目录
例7:LeetCode138.复杂链表的深度拷贝(hard)
例1:LeetCode206.链表逆序(easy)
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL 输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
思路:
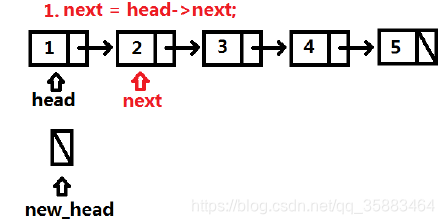
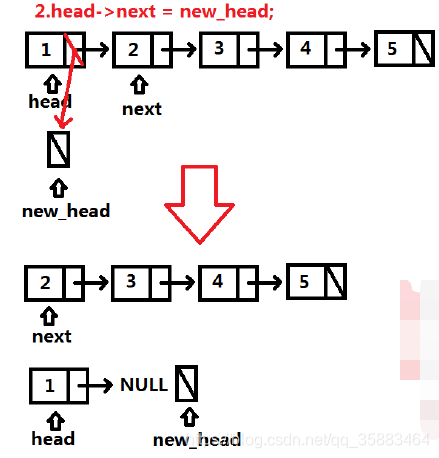
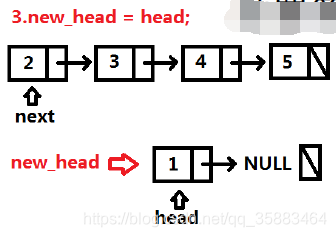
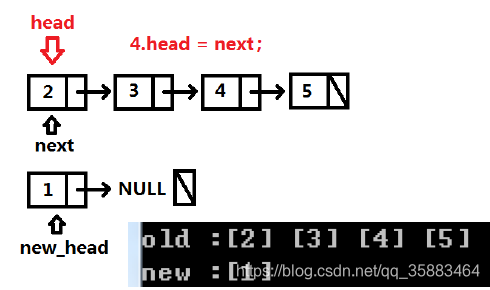
代码:
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
new_head, next = None,None
while head:
next, head.next, new_head = head.next, new_head, head
head = next
return new_head
例2:LeetCode92.链表中间段逆序(medium)
反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
思路:
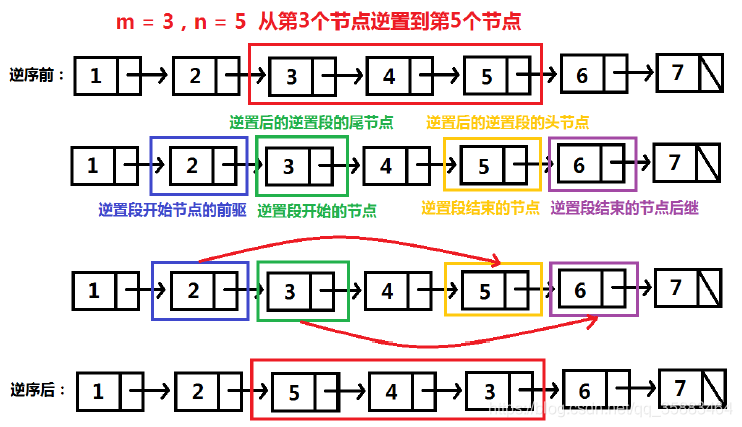
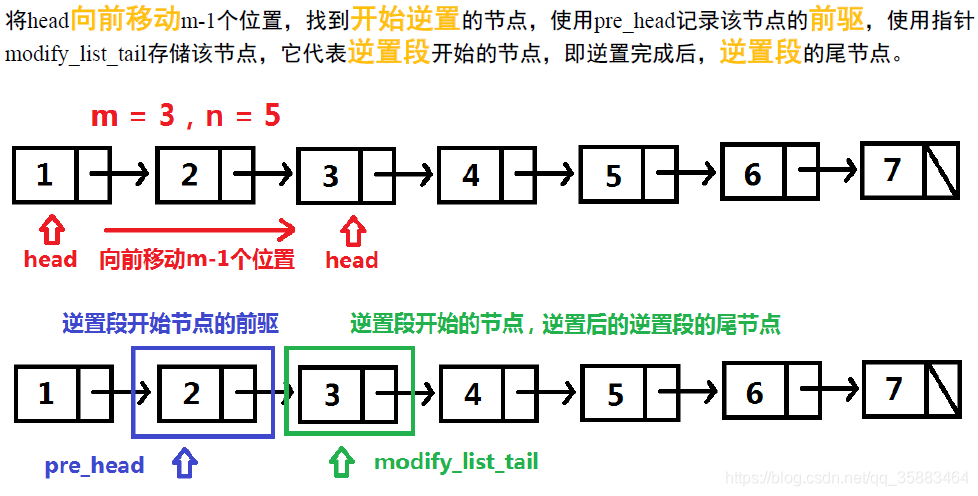
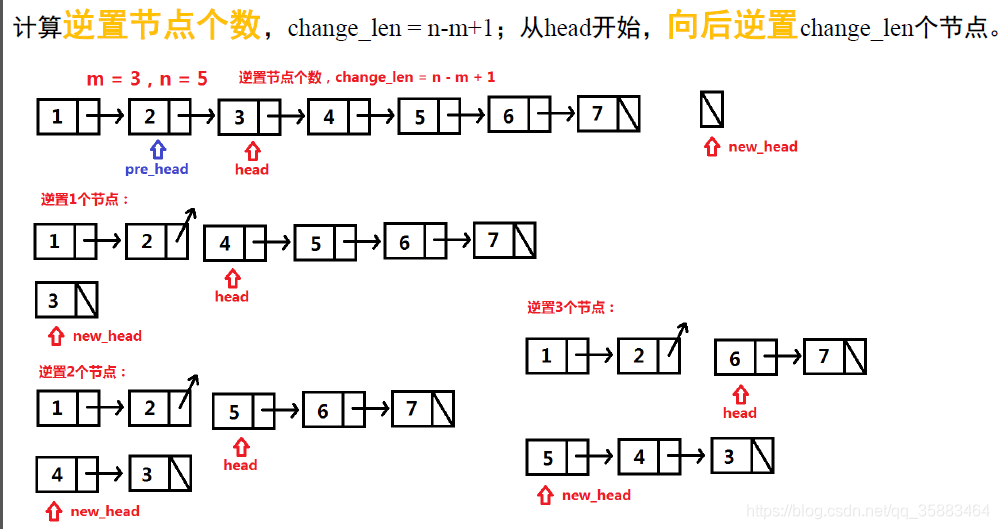
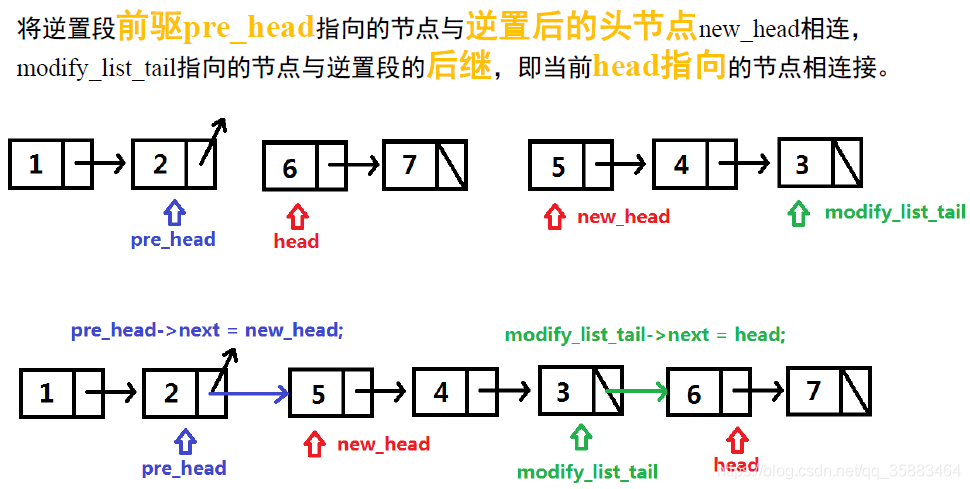
边界情况,m是否等于1:
当m!=1时,对应的 pre_head不为空,直接返回原始链表的头节点即可。
当m=1时是特殊情况,对应的 pre_head为空,所以应该返回 new_head指针指向的节点。
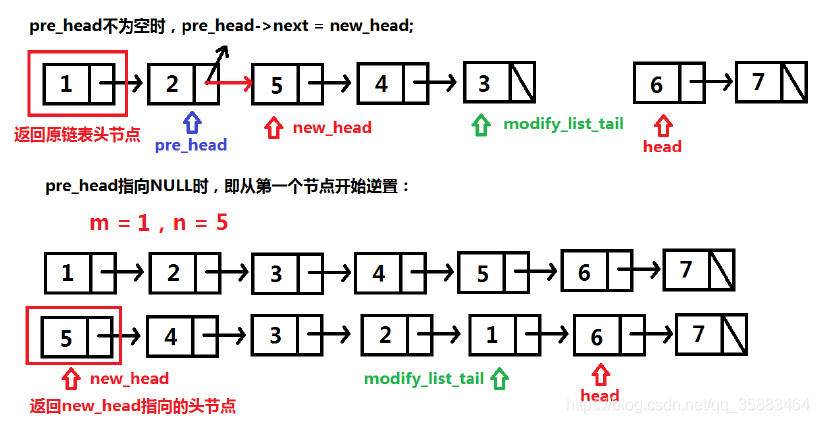
代码:
class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
