本文分为两部分——
第一部分介绍Hadoop开发的预备工作,即开发环境的准备;
第二部分以wordcount程序为例,编写第一个MapReduce程序,包括程序的运行、源码解析、Combiner自定义,加深对MapReduce运行过程的理解。
文章目录
1.预备工作
1.1 安装eclipse
- 可以参考下面的教程,Ubuntu 18.04安装Eclipse教程
1.2 安装hadoop-eclipse-plugin插件
- 从github上下载插件,winghc/hadoop2x-eclipse-plugin
- 解压后将其中的
plugins/hadoop-eclipse-kepler-plugin-2.2.0.jar移动到eclipse/plugins中
mv release/hadoop-eclipse-kepler-plugin-2.2.0.jar /opt/eclipse/plugins/
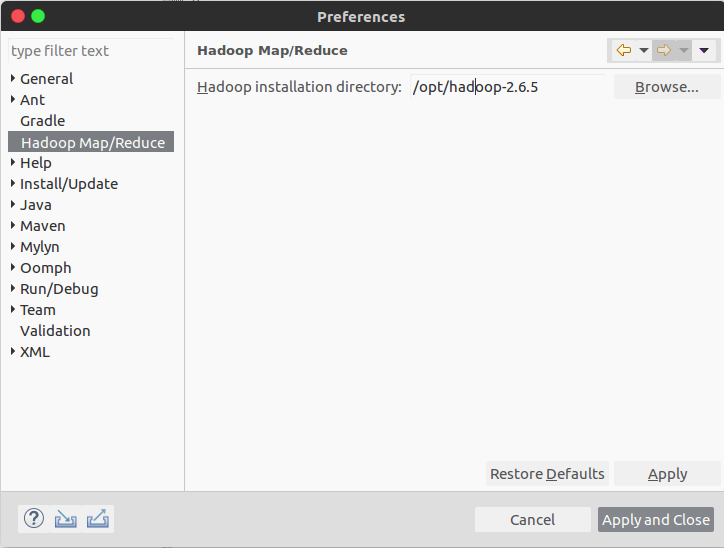
- 重启eclipse,点击菜单栏的window的preferences,如下图,可以看到多了
Hadoop Map/Reduce选项,填入hadoop的安装地址
- 新建一个Map/Reduce project,在下面的
Map/Reduce Locations右键新建一个Hadoop Location
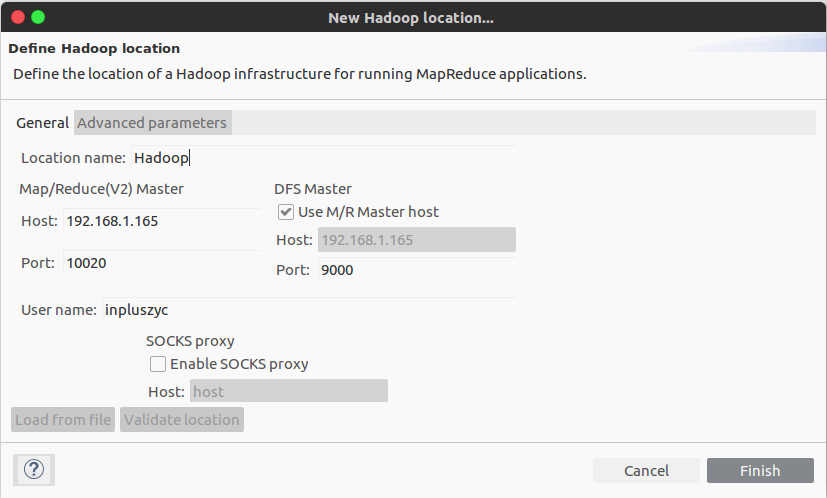
- 在之前的配置文件中找到两个端口,一个是
fs.defaultFS,我设置的是192.168.1.165:9000;另一个是mapreduce.jobhistory.address,我设置的是192.168.1.165:10020,填入下面的表格
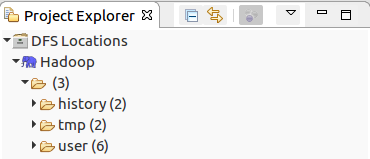
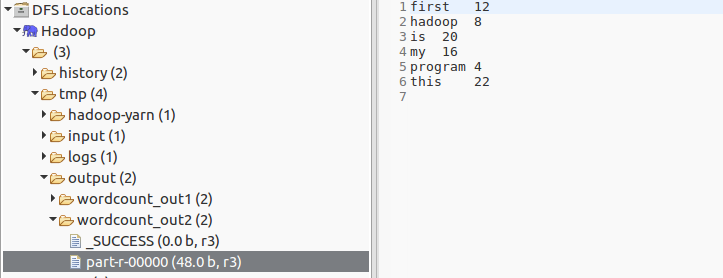
- 完成后可以看到左侧的
DFS Locations中有刚刚配置的Hadoop目录,且里面有之前运行example程序的一些文件
这样开发环境就配置完成了。
2. WordCount程序
2.1 数据准备
- 新建一个文本文件,随便写一点东西在里面,保存为
words,如下:
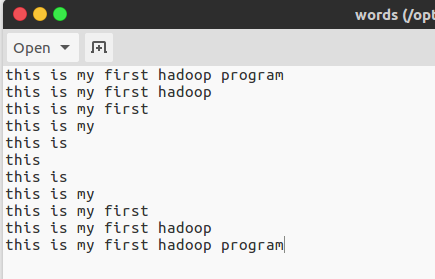
- 在HDFS的
/tmp文件夹创建input和output文件夹,并将words上传到input文件夹,如下:
- 使用命令行如下:
hdfs dfs -mkdir /tmp/input
hdfs dfs -mkdir /tmp/output
hdfs dfs -put words /tmp/input
- 或者使用eclipse插件的hdfs,右键新建、上传等即可
2.2 编写程序
- 新建一个Map/Reduce project,再直接建立一个class,不要package,不然执行时会报错如下:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: WordCount (wrong name: com/wordcount/WordCount)
-
直接复制官网
Example: WordCount v1.0的代码,后面再对代码进行解释,官网地址为MapReduce Tutorial -
