本系列博客汇总在这里:Java系列_汇总
目录
一、Map 集合
1、介绍
- Map 就是键值对的集合的接口抽象。
- 我们可以通过 key 的值来获得相应的值,将键映射到值的对象;一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射到一个值;键只允许有一个空值,值可以有多个空值。
- 注意:Map 集合和之前学过的 Collection 集合无关。
2、Map 的特点
- 数据成对出现
- 数据的键是唯一的
- 一个键只能对应一个值
- 值可以重复
- 键允许有一个为空,值可以多为空
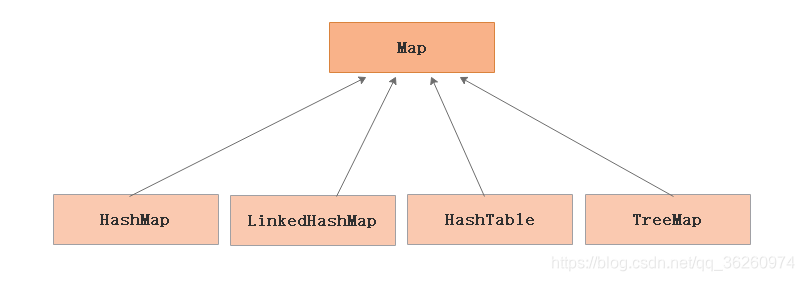
3、Map 的体系结构
4、Map 的常用功能
-
添加功能


示例// 定义一个Map Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); // 放入键值对 map.put("鼓上蚤", "时迁"); map.put("行者", "武松"); // map的键是不能重复的 // map.put("行者", "武大郎"); //一个值可以对应多个键 map.put("及时雨", "宋江"); map.put("呼保义", "宋江"); // 可以有一个键是空 map.put(null, "吴用"); // map.put(null, "公孙胜"); // 值可以有多个是空 map.put("赤发鬼", null); map.put("黑旋风", null); System.out.println(map);
// 定义另一个map Map<String, String> map1 = new HashMap<String, String>(); map1.put("花和尚", "鲁智深"); map1.put("青面兽", "杨志"); // 把一个Map内容加入到另一个map中 map.putAll(map1); System.out.println(map);
-
删除功能


示例// 清空 map map.clear();// 根据 key 来删除一个键值对 map.remove("青面兽"); -
获取功能


示例// 根据指定的键来获得对应的值,如果没有相应的 key 就返回 null String value = map.get("行者"); System.out.println(value);// 拿到Map中所有的键 Set<String> set = map.keySet(); System.out.println(set); // 根据key的集合来获得每一个key对应的value for (String key : set) { // 根据当前的key来获得对应的value String value1 = map.get(key); System.out.println(value1); }
-
对象操作
package cn.tx.map; public class Person { private int id; private String name; private int age; public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Person(int id, String name, int age) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; } }// 创建一个以字符串作为key,Person对象作为值的集合 Map<String, Person> map = new HashMap<String, Person>(); map.put("key1", new Person(1, "张三", 23)); map.put("key2", new Person(2, "李四", 25)); System.out.println(map); //很少向下面这样用,但有这个功能 Map<Person, String> map1 = new HashMap<Person, String>(); map1.put(new Person(1, "张三", 23), "key1"); map1.put(new Person(2, "李四", 25), "key2"); System.out.println(map1);
-
判断功能
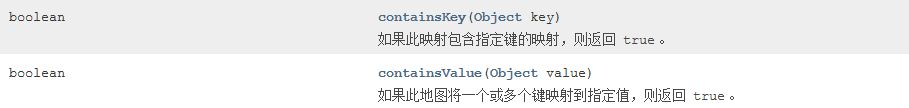

示例// 创建一个以字符串作为 key,Person 对象作为值的集合 Map<String, Person> map = new HashMap<String, Person>(); map.put("key1", new Person(1, "张三", 23)); map.put("key2", new Person(2, "李四", 25)); // 是否包含指定 key boolean isCon = map.containsKey("key3"); System.out.println(isCon);
//Person 类里重写 equals 方法和 hashCode 方法 @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (!(obj instanceof Person)) { return false; } Person p = (Person) obj; if (this.id == p.id && this.age == p.age && this.name != null && p.name != null && this.name.equals(p.name)) { return true; } return false; } @Override public int hashCode() { return 1; }// 是否包含指定 key boolean isConVal = map.containsValue(new Person(1, "张三", 23)); System.out.println(isConVal);
注意:此处之所以返回 true 是因为重写了equals 方法和 hashCode 方法!// 判断集合是否是空 boolean isEmpty = map.isEmpty(); System.out.println(isEmpty); -
遍历功能

示例Set<String> keys = map.keySet(); for (String key : keys) { Person p = map.get(key); System.out.println(p); }
// 获得键值对 set 集合 Set<Entry<String, Person>> entry = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, Person> sp : entry) { // 获得每一个项中的 key 和 value String key = sp.getKey(); Person value = sp.getValue(); System.out.println("键:" + key + " 值:" + value); }
// 把map变成线程同步的 map = Collections.synchronizedMap(map);
二、Map 的子类
1、HashMap