if not head:
return None
pre_head = None
result = head
while m > 1:
pre_head = head
head = head.next
m, n = m-1, n-1
modify_list_tail = head
new_head = None
while n :
next = head.next
head.next = new_head
new_head = head
head = next
n -= 1
modify_list_tail.next = head
if pre_head:
pre_head.next = new_head
else:
result = new_head
return result
例3:LeetCode21.两个排序链表的合并(easy)
将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
思路:
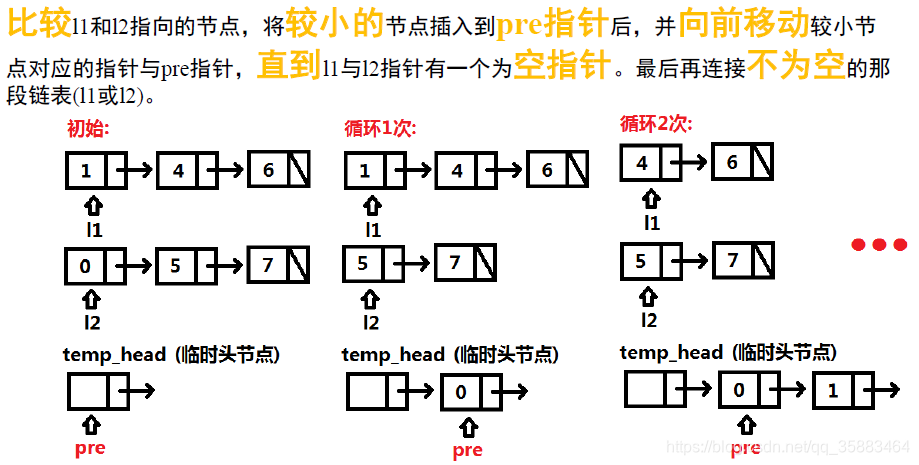
代码:
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
temp_head = ListNode(0)
pre = temp_head
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val < l2.val:
pre.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
pre.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
pre = pre.next
if l1:
pre.next = l1
if l2:
pre.next = l2
return temp_head.next
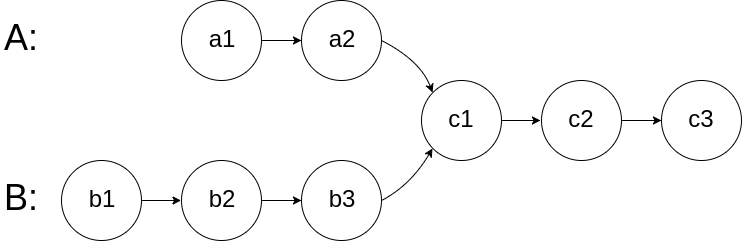
例4:LeetCode160.求两个链表的交点(easy)