导出jar文件,如下:
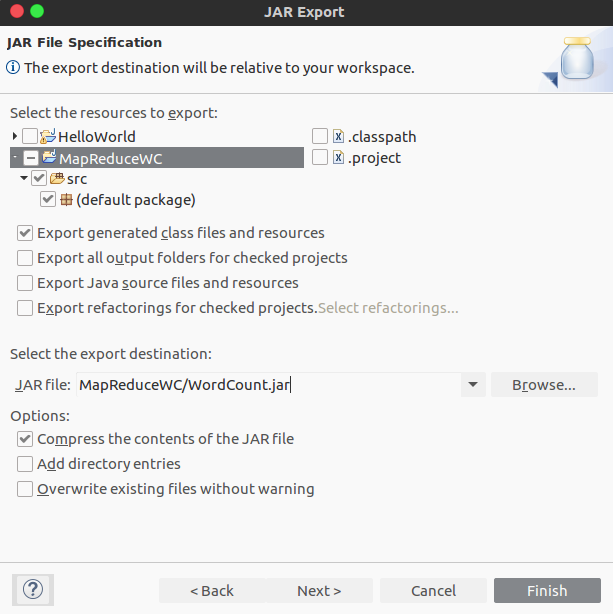
2.3 运行程序
- 切换到存放jar文件的目录,指定参数(主函数的名称、输入、输出),运行程序
cd MapReduceWC #切换到存放jar文件的目录
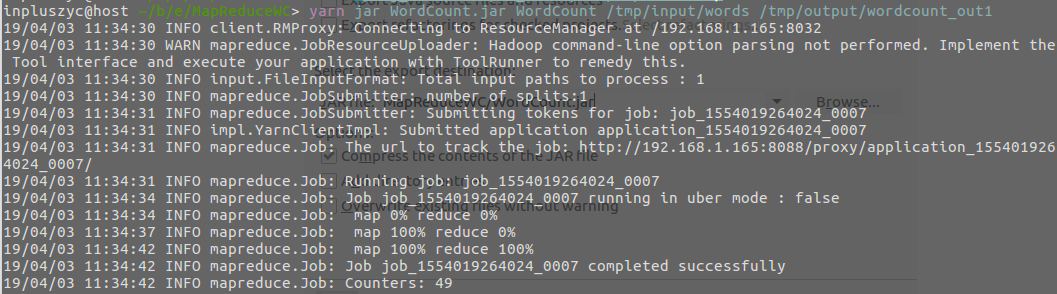
yarn jar WordCount.jar WordCount /tmp/input/words /tmp/output/wordcount_out1
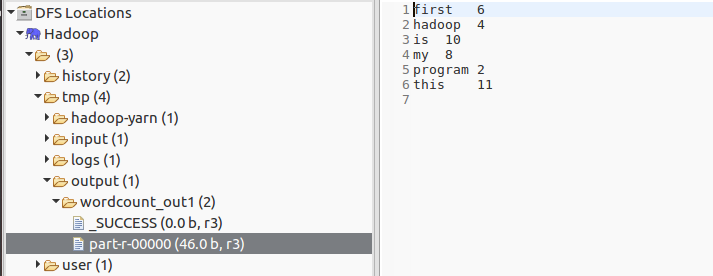
- 结果如下:
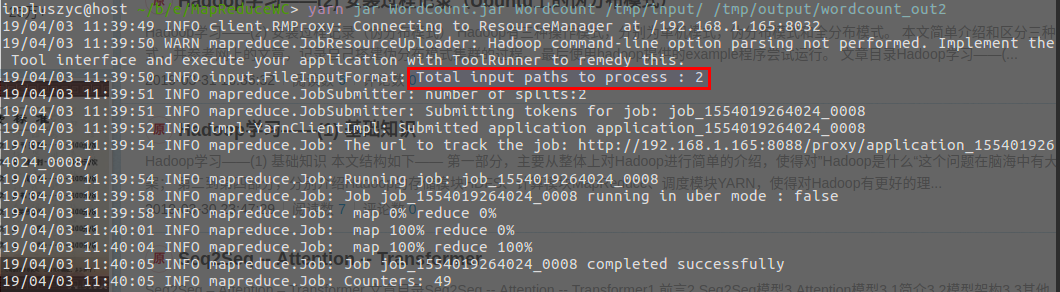
- 复制多一份
words到input文件夹,再次执行,如下:
3. 源码解析
3.1 MapReduce基本过程
一般的 MapReduce 程序会经过以下几个过程:输入(Input)、输入分片(Splitting)、Map阶段、Shuffle阶段、Reduce阶段、输出(Final result)。
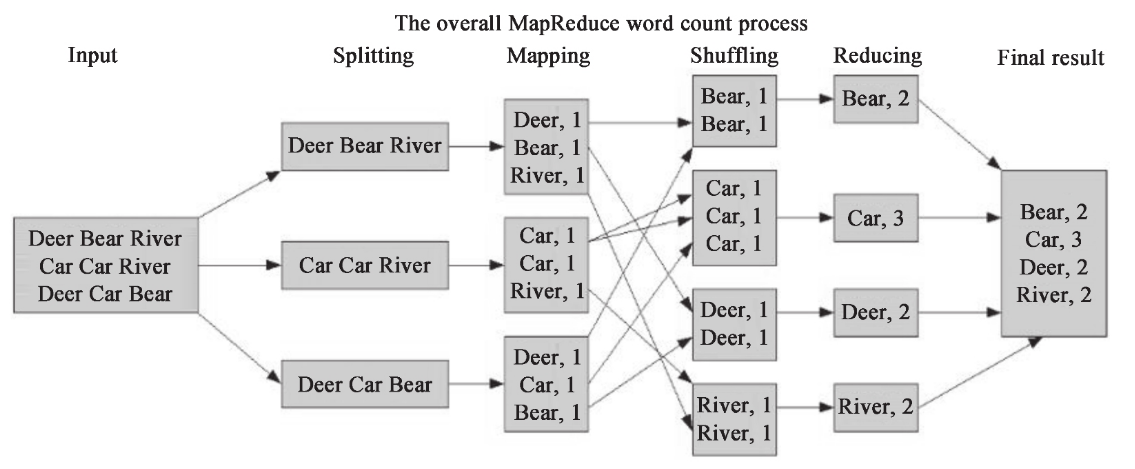
- Map阶段,用程序员编写的Map函数处理对应的分片,具体地,定义一个继承
Mapper类的内部类,重写其map函数,map函数接收一个<key, value>形式的输入,并产生<key, value>形式的输出 - Shuffling阶段,可简单理解为把Map的输出按照键进行排序,并把key相同的键值对整合到同一个组中,变成
<key, list(value)>形式的输出 - Reduce阶段,用程序员编写的Reduce函数整合Shuffling阶段的输出,具体地,定义一个继承
Reducer类的内部类,重写其reduce函数,reduce函数接收<key, list(value)>形式的输入,同样产生<key, value>形式的输出
3.2 Hadoop的数据类型
Hadoop中提供了下列数据类型,这些数据类型都实现了WritableComparable接口,以便用这些类型定义的数据可以被序列化进行网络传输和文件存储,以及进行大小比较。
BooleanWritable:标准布尔型数值
ByteWritable:单字节数值
DoubleWritable:双字节数
FloatWritable:浮点数
IntWritable:整型数
LongWritable:长整型数
Text:使用UTF8格式存储的文本
NullWritable:当<key,value>中的key或value为空时使用
3.3 源码详解
3.3.1 Map阶段
-
编写继承
Mapper的内部类TokenizerMapper,各个参数意义如下:Object:输入< key, value>对的key值,此处为文本数据的起始位置的偏移量。在大部分程序下这个参数可以直接使用 Long 类型,源码此处使用Object做了泛化Text:输入< key, value >对的 value 值,此处为一段具体的文本数据Text:输出<key, value >对的 key 值,此处为一个单词IntWritable:输出< key, value >对的value值,此处固定为1
-
创建
IntWritable和Text对象,用于后面的输出 -
