本文深入探讨了字符集编码的概念,包括ASCII、ISO-8859-1、GB2312、GBK、GB18030、BIG5、Unicode及UTF-8等常见编码方式,并通过实例演示了如何在Java中使用指定编码读写文件以及字符串编码的解析过程。
















 1183
1183

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