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
思路:
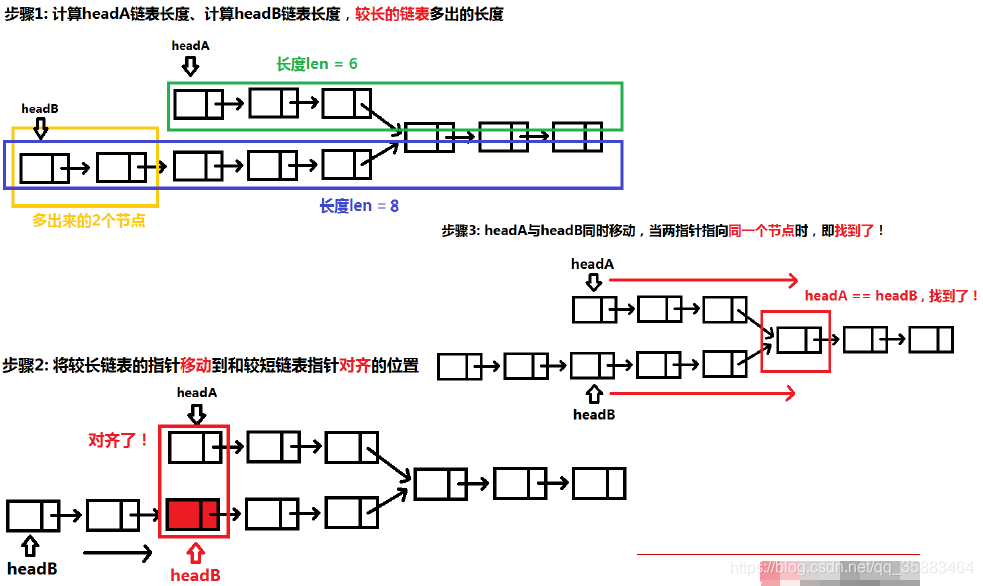
代码:
class Solution(object):
def get_list_length(self, head):
len = 0
while head:
len += 1
head = head.next
return len
def forward_long_list(self, long_len, short_len, head):
delta = long_len - short_len
while head and delta:
head = head.next
delta -= 1
return head
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
listA = Solution().get_list_length(headA)
listB = Solution().get_list_length(headB)
if listA > listB:
headA = Solution().forward_long_list(listA, listB, headA)
else:
headB = Solution().forward_long_list(listB, listA, headB)
while headA and headB:
if headA == headB:
return headA
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None
例5:LeetCode142.链表求环( medium)
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:tail connects to node index 1
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
思路:快慢指针
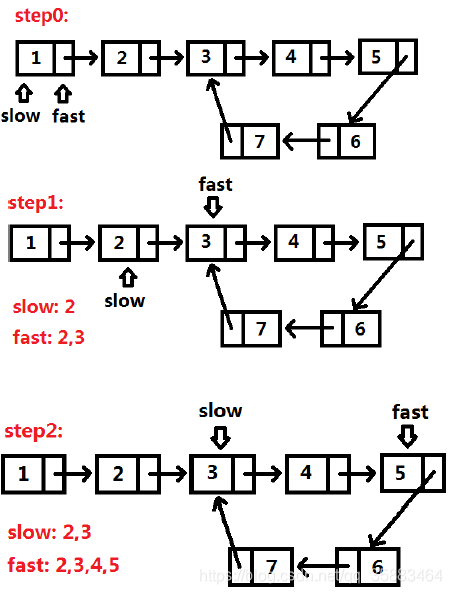