重写
map函数,定义map阶段的逻辑,具体地,把输入的文本数据使用StringTokenizer划分,并生成<word, 1>的键值对暂存在context中,各个参数意义如下:key: 输入数据在原数据中的偏移量value:具体的数据,此处为一段字符串context:用于暂时存储map处理后的结果
public static class TokenizerMapper
extends Mapper<Object, Text, Text, IntWritable>{
private final static IntWritable one = new IntWritable(1);
private Text word = new Text();
public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringTokenizer itr = new StringTokenizer(value.toString());
while (itr.hasMoreTokens()) {
word.set(itr.nextToken());
context.write(word, one);
}
}
}
3.3.2 Reduce阶段
- 编写继承
Reducer的内部类IntSumReducer,各个参数意义如下:Text:输入< key, value >对的 value 值,此处为一个单词IntWritable:输入< key, value >对的value值,在实例程序中设置了Combiner对输入做了一次处理,所以此处为在一台机器处理的数据中key出现的次数,若没有设置Combiner则为1,关于Combiner在本文的下一节介绍Text:输出<key, value >对的 key 值,此处为一个单词IntWritable:输出< key, value >对的value值,即为单词出现的总数
- 创建
IntWritable对象,用于计数作为后面的输出的value值 - 重写
reduce函数,定义reduce阶段的逻辑,具体地,对key对应的value序列遍历求和,并生成<word, result>的键值对暂存在context中,各个参数意义如下:key: 输入< key, value >对的 value 值,此处为一个单词values:shuffle阶段对Map阶段处理后的结果,是key值相同的序列化结构,如< hello,1,1,1>,此处的values即为后面的序列化结构,即(1,1,1),使用Iterable存储context:用于暂时存储reduce处理后的结果
public static class IntSumReducer
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable,Text,IntWritable> {
private IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values,
Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
result.set(sum);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