HashMap 的特点
① HashMap 是 map 的实现类;
② 允许多个 null 值和一个 null 键;
③ HashMap中的元素没有顺序(跟添加的顺序无关);
④ HashMap 不是线程安全的。
2、TreeMap
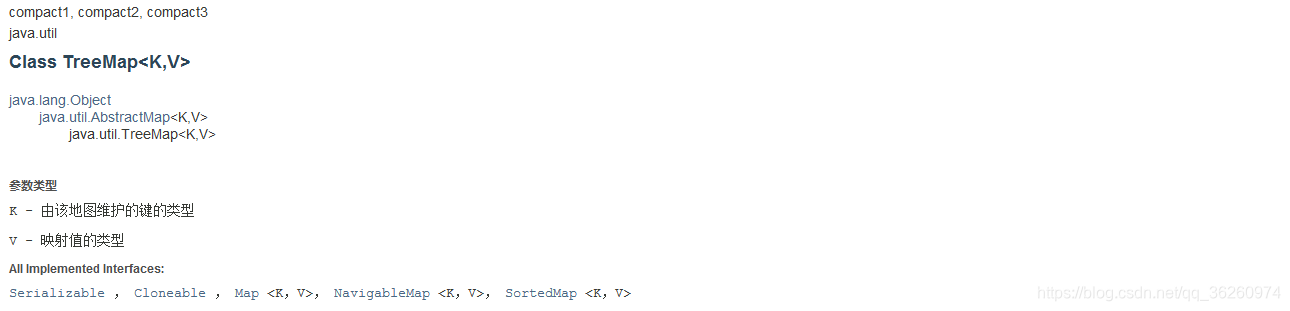
- 该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
- TreeMap 可以参考TreeSet,TreeMap 可以支持 Map 的排序。
TreeMap 特点
- 可以按着 key 来做排序;
- Key 不能 null,key不能重复,值可以有多个 null;
- 不是线程安全的。
- 示例
//TreeMap有排序功能,使用Key来排序 Map<String, Person> map = new TreeMap<String, Person>(); map.put("b", new Person(1, "张三", 23)); map.put("a", new Person(2, "李四", 25)); System.out.println(map);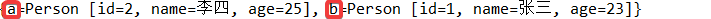
//Person 类里重写Compare 方法 @Override public int compareTo(Person o) { int val = this.getId() - o.getId(); if (val == 0) { val = this.age - o.age; if (val == 0) { val = this.name.compareTo(o.name); } } return val; }//TreeMap有排序功能,使用Key来排序 Map<Person, String> map1 = new TreeMap<Person, String>(); map1.put(new Person(4, "张三", 23),"b"); map1.put(new Person(2, "王五", 27),null); map1.put(new Person(2, "李四", 27),null); System.out.println(map1);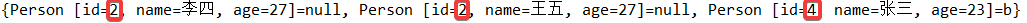
3、HashTable

HashTable 的特点
- HashTable是map的实现类;
- 不允许任何null值和null键;
- HashTable中的元素没有顺序(跟添加的顺序无关);
- HashTable是线程安全的。
- HashMap 和 HashTable 的区别 都是键值对集合 HashMap 允许有一个空键和多个控制,HashTable不允许有空值和空键。
- HashMap 不是线程安全的,HashTable 是线程安全的。
- 示例
// 定义一个Map Map<String, String> map = new Hashtable<String, String>(); // 放入键值对 map.put("鼓上蚤", "时迁"); map.put("行者", "武松"); map.put("及时雨", "宋江"); map.put("呼保义", "宋江"); // HashTable是不允许有空值和空键 // map.put(null, "晁盖"); // map.put("托天王", null); System.out.println(map);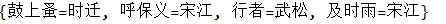
4、LinkedHashMap

LinkedHashMap 的特点
- LinkedHashMap是map的实现类;
- 允许多个null值和一个null键;
- LinkedHashMap有顺序(添加的顺序);
- LinkedHashMap不是线程安全的。
- 示例源码
// 定义一个Map Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>(); // 放入键值对 map.put("鼓上蚤", "时迁"); map.put("行者", "武松"); map.put("及时雨", "宋江"); map.put("呼保义", "宋江"); System.out.println(map);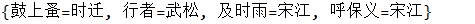
三、面试题
- 问:
Map 集合和 Collection 集合的区别? - 答:
① Map 集合是键值对的集合,Collection 是单一出现的数据的集合。
② Map 的键唯一的,而 Collection 的子接口 List 集合中的元素是可以重复的,set 是唯一的
③ map 是夫妻对,Collection 是光棍。
如有错误,欢迎指正!








 本文深入讲解Java中的Map集合,包括其特点、体系结构、常用功能及HashMap、TreeMap、HashTable、LinkedHashMap等子类的特性。同时,通过实例演示了如何在实际编程中运用这些Map子类。
本文深入讲解Java中的Map集合,包括其特点、体系结构、常用功能及HashMap、TreeMap、HashTable、LinkedHashMap等子类的特性。同时,通过实例演示了如何在实际编程中运用这些Map子类。
















 2837
2837

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