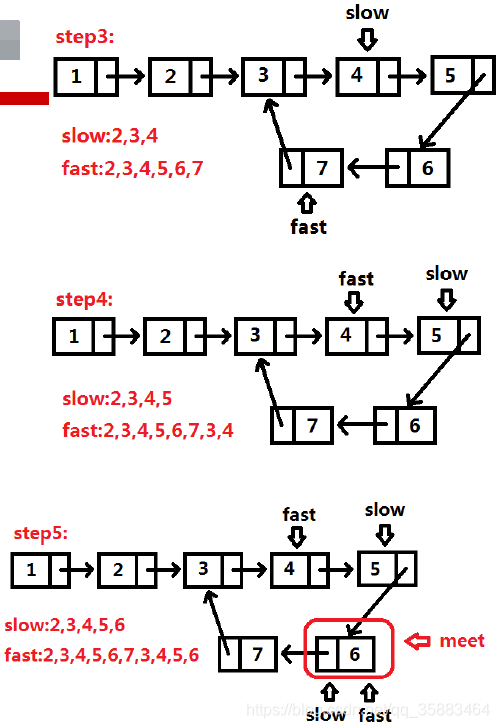
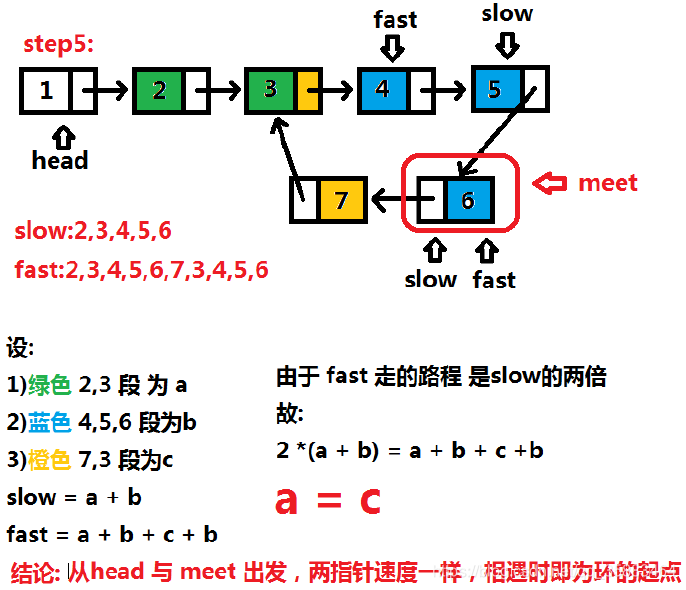
代码:
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
fast, slow = head, head
while True:
if not (fast and fast.next): return
fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.next
if fast == slow: break
fast = head
while fast != slow:
fast, slow = fast.next, slow.next
return fast
例6:LeetCode86.链表划分( medium)
给定一个链表和一个特定值 x,对链表进行分隔,使得所有小于 x 的节点都在大于或等于 x 的节点之前。
你应当保留两个分区中每个节点的初始相对位置。
示例:
输入: head = 1->4->3->2->5->2, x = 3
输出: 1->2->2->4->3->5
思路:
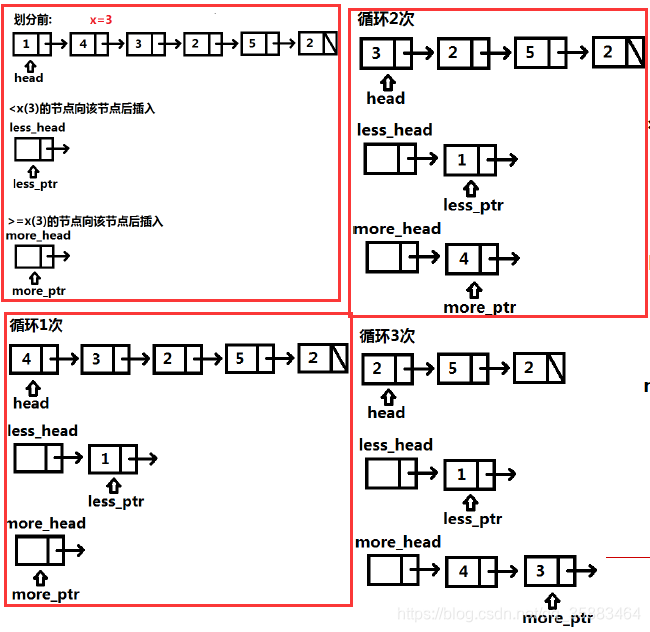
代码:
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:
less_head = ListNode(0)
more_head = ListNode(0)
less_p = less_head
more_p = more_head
while head:
if head.val < x:
less_p.next = head
less_p = less_p.next
else:
more_p.next = head
more_p = more_p.next
head = head.next
less_p.next = more_head.next
more_p.next = None
return less_head.next