3.3.3 main函数
- 获取参数,如输入数据和输出数据的路径等
- 实例化
Job,传入参数并命名 - 加载
Jar程序,设置map、combine、reduce阶段的执行类 - 设置输出的key、value类型
- 获取参数中输入、输出文件的路径
- 任务完成后退出
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "word count");
job.setJarByClass(WordCount.class);
job.setMapperClass(TokenizerMapper.class);
job.setCombinerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(IntSumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
}
4.Combiner
上文介绍了wordcount的源码,其中有一个新的概念——Combiner,此处做简单介绍。
4.1 Combiner简介
上文可以看到,MapReduce通过map阶段生成键值对,reduce阶段对键相同的键值对进行求和。同样是计数问题,假设是下列的数据——
有100G的体育新闻,假设map阶段生成了10亿个键值对,则有下列两个问题:
- 网络必须传输这10亿个键值对进行reduce操作
- 10亿个键值对中key为
basketball的远远多于key为computer的,则处理basketball的reduce节点任务过重,降低整体性能
Combiner出现的目的是就是为了处理上述的两个性能瓶颈,具体地,通过在对一台机器的map输出进行combine(如wordcount中的计数,即同reduce做一样的操作),再传输到reduce节点,使得:
- 大大降低了网络传输的工作量
- 平衡各个节点的工作量
4.2 Combiner的输入输出
Combiner的位置如下,位于Map之后,Reduce之前,负责将Map的结果做本地处理(如本地规约)。

- Combiner的输入与reduce相同,可以看作做了本地reduce
- Combiner的输出与map相同,即输出的结果代替map的结果,作为reduce的输入
map: (K1, V1) → list(K2, V2)
combine: (K2, list(V2)) → list(K2, V2)
reduce: (K2, list(V2)) → list(K3, V3)
4.3 Combiner编写
- 继承Reducer,编写Combiner类如下,作用是去除掉长度小于5的单词,对于长度满足条件的单词,在本地计数,如下(基本与reduce相同,增加了输出信息):
public static class DropShort
extends Reducer<Text,IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
IntWritable result = new IntWritable();
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context)
throws java.io.IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("Combiner输入:<" + key.toString() + ",N>...");
if (key.toString().length() < 5) {
System.out.println("the length is less than 5, drop it!");
return;
}
int count = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
count += value.get();
System.out.println("Combiner输入键值对<" + key.toString() + "," + value.get() + ">");
}
result.set(count);
context.write(key, result);
System.out.println("Combiner输出键值对<" + key.toString() + "," + count + ">");
}
}
- 在main函数设置combiner的执行类,如下:
job.setCombinerClass(DropShort.class);
- 运行,查看输出结果如下,可以看到长度小于5的单词被过滤掉了
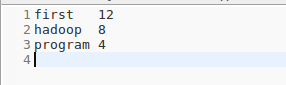
- 查看log文件,可以看到Combiner接收map阶段的输出,并进行求和生成新的键值对
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输入键值对<first,1>
Combiner输出键值对<first,6>
Combiner输入:<hadoop,N>...
Combiner输入键值对<hadoop,1>
Combiner输入键值对<hadoop,1>
Combiner输入键值对<hadoop,1>
Combiner输入键值对<hadoop,1>
Combiner输出键值对<hadoop,4>
Combiner输入:<is,N>...
the length is less than 5, drop it!
Combiner输入:<my,N>...
the length is less than 5, drop it!
Combiner输入:<program,N>...
Combiner输入键值对<program,1>
Combiner输入键值对<program,1>
Combiner输出键值对<program,2>
Combiner输入:<this,N>...
the length is less than 5, drop it!





 本文详细介绍Hadoop开发环境搭建步骤,包括Eclipse及插件安装,并通过WordCount实例讲解MapReduce编程,涉及程序编写、运行及源码解析,最后介绍Combiner优化方法。
本文详细介绍Hadoop开发环境搭建步骤,包括Eclipse及插件安装,并通过WordCount实例讲解MapReduce编程,涉及程序编写、运行及源码解析,最后介绍Combiner优化方法。
















 1661
1661

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