例7:LeetCode138.复杂链表的深度拷贝(hard)
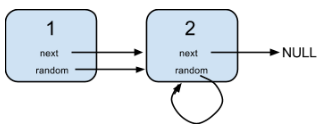
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
要求返回这个链表的深拷贝。
示例:
输入:
{"$id":"1","next":{"$id":"2","next":null,"random":
{"$ref":"2"},"val":2},"random":
{"$ref":"2"},"val":1}
解释:
节点 1 的值是 1,它的下一个指针和随机指针都指向节点 2 。
节点 2 的值是 2,它的下一个指针指向 null,随机指针指向它自己。
思路:
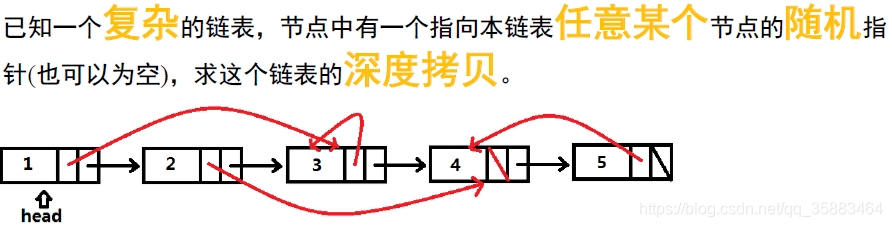
两种遍历(DFS, BFS):
深度遍历DFS:
class Solution:
def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Node') -> 'Node':
lookup = {}
def dfs(head):
if not head: return None
if head in lookup: return lookup[head]
clone = Node(head.val, None, None)
lookup[head] = clone
clone.next, clone.random = dfs(head.next), dfs(head.random)
return clone
return dfs(head)








 本文深入解析了链表数据结构的七大经典算法题,包括链表逆序、链表中间段逆序、两个排序链表合并等,每题附有详细思路及Python代码实现。
本文深入解析了链表数据结构的七大经典算法题,包括链表逆序、链表中间段逆序、两个排序链表合并等,每题附有详细思路及Python代码实现。
















 391
391

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








